Cell structure anmd function
- 1. School Name : DCS International School Class : VIII Sub : General Science Date : 6-7-2019 Period : 1 Duration : 45 min Topic : Cell Structure and Function
- 2. Some Facts about Cells ? The word cell is derived from the Latin word Ī░cellulaĪ▒ which means Ī░a little roomĪ▒ ? It was the British botanist Robert Hooke who, in 1665, while examining a slice of cork ( bark of a plant) under a microscope, found compartments like structures. They look like honey comb and they are separated from each other by walls and he called them Ī░cellsĪ▒. ? He actually saw dead cells. ? The cells that make up our body are so small that you could fit over 200 of them on the full stop at the end of this sentence.
- 3. Cells: An Introduction ? A cell is the structural and functional unit of all life forms. ? All living organisms, whether plants or animals, are made up of microscopic units called cells. ? The cell occupies the same central position in biology as the atom in the physical sciences. ? Organisms may be broadly classified into two kinds: ? ©C Unicellular ? ©C Multi-cellular
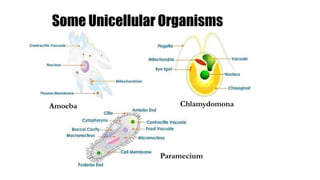
- 4. Unicellular Organisms ? All living beings, plants and animals, start their life with a single cell. ? Some organisms exist as a single cell and carry out the various metabolic life processes such as assimilation, respiration, reproduction, excretion, etc., that are essential for their survival. ? These are known as unicellular organisms. ? Example: Yeast, bacteria, chlamydomonas, amoeba
- 5. Some Unicellular Organisms Amoeba Chlamydomona Paramecium
- 6. Multicellular Organism ? Some cells divide and give rise to organisms with more than one cell, these organisms are termed as multi-cellular. ? Example: animals, humans, most plants
- 7. Onion Peel Cells Cells from the cheek Some Multi-cellular Organisms
- 8. Structure of a Cell ? Cells vary in shape and size. They may be oval, spherical, rectangular, polygonal, spindle shaped, star shaped, rod-shaped or totally irregular like the nerve cell. ? The diversity in cells is in accordance with the role or function it has to perform as part of the tissue or organ system. ? In general, there is no typical shape for cells.
- 9. Various Cells from the Human Body
- 10. Structure of a Cell ? Each cell has got certain specific components within it known as cell organelles, each of which performs a special function ? A cell is able to live and perform all its functions because of these organelles ? These organelles together constitute the basic unit called the cell ? All cells have the same organelles, no matter what their function is or what organism they are found in
- 11. Structure of a Cell ? There are three features in almost every cell: ? ©C Plasma Membrane ? ©C Nucleus ? ©C Cytoplasm ? All activities inside the cell and interactions of the cell with its environment are possible due to these features
- 12. Plasma Membrane or Cell Membrane ? Cell membrane is present in both plant and animal cells. ? It is living, elastic and made of proteins and lipids (fats). ? Its function is to provide a mechanical barrier for the protection of the inner cell contents and to regulate the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. ? It is called a selectively permeable membrane
- 13. Cell Wall ? The cell wall is present only in plant cells and lies outside the plasma membrane ? It is made up of a complex polysaccharide (carbohydrate) called cellulose. ? Its function is to give strength and rigidity to the cell. It is non-living. ? Cell walls permit the cells of plants, fungi and bacteria to withstand hypotonic external media without bursting
- 14. Nucleus ? This is a prominent, spherical or oval structure found at the centre of the cell. ? It is the controlling centre of all cell activities and has been described as the brain of the cell. ? It regulates all metabolic and hereditary activities of the cell ? It also plays a central role in cellular reproduction - the process by which a single cell divides and forms two new cells
- 15. Thank you