Case Study
- 1. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY CASE STUDY F- Ansar I- KM- AslamJunaid Iqbal ? What is case study? ? Purposes of case study ? Prominent places of case study ? Methods Involve in case study ? Strategies for case study ? Approaches of case study ? Advantages & Disadvantages of case study ? Guideline for case study
- 2. WHAT IS CASE STUDY? ? Case: An occurrence of something or a situation. ? Study: A detailed critical inspection or elaboration. ? Cases are bounded by time and activity, and researchers collect detailed information using a variety of data collection procedures over a sustained period of time (Yin, 2009, 2012). ? ˇ°Case study is the meaningful study of thoughts of the world which are engaging the realitiesˇ± (Crotty).
- 3. PURPOSES OF CASE STUDY IN DIFFERENT FIELDS ? To generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. ? To explaining the reasons of certain situations and exploring different outputs. ? Case study of sociologist and psychologist would be similar, both expect that looking into behavior or interactions within, between or around communities group or organization. ? Scientist case study is to experiment between theories or come up with new theories, scientists are able to develop hypothesis.
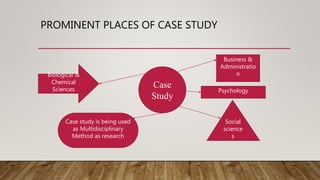
- 4. PROMINENT PLACES OF CASE STUDY Case Study Business & Administratio n Social science s Biological & Chemical Sciences Case study is being used as Multidisciplinary Method as research Psychology
- 5. METHOD INVOLVES IN CASE STUDY ? Case study research can be used as both Qualitative or Quantitative. ? Mostly, it is based on case or discipline whether to choose Qualitative or Quantitative. ? Qualitative case study methodology provides tools for researchers to study complex phenomena within their contexts. ? In qualitative Case study interviews, observations and documents are involved. ? Case study is a multidimensional study of a topic, so multiple methods are involved in case study.
- 6. CONTINUED ? Example of Case Study as Qualitative Research Method: ? In 2007, at San Francisco, the fuel of plane runout and its engines were seized. Piolet was instructed to land the plane on water and manage the situation. Then the piolet gave instructions to his staff to wear lifejackets and stand on fins and tale of plane for 15 minutes, and boats was also reached at the spot in 13 minutes. After exact 15 minutes plane drown in water and no one is injured. After all this, piolet explain everything that happen to plane, to the authorities. Black box of that plane observed and that piolet was interviewed for next. 2 months. ? Example of case study as Quantitative research method: ? In 1998, a man clamed to be John Titor, that he arrived from, 2036, future. He predicted somethings that will happen onwards to 2036, (Pak-India war in 2022, 32 bit computers will automatically stopped in 2034 and big explosion in San Francisco) most of his predications were wrong(end of Olympic games in 2004, comet explosion for 2012) after 2 hour he vanished and no one is able to locate his IP address of computer and he is a mysterious person for scientist. So whenever scientist try to go for qualitative data his wrong predications stop them and most of time they rely on quantity of data and waiting for next predication could it be true or bluff.
- 7. STRATEGIES FOR CASE STUDY ? Surveys: Who. What. How many. How much. ? Experiments: How. Why. ? Reviewing historical background: How. Why. When. Where. ? Assumptions of past and future: Why. What. Where. Who.
- 8. APPROACHES OF CASE STUDY: ? Explanatory: Intend to explain or make more clear. ? Exploratory: Intend for discovery. ? Descriptive: Describe or characterized by description. ? Intrinsic: Looking for genuine quality. ? Instrumental: Providing insight into a particular issue or build a theory ? Collective:
- 9. ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES ? ADVANTAGES: ? Long latency period between exposure manifestation. ? Less costly and less time-consuming. ? Advantageous while studying dynamic populations. ? DISADVANTAGES: ? Subject to selection bias. ? Inefficient for rare exposures. ? Information on exposure is subject to observation bias.
- 10. GUIDELINE FOR WRITING CASE STUDY ANALYSIS: ? Preparing the Case ? Read and examine the case thoroughly ? Focus your analysis ? Uncover possible solutions ? Select the best solution ? Drafting the Case ? Introduction ? Background ? Alternatives ? Proposed Solution ? Recommendations ? Finalizing the Case