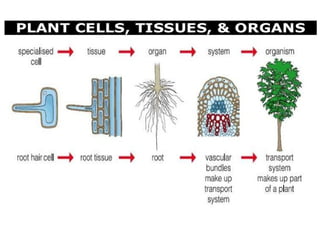
Cell - cell structure - Tissues, Organ systems and organisms (IGCSE Biology)
- 1. The best presentations are conversationsThe best presentations are conversations
- 2. The cell (from Latin cella, meaning "small room") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. A cell is the smallest unit of life. Cells are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is called cell biology. Onion (Allium cepa) root cells in different phases of the cell cycle (drawn by E. B. Wilson, 1900)
- 25. 1.What is the part of the animal cell that is labelled by A? [1 mark] A Cell membrane B Chloroplast C Mitochondrion D Nucleus 2.Which of these units is most suitable for measuring the length of a cell? [1 mark] A Kilometre B Metre C Centimetre D Micrometre 3.A cell of the pancreas produces digestive enzymes, which are proteins. The enzymes are released into the small intestine. Suggest which two of the following are adaptations to its role? Tick two boxes. [2 marks] A A small surface area to volume ratio B Large numbers of ribosomes C Mitochondria with well-developed internal membranes D The ability to move 4.Give two differences between plant and animal cells. [2 marks] 5.Compare the advantages and disadvantages of light and electron microscopes. [4 marks] 6.The student measured a cell they were looking at as 0.5 mm. Convert this into micrometres.
- 26. 7.The student measured a cell they were looking at as 0.5 mm. Convert this into micrometres. 8.Describe how to prepare a stained slide of onion epidermal tissue. [6 marks] 9.Compare the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. [6 marks] 10.Explain what is an organism [7marks]




















![1.What is the part of the animal cell that is labelled by A?
[1 mark]
A Cell membrane
B Chloroplast
C Mitochondrion
D Nucleus
2.Which of these units is most suitable for measuring the length of a cell?
[1 mark]
A Kilometre
B Metre
C Centimetre
D Micrometre
3.A cell of the pancreas produces digestive enzymes, which are proteins. The
enzymes are released into the small intestine.
Suggest which two of the following are adaptations to its role?
Tick two boxes.
[2 marks]
A A small surface area to volume ratio
B Large numbers of ribosomes
C Mitochondria with well-developed internal membranes
D The ability to move
4.Give two differences between plant and animal cells.
[2 marks]
5.Compare the advantages and disadvantages of light and electron microscopes.
[4 marks]
6.The student measured a cell they were looking at as 0.5 mm.
Convert this into micrometres.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cells-cellstructure-cellsandorganisms-181103154757/85/Cell-cell-structure-Tissues-Organ-systems-and-organisms-IGCSE-Biology-25-320.jpg)
![7.The student measured a cell they were looking at as 0.5 mm.
Convert this into micrometres.
8.Describe how to prepare a stained slide of onion epidermal tissue.
[6 marks]
9.Compare the structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. [6 marks]
10.Explain what is an organism [7marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cells-cellstructure-cellsandorganisms-181103154757/85/Cell-cell-structure-Tissues-Organ-systems-and-organisms-IGCSE-Biology-26-320.jpg)