CEG_Cards_2016_A4 v 6
- 1. LITHOLOGY 1 Confidence Index - 1: positive 2: confident 3: probable 4: guess pad fillPF SURFICIAL DEPOSITS gravelGr perched gravelGrp fluvial sedsFs alluviumAlv glacial tillGlt screeSc soilSo conglomerateSCg SSdb carb sandstone SEDIMENTS (S) SAr arkose SSd sandstone calc sandstoneSSdc SSsc calc siltstone SSs siltstone SSsb carb siltstone lamin siltstoneSSsl SMsb carb mudstone SMs mudstone SMsf fer mudstone calc mudstoneSMsc SShg graphitic shale SMsp peb mudstone SSh shale carb shaleSShb SCl chalk SGw greywake SCh chert limestoneSLs SEv evaporite SLso oolitic limestone SLsc marly limestone gneissMGn MSk skarn METAMORPHICS (M) MHf hornfels MMb marble mt skarnMSKmt MSkgtep gt-ep skarn MSkmtgt mt-gt skarn MSkgt gt skarn ep skarnMSkep MSksc sc skarn MSkac ac skarn MSkdp di skarn meta basaltMVb MSd meta sandstone MMs meta mudstone MSs meta siltstone phylliteMPh MShg green schist MSh schist MShp glauc schist amphiboliteMSha MHfp pyx hornfels MShu granulite MHfh hb hornfels LITHOLOGY DATA RECORDING COLUMNS LITH BXT BXC BXM %BM CI S** bxtype/facies M** bxclasts V** bxmatrix I** %bxmatrix confidenceindex IDY** IDM** IH** IP** sedimentary metamorphic volcanic igneous dyke dome hypabyssal plutonic glacial moraineGmor r clastrounding SKE endoskarn SKX exoskarn OXIDATION STATE Complete Oxidation Strongly Oxidised Moderately Oxidised Weakly Oxidised Trace Oxidation Unoxidised - no sulphides remaining - trace Sx, strong FeO development - approx 50% Sx oxidised - most Sx preserved, signif FeO on partings - trace FeO on partings, Sx - fresh, no FeO, Sx 5 3 4 2 1 0 MINERAL EXPLORATION Mine concentrate grab DDH select RCH composite Open hole composite Mine mill feedSoil pit BLEG DDH composite GEOLOGICAL REFERENCE CODES Mine dump grab Float Sample Pit channel sample Subcrop grab Outcrop pannel Outcrop grab Outcrop channel Outcrop chip SAMPLE TYPE SCGR PTCH OCPN OCCH OCRC OCGR FLGR MIDP Soil auger mesh MIFD SOAG SOBL OHCO RCCO DDSL DDCO MICO Soil pit meshSOPT Mobile metal ionSMMI Underground Select Underground channel Underground chipUGRC UGCH UGSL SSED BLEG SSED meshSSMS SSBL S J MELDRUM 2016 PORPHYRY, SKARN & EPITHERMAL SYSTEMS ver 6 / 2016 Calle las Tres Marias 363/6 Monterrico, Surco Lima. Peru CEL: ++51 19 9906 8514 meldrum.geo@gmail.com SSED pan conSSPC ferricreteFct SLsd dirty LS SLsh sinkhole fill B bedded SLd dolomite SLsy shelly limestone SVcl volcaniclastic SFlch flysch seds quartziteMQz MMg migmatite GB graded bedding RB reverse bedding I indurated CB cross bedded F fossiliferous Features: SNd sinter distal apr <35 SNn sinter near vent >60 SNs sinter mid slope <60
- 2. LITHOLOGY 2 VOLCANICS (V) igneous designator intrusive facies composition phenocrysts / crystals textures grain size features volcanic designator composition minerals (abundance order) volc facies grain size features COMPOSITION D dacite A andesite rhyodaciteRD R rhyolite basaltB BA basaltic andesite P phonolite TA trachyandesite tephriteE L latiteT trachyite VOLCANIC FACIES clt crystal lithic tuff ct crystaltuff lithic tufflt ft pyroclastic flowtufft at ash tuff lpt accret lapilli tuff vtt vitric tuff fragmentalfgm lhr lahar ba block and ash MINERALS b biotite h hornblende pyroxenep m magnetite quartzq f feldspar GRAIN SIZE fm fine to medium mediumm mc medium coarse very finevf f fine c coarse pillow basaltp ign ignimbrite FEATURES VE vessicular L leucocratic W welded flow bandedFB D melanocratic RB reverse graded bedded GB graded bedded EXAMPLES VAct fhq D dark andesitic crystal tuff with feld hornblend and quartz crystals/phenos VRDign fqh W welded rhyodacitic ignimbrite with feld & quartz phenos/crystals EXTRACT AS MUCH INFORMATION IN A CODED FORM AS POSSIBLE LITHOLOGY 3 INTRUSIVES (I) INTRUSIVE FACIES IP plutonicIH hypabyssaldykeIDY IDM dome pg pegmatite gb gabbro lamprophyrela sp serpentenitemonzonitemz mzg monzogabbro sy syenite pl aplite COMMON MINERALS b biotite h hornblende pyroxenep m magnetite quartzq f feldspar ROCK TEXTURES PE porph > equigranularaphaniticA PA porphyritic, aphanitic gmass equigranularE P porphyritic G graphictic FEATURES VE vessicular L leucocratic FY feltyflow bandedFB D melanocratic COMPOSITION an andesitic dm microdiorite daciticda rd rhyodacitic doleritedo di diorite gd granodiorite g granitic tonaliteto rh rhyolitic GRAIN SIZE fm fine to medium mediumm mc medium coarsevery finevf f fine c coarse olivineo a augite VT vitric ba basaltic andesite EP equi > porphyritic BRECCIA FACIES TABLE BRECCIA FACIES TABLE CONTD g glass DX proximalPX distal FACIES VI vitric a augite UT tephra CR crystal crowded fl lava flow CR crystal crowded
- 3. BXi intrusion bx BRECCIAS (BX) BXf fault bx BXt tectonic bx jigsaw bxBXj BXs pseudomicro bx BXc crackle bx BXp phreatic bx rock flour bxBXr BXb pebble bx BXrc rf-clastic bx BXh hydrothermal bx very angularva CLAST ROUNDING (r) an angular sub-angularsa sr sub-rounded roundedro wr well rounded ploymictPL BRECCIA CLASTS (BXC) ML monolithic meta sedsMS IG igneous porphyryPO MM metamorphic *** 'specified lithologies' quartzqz fe iron oxides BRECCIA MATRIX (BXM) qz-sx qz-sulphide sx sulphide qz-fe oxqz-fe ja jarosite qz-al qz-alunite al alunite qz-jarositeqz-ja al-pf al-pyrophyllite cl clay pf pyrophyllite OR - a lithology or other mineral species LITHOLOGY 4 BXv volcanic bx BXg phreatomagmatic BXp phreatic bx BX9 BX1 BX4 BX3 BX6 BX7 TECTONICPHREATIC BX2 coarse poor sort coarse well sort fine poor sort (dykes) fine well sort (dykes) hydrothermal matrix qz clast qz matrix ign matrix fine BXl acid drain back bx BX8 ha cl matrix BXg phreatomagmatic BX5 ign matrix coarse BXd diatreme bx BSs barren silica shoulder pseudo bx coarse qz-al alt FACIES alternative rf rock flour typicaltohighsulphidation porphyry/brecciacomplexes ALTERATION nul0 trace1 weak2 moderate3 strong4 intense5 PS sub propylitic ALTERATION FACIES (AFAC) UA unaltered PR propylitic potassicPT AR argillic IA intermediate arg AA - acid sulphate facies SV silica vuggy CS clay silica SM silica massive vein selvageVNS ALTERATION STYLE (ASTY) sed selectSED adulariaad ax andalusite ALT MINERALS (AMIN) al alunite (udif) aK K-alunite clay (udif)cl di diaspore do dolomite dk dickite pyrophyllitepf se sericite qz quartz sc scapolite pervasivePER PAT patchy FRC fracture structureSTR BXM bx matrix BXC bx clast clottedCLT CAV cavities mordenitemr an andradite feldspar (udif)fp gt garnet (udif) smectitesm su specularite carbonatecb ch chlorite halloysiteha hu heulandite tourmalineto vs vesuvianite corundumco cx clinopyroxene cs cristobalite jarositeja ka kaolinite lx lucoxene zeoliteze zu zunyite P2 biotite (2nd PT event) phyllic:pro-ms ret-sePH SI silicification silica aluniteSA SK skarn SG silica granular QT qz-tourmaline ALT INTENSITY (AINT) mt magnetite ep epidote sd siderite bi bioite gp gypsum tr tridymite cz chabazite il illite wa wairakite cd chalcedony im ilmenite wo wollastonite ac actinolite ca calcite os opaline silca ab albite ms muscovite na natrolite SE sericitic (IA) silica claySC ICO int contact px pyroxene ba barite ah anhydrite native SS aN Na-alunite ce celadonite dp diopside gf graphite kf k-spar palygorskitepa pg phlogopite ro roscolite topaztp zw zinnwaldite selectSEL REP replacement phenocrystPHN matrixMTX o'printOPN aplite (ab or kf)AB CB carbonate ZE zeolite SO silica opaline S1 silica mas vuggy S2 silica vuggy mas CA clay alunite SP silica patchy SW silica wormy advanced argAA PROGRADERETROGRADE Silica Group Alunite Group al-ka Group kaolin Group il-ka Group illite Group Chlorite Group Calc-Silicate Group SO SG SC CS AR SM SM PH se-kf PH mica PT bi-mt PT SD kf-bi-og SK cx-gt SK tm-qz Increasing pH IncreasingTemperature PT ac-kf SK mt-gt EPITHERMALDEEPEPITHERMALPORPHYRY 2 3 4 5 6 100 250 300 ALTERATION FACIES AND SUB FACIES - CEG SJM alteration sub facies overlain on the Corbett & Leach alteration table PT SK PH PR PS AR AAIA SA SV S2 S1 SP SW SG IA IA ch-il il-sm AR ka sm CA AA pf-al PH kf-mica PR bi-ep-ac-kf PR ch-ep-ca-ad PS PH-AA se PH se CEG ALTERATION FACIES TABLE (SVM) (SMV) qz-ha cl-ha SG SH mm montmorilonite SY pr paragonite la laumonite rt rutile conditions of non-dissociation retrograde prograde Includes the addition of IA to the original Corbett & Leach diagram - codes changed to suit this reference set tremolitetm AA di-dk epitherm al porphyry transition anataseaa BXx collapse breccia RX recrystallised HF hornfels BRECCIA FACIES (BXT) THE BRECCIA MATRIX COMPONENT NORMALY DEFINES THE BRECCIA FACIES breccia designator breccia facies clast component clasr rounding (optional) matrix component estimate % matrix phreatic breccias - sourced at depth & drill upwards. diatreme breccas - originate at surface and drill downwards. Matrix is clay rich & hydrothermal fluids hydrothermal breccias - matrix is sourced from clasts are sourced form near surface Matrix is pulverised rock flour & clasts are sourced from depth passive process explosive origin 'BRECCIA RULES OF THUMB' blockdesignator RO roscolite (alkalic epi) CE celadonite (LSE) MT magnetite (deep PT) chloritic (IA)CH Principal Facies Variant Facies cavity fillCFL structureSTR VNM vein matrix GMS groundmass BED bedding select vesicleVES aH NH-alunite nc nacrite nt nontronite talctc chalcedonic silSH SY creamy silica BXo 'overbank' phreatic breccias - weaker retrograde alt typ / oganic material alternative numericnumeric VBx vein matrix breccia glassgl HM heamatite K2 kspar (2nd PT event) sodic - calcicSD og oligoclase Note: Deep porphyry SODIC-CALCIC (SD) & aplite (AB) inserted - approximate AB kf qz ab SQ sugary quartz (LSE) DS dark silica (py?) SQ
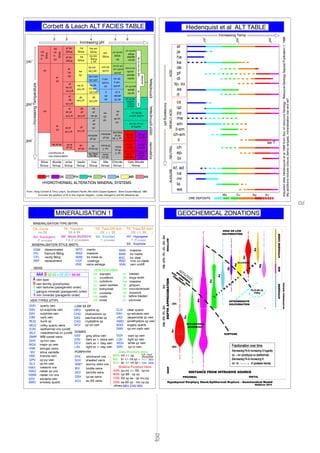
- 4. MINERALISATION 1 boxworkbx bm microbotriodalbo botryoidal buck qzBUQ MINERALISATION TYPE (MTYP) Oxide Transition Supergene Enriched OX TR SG ENMixed SG/EN/HY MAS massive vein undiffVNN MAB bx mass sx coatingsCOT VBX breccia vein FFL fracture fillling MINERALISATION STYLE (MSTY) DSM disseminated cavity fillingCFL REP replacement MTO CBV carb vein manto BVN qz-SX - cp su SX qz se - cp mo pyCVN qz-mt +/- SX - cp bnAVN opaline qzOPQ SAQ saccharoidal qz crystalline qzCXQ chalcedonic qzCHQ cr crustiform colloformco dt dogs tooth ma massive oc open cavities gingurogi QAV qz-adularia vein MM sweat veinsQMM HypogeneHY epithermal vns (undif)EVN MLV mesothermal vn (undif) MQV major qz vein VNR stringer veins SIV silica veinletts milky quartz veinsMLQ rind on clastsRND MAS massive BXM bx matrix bx clastBXC JAQ jasperoidal qz vein AMQ amethystine qz vein DSV dark sx + silica vein DCV dark sx + clay vein LSV light sx + clay vein clear quartzCLQ no SX 2 process 1 & 2 processes OX & SX 1 process 1 Process MX GSV grey silica vein Trans OX domTO OX >> SX Trans SX domTS OX << SX QVN quartz vein QXV qz-sulphide vein QCV qz-cb vein SXV sulphide vein STK stockwork vns SHV sheeted veins WMY wormy silics vns PORPHYRY DOMES LOW SX EP VEIN TYPES (VTYP) mt +/- qzMVN Deep Porphyry Veins BIV biotite veins SEV sericite veins QSV qz-se veins LQV light qz vein DQV dark qz vein QRV qz-ro vein QLV qz-lm vein qz-hm veinQHV ba banded bl bladed VEINS WQV white qz vein Corbett & Leach ALT FACIES TABLE Silica Group Alunite Group al-ka Group kaolin Group il-ka Group illite Group Chlorite Group Calc-Silicate Group op cs tr qz al ha Silica op cs tr qz ha Silica ha sm Silica Silica Silica al ka Silica ka Silica ka sm Silica + sd sm Silica al qz al ka qz ka qz qz conditions of al qz al ka di qz+di al dk al al pf qz+di qz+di dk pf qz+di ax ka sm qz+sd ka di qz+di ka il sm qz+sd sm cb qz/cz il sm dk qz+sd cb qz/cz il cb qz ka dk il/il sm qz+sd dk qz+di pf dk se qz pf pf qz+di pf qz se se cb qz mica/se ax pf qz + cb mica qz se qz ch kf ax al qz pf qzpf qz ax al mica qz ax mica mica co qz kf qz mica bi kf cx mt bi ac kf qz kf cb cx qz ca/do tm qz ca/doqz + ch se/mica Increasing pH IncreasingTemperature ac qz kf ch ep ac ch qz kf ca/do ch qz ep ad/ab ca/do gt qz wo vs mt ch il qz cb ab/ad ch cb qz/cd il-sm ch/ch-sm qz/cd sm qz/cd ch-sm/ch cb silica ch-sm/ch cb/do silica ch/ch-sm zeolite qz/cd ch qz/chd ca do ad/ab zeolite ca/do ch qz ep ad/ab ca/do zeolite zeolites stbhumocznawala EPITHERMALDEEPEPITHERMALPORPHYRY PT SK PH AR AA 2 3 4 5 6 100 250 300 HYDROTHERMAL ALTERATION MINERAL SYSTEMS From: Greg Corbett & Terry Leach, Southwest Pacific Rim Gold Copper Systems - Short Course Manual, 1997 Includes the addition of IA to the original diagram - codes changed to suit this reference set IA cb + cb co qz mica/se pf qz non-dissociation PT SK PH PR PS AR AAIA dk qz+di sugary quartzSGQ VEIN TEXTURES ck cockade cm comb ms moss lb lattice bladed pl plumose - - Increasing Temp 100 200 300 al ja ha ka dk pf di tp, zu aa rt cs qz py ma sm il-sm ch-sm il ch ep bi kf, ad ca mr la wa IncreasingpH WEAKLYACIDACIDNEUTRALALKALINE ORE DEPOSITS AuAgCuMo Hedenquist et al ALT TABLE AdjustedafterHedenquistetal1996fromSocofresourceGeology-ResourceGeologySepcialPublication1,1996 se ? VNS veins selvage NWV network vns NWQ netwk qz vns NWM netwk mn vns SulphideSX vein type vein familly (porphyries) gangue minerals (paragenetic order) vein textures (paragenetic order) min minerals (paragentic order) QPV qz-py vein qz-mn carb veinQMV GEOCHEMICAL ZONATIONS ADV adularia vein SMQ smokey quartz Myadditionsincludecolours(tempranges),mineralisationbarandse? bi +/- mt qzBIV ac +/- mt qzACV Shallow Porphyry Veins se-SX qz - mo cp pyDVN SEV CHV SXVothers ACV CHV SEV WQV retrograde ILP / HLP ACV ac-SX veins
- 5. MINERAL RATIOS FOR VECTORING AND MODELLING ox - no sx cp (only) cp > bn 0 A B C D PRINCIPAL COPPER MINERALS bn cp cc cu cv Cu br tn cn mc az ck cr pm bornite chalcopyrite chalcocite cuprite covellite native copper brochantite tenorite cubanite malachite azurite chalcantite chrysocolla pitch limonite Cu FeS CuFeS Cu S Cu O CuS Cu Cu (OH) SO CuO CuFe S Cu CO (OH) Cu (CO ) (OH) CuSO .5H O Cu H (Si O )(OH) 5 4 2 2 2 4 6 4 2 3 2 3 2 3 3 2 2 4 2 2 2 2 5 4 57.3% 79.9% 36.0% 79.8% 55.0% 35.0% 63.3% 56.0% 31-34.5% 88.8% 66.4% 23.0% Cu % en enargite Cu AsS3 4 100% OX TR SG HY py (only) py > cp py = cp py < cp 1 2 3 4 cp < bn cp = bn MINERALISATION 3 sol Cu (only) cc (only) cc > cv F sol Cu > py sol Cu = py sol Cu < py G H I cc < cv cc = cv en (only) en > py cv > en cv = en cv < en O P Q R T U V cv (only) S en < py en = py en (only) W bn (only) E Cu-Au PORPHYRY cv (only) J K L M N ENRICHMENT BLANKETS HS SYSTEMS py > po py = po cp > po cp = po cp < po 5 6 7 8 W X Y cp (only) V po (only) py < po po (only) Z PYRRHOTITE -Cu SKARNS MINERALISATION 2 antimonysb at atacamite MIN MINERALS (MMIN) ar argentite as arsenopyrite chalcopyritecp ct cuprite cv covellite cn cubanite orpimentor pl pyrolusite pm pitch limonite py pyrite malachitemc az azurite electrumel en enargite realgarre sh scheelite bismuthinitebt bn bornite flouritefl ga galena sideritesd sp sphalerite cassiteritesn ct cerussite ck chalcantite hessitehs hz hydrozincite ja jarosite native sulphurS te tellurides lm limonite dg digenite po pyrrhotite ba barite fb ferberite sl selenides br brochantite go geothite st stibnite ci calverite hm heamatite ss sulphosalts ae anglesite cc chalcocite ai alcantite ma marcasite tt tennantite cinnabarnn molybdenitemo cr chromite tenoritetn Hg mercury cy chrysocolla Ag native silver wd mn wad ah anhydrite Cu native copperAu native gold neotocitene DS dark sulphides LS light sulphides quartzqz calciteca carbonatecb rhodochrositerc gypsumgp tourmalineto roscolite micaro rhodoniterd magnetitemt Common vein gangue minerals magnetitemt ba barite ze zeolite adulariakf rhodochrositerc mn mn wad so scorodite lx lucoxene zc zincite mn oxidemn ENRICHMENT PERIPHERY CORE Useful mineral ratios for vectoring purposes
- 6. 25 °/045° 315°/25° NE N45W/25NE BEDDING E PUMICE ALIGNMENT IGNEOUS BANDING FLOW LINEATION D/DAZM W S LINEAR FEATURES 315° N DIPS 25° 045° DIP/DIP AZIM STRIKE/DIP (UK) STRIKE/DIP (US) CONTACT (OBSERVED) DISCONFORMITY UNCONFROMITY FOLD AXIS FOLDS BOUNDARIES VEIN CLEAVAGE FRACTURE FOLIATION FAULT-THRUST FAULT-REVERSE FAULT-NORMAL FAULTS JOINT STRUCTURE & EVENTS PLANNAR FEATURES BED LPU LFL LIB UNC CON VEN DIS FAX FLN FTH FLR SCL FOL SJO SFR FAULT (UNDIF) FLT SCHISTOSITY SCH BASE PARTIAL OX BASE SOLUBLE Cu BASE COMPLETE OX EVENTS BCO BPO BSO CONTACT (INFERRED) CIN MAPPING CA - ANGLE COREAXIS 45° LOGGING TO CORE AXIS STRAIN ELLIPSE
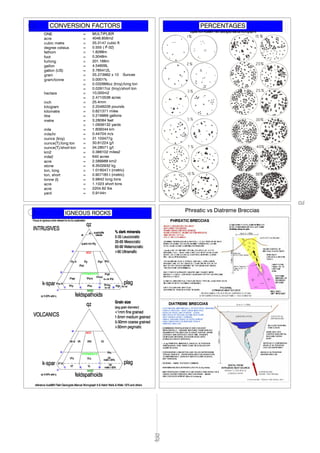
- 7. =ONE =acre MULTIPLIER 4046.856m2 =cubic metre 35.3147 cubic ft =degree celsius 0.555 ( F-32) =fathom 1.8288m =foot 0.3048m =furlong 201.168m =gallon 4.54609L =gallon (US) 3.785412L =gram 35.273962 x 10 ounces =gram/tonne 0.0001% 3 = 0.032666oz (troy)/long ton = 0.02917oz (troy)/short ton =hectare 10,000m2 = 2.4710538 acres =inch 25.4mm =kilogram 2.2046226 pounds =kilometre 0.621371 miles =litre 0.219969 gallons =metre 3.28084 feet = 1.0936132 yards =mile 1.609344 km =mile/hr 0.44704 m/s =ounce (troy) 31 103477g =ounce(T)/long ton 30.61224 g/t =ounce(T)/short ton 34.28571 g/t =km2 0.386102 miles2 =mile2 640 acres =acre 2.589988 km2 =stone 6.3502932 kg =ton, long 1.016047 t (metric) =ton, short 0.907185 t (metric) =tonne (t) 0.9842 long tons =acre 1.1023 short tons =acre 2204.62 lbs =yard 0.9144n CONVERSION FACTORS PERCENTAGES IGNEOUS ROCKS Phreatic vs Diatreme Breccias