Cefiderocol - Dr. ANCY GEORGE
- 1. NEW DRUG CEFIDEROCOL Dr. Ancy George JR Pharmacology
- 2. Cefiderocol versus imipenem-cilastatin for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections caused by Gram-negative uropathogens: a phase 2, randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial Simon Portsmouth, David van Veenhuyzen, Roger Echols, Mitsuaki Machida, Juan Camilo Arjona Ferreira, Mari Ariyasu, Peter Tenke, Tsutae Den Nagata Lancet Infect Dis 2018 October 25, 2018
- 3. Objective To assess the efficacy and safety of Cefiderocol vs Imipenem ŌĆō Cilastatin for treatment of complicated UTI in patients with risk of multidrug resistant Gram negative infections Methods Phase 2, multicenter, double blind, parallel group, non- inferiority trailat 67 hospitals in 5 countries
- 4. Inclusion criteria Adults admitted with clinical diagnosis of complicated UTI (cUTI) with or without pyelonephritis or thoses with acute uncomplicated pyelonephritis. Randomly assigned as 2:1 into Cefiderocol (2g) and Imipenem- Cilastatin ( 1g each) Q8H for 7-14 days Exclusion ŌĆó Baseline urine culture with more than 2 uropathogens ŌĆó Fungal UTI ŌĆó Carbepenem resistant uropathogen
- 5. Primary endpoint Composite of clinical and microbiological outcomes at test of cure (7 days after treatment cessation), which was used to establish non-inferiority (15% and 20% margins) of cefiderocol versus imipenem-cilastatin.
- 6. Results 1 year study Cefiderolcol Assigned ŌĆō 303 Got treatment ŌĆō 300 GN uropathogen ŌĆō 252 Effective treatment ŌĆō 183 (73%) (p value = 0.0004) Adverse effects ŌĆō 122(41%) Imipenem-cilastatin Assigned ŌĆō 149 Got treatment ŌĆō 148 GN uropathogen ŌĆō 119 Effective treatment ŌĆō 65 (55%) Adverse effects ŌĆō 76(51%)
- 7. Inference Intravenous infusion of cefiderocol (2 g) three times daily was non-inferior compared with imipenem-cilastatin (1 g each) for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infection in people with multidrug-resistant Gram negative infections. The results of this study will provide the basis for submission of a New Drug Application to the US Food and Drug Administration.
- 9. CEFIDEROCOL Phase III drug Cefiderocol is a novel catechol substituted siderophore cephalosporin INDICATIONS It is against Gram negative bacteria including ’āśCarbapenem- resistant strains of Enterobacteriaceae ’āśAcinetobacter baumannii ’āś Pseudomonas aeruginosa ’āśStenotrophomonas maltophilia
- 10. USES Cefiderocol is being developed as a therapeutic drug for the treatment of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections, including ’āśnosocomial pneumonia, ’āśbloodstream infections, ’āścomplicated urinary tract infection (cUTI).
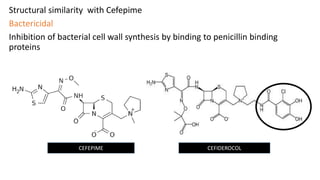
- 11. Structural similarity with Cefepime Bactericidal Inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to penicillin binding proteins CEFEPIME CEFIDEROCOL
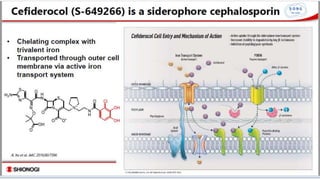
- 13. ŌĆ£TROJAN HORSEŌĆØ It form a chelating complex with ferric iron and utilize the bacterial iron transport system to penetrate the outer membrane of GN organisms.
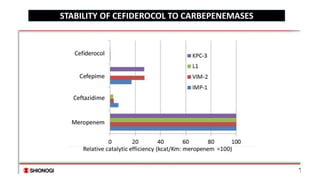
- 14. Highly stable to various types of carbapenemase KPC, OXA, IMP, VIM and NDM Potent activity against Gram-negatives including CR strains ’āśAcinetobacter baumannii ’āśPseudomonas aeruginosa ’āśEscherichia coli ’āśKlebsiella pneumoniae ’āśStenotrophomonas maltophilia Not active against Gram positives or anaerobes APEKS
- 15. STABILITY OF CEFIDEROCOL TO CARBEPENEMASES
- 16. Pharmacokinetics ’é¦ Terminal elimination half-life -1.98 to 2.74 hr. in healthy subjects. ’é¦ Cefiderocol is excreted mainly via the kidneys, with 60 to 70% of the dose in urine as the unchanged parent drug. ’é¦ The total clearance (CL) of cefiderocol was dependent on renal ’é¦ Dose adjustment required in renal failure ’é¦ No accumulation was observed at the 2 g every 8 hours dose intravenous infusion, and this dose was well tolerated when administered over 10 days.
- 17. Dosage and administration 2-g q8h dosing with a 3-h intravenous infusion was selected as the standard dose regimen
- 18. ŌĆó Diarrhoea (4%) ŌĆó Hypertension (4%) ŌĆó Constipation (3%) ŌĆó Infusion site pain (3%) ŌĆó Headache (2%) ŌĆó Nausea (2%) ŌĆó Cough (2%) ŌĆó Vomiting (2%) ŌĆó Hypokalaemia (2%) ŌĆó Insomnia (1%) ŌĆó Renal cyst (1%) ŌĆó Infusion site erythema (1%) ŌĆó Abdominal pain upper (1%) ŌĆó Cardiac failure (1%) ŌĆó Clostridium difficile colitis (<1%) ŌĆó Vaginal infection
- 19. Adverse Effect Single dose effects Diarrhea Contact dermatitis Rash Abdominal pain Blood in urine WBC in urine Increased total counts Multiple dose effect Increased TSH Elevated AST, ALT
- 20. THANK YOU