Ce463juhj
- 1. Jordan University of Science and Technology College of Engineering CE 463 Soil Mechanics Lab Catalog Data CE 463 Soil Mechanics Lab (0 â 3 â 1) â 1 credits Soil Description and Identification, Moisture Content, Sieves and Hydrometer Analysis; Atterberg Limits (Liquid, Plastic and Shrinkage Limits); Compaction; Permeability tests (constant and falling head); Consolidation; Swell test; Direct Shear; Unconfined Compression test; Triaxial Compression test. Textbook Soil Mechanics Laboratory Manual by Braja Das, Sixth Edition Oxford; ISBN 0-19-515046-5 Reference Engineering Properties of Soils and Their Measurements By J. Bowles McGraw Hill; ISBN 0-07-006752-X Coordinator Dr. Omer Goals 1. Learn how to measure the basic properties of soils. 2. Learn how to determine typical ranges of numerical values expected from those tests. 3. Learn how to use soil properties in Geotechnical designs. 4. Design and conduct laboratory experiments. Pre-Requisites by Topic Corequisite: Students perform basic experiments in soil mechanics. Learning Outcomes 1. Provide experience with the geotechnical laboratory procedure 2. Exposed to experiments to develop a âfeelâ for the different soil types 3. Understand the use, significance, and limitations of properties obtained from laboratory tests and Learn how to utilize them to perform various types of engineering calculations. 4. Reinforce those concepts that are being presented in the lecture 5. Interact professionally among themselves during laboratory sessions. They will perform tests and collect data. They will share data with other groups and also share their experiences. Topics 1. Soil Identification and Description 2 Lab hours 2. Sieve Analysis 2 Lab hours 3. Hydrometer Analysis 3 Lab hours 4. Liquid, Plastic and Shrinkage Limits 3 Lab hours 5. Standard Proctor Compaction Test 3 Lab hours 6. Permeability Test (Constant Head) 2 Lab hours 7. Permeability Test (Falling Head) 2 Lab hours 8. Consolidation Test 4 Lab hours 9. Swell Test 4 Lab hours 10. Direct Shear Test 2 Lab hours 11. Unconfined Compression Test 2 Lab hours 12. Triaxial Compression Test 3 Lab hours Computer Usage Spreadsheets, word processing, and the use of software at the end of the soil manual book. Method of Assessm ent Lab Reports 30% Midterm 30% Final Exam 40% Estimated Content Engineering Science 1 Credit Engineering Design 0 Credit Prepared by Dr. Omer Mughied Date March 7th, 2007
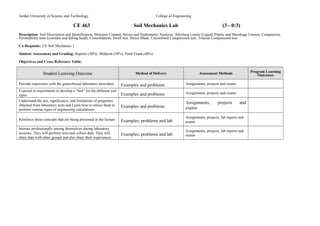
- 2. Jordan University of Science and Technology College of Engineering CE 463 Soil Mechanics Lab (3 - 0:3) Description: Soil Description and Identification, Moisture Content, Sieves and Hydrometer Analysis; Atterberg Limits (Liquid, Plastic and Shrinkage Limits); Compaction; Permeability tests (constant and falling head); Consolidation; Swell test; Direct Shear; Unconfined Compression test; Triaxial Compression test. Co-Requisite: CE Soil Mechanics 1 Student Assessment and Grading: Reports (30%), Midterm (30%), Final Exam (40%) Objectives and Cross Reference Table: Student Learning Outcome Method of Delivery Assessment Methods Program Learning Outcomes Provide experience with the geotechnical laboratory procedure Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams Exposed to experiments to develop a âfeelâ for the different soil types Examples and problems Assignments, projects and exams Understand the use, significance, and limitations of properties obtained from laboratory tests and Learn how to utilize them to Examples and problems perform various types of engineering calculations. Assignments, projects and exams Reinforce those concepts that are being presented in the lecture Examples, problems and lab Assignments, projects, lab reports and exams Interact professionally among themselves during laboratory sessions. They will perform tests and collect data. They will share data with other groups and also share their experiences. Examples, problems and lab Assignments, projects, lab reports and exams