Cell transport 2011a
Download as ppt, pdf1 like605 views
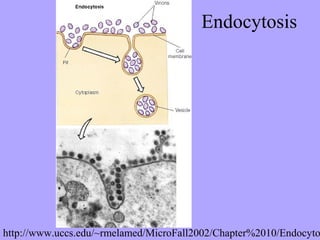
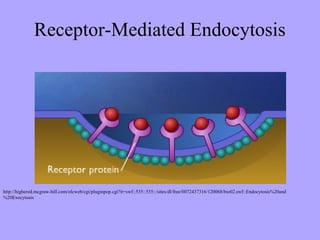
The cell membrane functions as a selectively permeable barrier that allows some substances to pass through via diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport processes. Diffusion allows for the passive movement of small molecules and ions according to their concentration gradients. Larger molecules and ions require membrane transport proteins like channel and carrier proteins to cross. The cell takes in nutrients and disposes of waste through endocytosis and exocytosis, respectively. Active transport requires energy to pump molecules against their gradients via proteins like the sodium-potassium pump.
1 of 29
Downloaded 18 times





Ad
Recommended
Cells
CellsSUSAN MATHEW
╠²
All cells, whether animal or plant, have three basic features - a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus. Plant cells also contain additional structures that distinguish them from animal cells. The document provides an overview of the key components of plant cells and how to view them under a microscope.Revision questions on 1.6. Cell division of IB Biology
Revision questions on 1.6. Cell division of IB Biology Miltiadis Kitsos
╠²
This document contains revision questions about cell division, including mitosis and cytokinesis. It begins by defining key terms like mitosis, interphase, and the phases of the cell cycle. It then provides questions to test understanding of topics like DNA supercoiling during mitosis, the stages of mitosis, and calculating mitotic indices from micrographs. Later questions address the differences between animal and plant cytokinesis and the role of cyclins in cell cycle control. It concludes by defining cancer-related topics and analyzing a graph showing the correlation between cigarette smoking and lung cancer deaths.Cell structure function
Cell structure functionmqblack
╠²
All living things are made up of cells, which are the smallest units capable of performing life functions. Cells come in two main types: prokaryotic cells, which lack internal membrane-bound structures and are found in bacteria; and eukaryotic cells, which contain membrane-bound organelles and include plants, animals, and most living organisms. A typical animal or plant cell contains a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and various organelles that perform important functions like producing energy, packaging and transporting materials, and breaking down waste.Challenges in vascular tissue engineering
Challenges in vascular tissue engineeringYogeshJoshi166
╠²
The document discusses the challenges in vascular tissue engineering, including the complexities of growing blood vessels and integrating them into living systems. Key approaches include the use of endothelial cell-seeded synthetic grafts and various biomaterials, each with distinct advantages and limitations. Major challenges involve ensuring non-thrombogenic surfaces, managing immunogenicity, and achieving reproducibility, with suggested remedies like adhesive coatings and the selection of appropriate cell types.Cell flip notes organelles in order
Cell flip notes organelles in orderwja10255
╠²
The document summarizes key cellular structures found in plant and animal cells. It describes organelles such as the nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and cytoskeleton. These organelles have specific functions, such as protein synthesis, photosynthesis, energy production, modification and transport of materials. The document notes which structures are found in all eukaryotic cells, and which are unique to plant cells, such as chloroplasts and cell walls.Diptipresentation24
Diptipresentation24Mazhar Laliwala
╠²
The document provides an overview of cell structure and function. It defines the cell as the basic unit of life and outlines the cell theory. It describes the two main types of cells - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Key structures of the typical animal and plant cell are then discussed, including the cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, vacuoles, and chloroplasts. Each cellular structure's function is briefly explained.Isolating Primary Cells 101
Isolating Primary Cells 101allcells
╠²
The document presents insights from a webinar hosted by AllCells and Nexcelom Bioscience discussing methods for isolating and measuring the viability of primary cells. Key topics include the processes for obtaining cells from bone marrow and peripheral blood, along with recommended viability methods and equipment for accurate cell counting. The document emphasizes the importance of reducing variability and increasing accuracy in cell measurement for effective research applications in drug development, toxicology, and regenerative medicine.Specialised Cells
Specialised CellsCarla Smedberg
╠²
This document discusses specialized cells and their functions. It provides examples of specialized plant cells like those with thick cell walls that allow bending as they fill with water and have large surface areas for absorbing water and minerals. Specialized animal cells discussed include cilia for moving mucus, elongated muscle cells for contraction, flat disc-shaped red blood cells for oxygen transport, and nerve cells with long axons and dendrites for transmitting electrical signals. Students are asked to order complexity from cell to organism and describe cellular adaptations and functions.6 human physiology syllabus statements
6 human physiology syllabus statementscartlidge
╠²
The document discusses several topics related to human physiology:
- Digestion and absorption in the small intestine, where villi increase surface area for absorption and different transport methods absorb nutrients.
- The blood system, including the structure and function of arteries, capillaries, and veins in circulating blood and transporting substances.
- Defense against infectious diseases, with the skin, mucous membranes, white blood cells, antibodies, and antibiotics providing protection.
- Gas exchange in the lungs, which are actively ventilated to maintain oxygen and carbon dioxide concentration gradients to enable passive exchange in alveoli.26254477 ap-biology-cells-chapter-8-the-cell-membrane-2008-teacher
26254477 ap-biology-cells-chapter-8-the-cell-membrane-2008-teacherGuruMASTURABINTIMUHA
╠²
The cell membrane controls what enters and exits the cell. It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded. Phospholipids have hydrophobic fatty acid tails and hydrophilic phosphate heads, arranging in a bilayer. Proteins allow selective permeability and perform functions like transport. Movement across the membrane includes passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion through protein channels, and active transport using protein pumps and ATP. Water moves across by osmosis, from high to low concentration areas. Cells regulate water balance in different conditions like hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic environments.Cell Theory
Cell TheoryStephen Taylor
╠²
The document discusses cell theory and provides a brief history and overview of key concepts. It states that all living things are made of cells, which are the smallest units of life. Unicellular organisms consist of single cells, while multicellular organisms have specialized cell types. Cells come only from existing cells through division.Cell Division - Mitosis
Cell Division - MitosisStephen Taylor
╠²
Eukaryotes cannot divide by binary fission like prokaryotes because they have complex internal structures that need to be divided equally. An online lab allows users to create a pie chart showing the relative lengths of the stages of mitosis. Observing an onion root tip under a microscope can also demonstrate the stages of mitosis. Mitosis ensures genetically identical daughter nuclei by equally dividing the genetic material of the parent cell between the two daughter cells during cell division.Anatomy 1 ppt
Anatomy 1 pptUPUL UDAYARAJ
╠²
This document contains a series of multiple choice questions about human anatomy from a YouTube video. It provides the questions, correct answers, and brief explanations for each answer. There are 5 sample questions covering topics like the structure of the cell membrane, characteristics of cytoplasmic organelles and exocrine glands, the number of major salivary glands in humans, and the percentage of total saliva produced by the parotid glands. The document is intended to help medical students and professionals refresh their knowledge of essential human anatomy concepts.Abstract_GDR_CellTiss_JLJ
Abstract_GDR_CellTiss_JLJSidney Perkins
╠²
1) Researchers developed a microfluidic platform to study how blood flow influences endothelial cell function and the development of atherosclerosis.
2) The platform allows independent control of fluid flow parameters like amplitude and direction, as well as cell shape, density, and orientation relative to flow.
3) Preliminary experiments compared calcium signaling responses in cuboidal versus elongated bovine endothelial cells under different flow conditions using the platform.Biology theory 5 (cell division in Eukaryotic cell)
Biology theory 5 (cell division in Eukaryotic cell)Dr. Shameeran Bamarni
╠²
This document provides an overview of cell division processes in eukaryotic cells, including mitosis and meiosis. It describes the key stages and outcomes of each process. Mitosis involves one nuclear division that results in two identical daughter cells. Meiosis involves two nuclear divisions that produce four haploid gametes with half the number of chromosomes, allowing for sexual reproduction. The stages of mitosis are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Meiosis has two rounds: meiosis I which separates homologous chromosomes, and meiosis II which separates sister chromatids. Mitosis occurs in body cells for growth and repair, while meiosis occurs in sex cells and combines with fertilization to2 syllabus statements
2 syllabus statementscartlidge
╠²
This document outlines the key concepts and statements from the Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry syllabus regarding the organization of organisms. It discusses the structure and functions of plant and animal cells, including major cell organelles like the nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. It also defines the different levels of biological organization from cells to tissues to organs to organ systems. Finally, it mentions calculating magnification and sizes of biological specimens.Basic unit of life
Basic unit of life55146
╠²
This document provides an overview of cells, including their basic structures and functions. It discusses the common features of plant and animal cells, such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, and ribosomes. The document also notes additional structures in plant cells, like the cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. It defines and provides examples of diffusion and osmosis, the processes by which substances move across cell membranes. Specialized cell types in multicellular organisms are also briefly mentioned.Primary Cells 101
Primary Cells 101allcells
╠²
This document discusses primary cells and their use in biomedical research. Primary cells are isolated directly from tissues and have important advantages over cell lines, including greater biological relevance. Primary cells are used in applications such as biomarker research, drug development, immunotherapeutics, and tissue engineering. The document reviews techniques for working with primary cells, including isolation, culture, differentiation, and characterization using methods like flow cytometry and immunoassays. Primary cells provide a more physiologically relevant model for research compared to cell lines.Cell & its organells
Cell & its organellsdinesh bawankar
╠²
The document summarizes key components and functions of the cell. It defines cells as the basic unit of life that carry out essential functions of growth, metabolism, and reproduction. The summary describes the main parts of the cell including the cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, and lysosomes. It provides a brief overview of the structure and role of each organelle in cellular processes.Isolation of pbmc
Isolation of pbmcShreewardhan Rajopadhye
╠²
This document summarizes the process of isolating peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from whole blood. It describes that PBMCs contain lymphocytes and monocytes that are important for the immune system. The process involves layering blood on top of ficoll-hypaque, then centrifuging to separate the buffy coat containing PBMCs from other blood components. The PBMCs are then cultured for research applications such as studying HIV infection of CD4+ cells.Cell
Cellkh Ripon
╠²
The document summarizes key components and functions of eukaryotic cells. It describes the cell membrane as composed of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates that act as a selective barrier. It also discusses several intracellular organelles - the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, ribosomes, lysosomes - and their roles in processes like protein synthesis, energy production, metabolism, and waste digestion. The plasma membrane, organelles, and their specialized functions allow cells to carry out life's processes.Erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesisakash chauhan
╠²
Erythropoiesis is the process where red blood cells develop from stem cells in the bone marrow. It proceeds through several stages, starting with stem cells that differentiate into progenitor cells and then normoblasts as the cells mature. Key changes occur like decreasing size, loss of nucleus and organelles, and increasing hemoglobin content. Erythropoietin is the main hormone that stimulates and regulates red blood cell production in response to hypoxia. Other factors like iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid are also necessary for erythropoiesis.Cell culture 06
Cell culture 06Suk Namgoong
╠²
This document contains the syllabus for an advanced animal cell culture course from the Department of Animal Science at Chungbuk National University. The syllabus lists 8 topics that will be covered between September 2013 and December 2013, including introductions to cell culture and stem cells, using cell culture for antibody and protein production, transgenic and knockout animals, and genome engineering. Student groups are assigned to present on specific dates, including topics like stem cell I and II and protein production/purification. The document also includes an excerpt from the November 14th lecture on stem cell II, discussing the mechanisms of cellular reprogramming and how induced pluripotent stem cells were discovered.SNAX 07
SNAX 07Sergey Kanatyev
╠²
ąöąŠą║čāą╝ąĄąĮčé ąŠą┐ąĖčüčŗą▓ą░ąĄčé ą╝čÅčüąĮčŗąĄ čüąĮąĄą║ąĖ, ą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĮą░ąĘąĮą░č湥ąĮąĮčŗąĄ ą┤ą╗čÅ ą╝čāąČčćąĖąĮ, ąĘą░ąĮąĖą╝ą░čÄčēąĖčģčüčÅ čüąĖą╗ąŠą▓čŗą╝ąĖ ą▓ąĖą┤ą░ą╝ąĖ čüą┐ąŠčĆčéą░, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ąĮčāąČą┤ą░čÄčéčüčÅ ą▓ čćąĖčüč鹊ą╝ ą▒ąĄą╗ą║ąĄ. ąŻą┐ą░ą║ąŠą▓ą║ą░ ą┤ąŠą╗ąČąĮą░ ą▒čŗčéčī ą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝ąĖčćąĮąŠą╣ ąĖ ąŠčéą╗ąĖčćą░čéčīčüčÅ ąŠčé čéčĆą░ą┤ąĖčåąĖąŠąĮąĮčŗčģ čüąĮąĄą║ąŠą▓, ą░ č鹊čćą║ąĖ ą┐čĆąŠą┤ą░ąČąĖ ą▓ą║ą╗čÄčćą░čÄčé ą╝ą░ą│ą░ąĘąĖąĮčŗ čüą┐ąŠčĆčéąĖą▓ąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐ąĖčéą░ąĮąĖčÅ ąĖ ą░ą▓č鹊ą╝ą░č鹊ą▓ ą▓ čéčĆąĄąĮą░ąČąĄčĆąĮčŗčģ ąĘą░ą╗ą░čģ. ą¤čĆąŠą┤čāą║čé ą┐ąŠąĘąĖčåąĖąŠąĮąĖčĆčāąĄčéčüčÅ ą║ą░ą║ ą┐ąĖčéą░ąĮąĖąĄ ą┤ą╗čÅ čüąĖą╗čīąĮčŗčģ ą┤čāčģąŠą╝ ą╗čÄą┤ąĄą╣, čü ą░ą║čåąĄąĮč鹊ą╝ ąĮą░ čüą░ą╝ąŠčĆą░ąĘą▓ąĖčéąĖąĄ ąĖ ą▓čŗčüąŠą║čāčÄ čäąĖąĘąĖč湥čüą║čāčÄ č乊čĆą╝čā.Chem of lifea
Chem of lifeaCaroline Holmes
╠²
The document discusses the four major classes of chemical compounds found in living organisms: carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids. It provides examples and functions of important molecules within each class, including how they are constructed from smaller building blocks and bonded together. Key molecules like ATP store and transfer energy through bonding, while lipids like fatty acids store energy and form biological membranes.Il mio compleanno
Il mio compleanno Marisa Argentiero
╠²
Il narratore riflette sul proprio compleanno, rivelando come la celebrazione si sia trasformata in un'occasione in cui nessuno sembra ricordarsi di lui, nonostante il clamore di festeggiamenti. Egli si sente escluso e disinteressato, desiderando che le persone riconoscano il suo vero significato e la sua esistenza. Alla fine, esprime il desiderio di organizzare una festa grandiosa e invita tutti a partecipare, sottolineando l'importanza della fede.Kanatyev brief 04_revolta
Kanatyev brief 04_revoltaSergey Kanatyev
╠²
ąöąŠą║čāą╝ąĄąĮčé ąŠą┐ąĖčüčŗą▓ą░ąĄčé ą┐čĆąŠąĄą║čé čĆą░ąĘčĆą░ą▒ąŠčéą║ąĖ ą▒čĆąĄąĮą┤ąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĖčÅ ą║ąŠą╝ą┐ą░ąĮąĖąĖ ┬½revolta motors┬╗, čüą┐ąĄčåąĖą░ą╗ąĖąĘąĖčĆčāčÄčēąĄą╣čüčÅ ąĮą░ ą┐čĆąŠą┤ą░ąČąĄ 菹╗ąĄą║čéčĆąŠą╝ąŠą▒ąĖą╗ąĄą╣. ą×čüąĮąŠą▓ąĮčŗąĄ ą┐čĆąŠą▒ą╗ąĄą╝čŗ ą▓ą║ą╗čÄčćą░čÄčé čĆą░ąĘą╝čŗč鹊ąĄ ą┐ąŠąĘąĖčåąĖąŠąĮąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĖąĄ ąĖ ąĖą╝ąĄčÄčēąĖą╣čüčÅ ą┤ąĄčéčüą║ąĖą╣ čüčéąĖą╗čī ą╗ąŠą│ąŠčéąĖą┐ą░. ą¤čĆąŠąĄą║čé ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╗ą░ą│ą░ąĄčé čĆąĄčłąĄąĮąĖąĄ ą▓ ą▓ąĖą┤ąĄ čüąŠąĘą┤ą░ąĮąĖčÅ ąŠčéą┤ąĄą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ ą║ąŠą╝ą┐ą░ąĮąĖąĖ čü čüąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╝ ąĖą╝ąĖą┤ąČąĄą╝ ąĖ ą▓čŗčüąŠą║ąŠą║ą▓ą░ą╗ąĖčäąĖčåąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĮčŗą╝ąĖ čüą┐ąĄčåąĖą░ą╗ąĖčüčéą░ą╝ąĖ, ąŠčĆąĖąĄąĮčéąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĮąŠą╣ ąĮą░ čāčüą┐ąĄčłąĮčŗčģ ą║ą╗ąĖąĄąĮč鹊ą▓, čåąĄąĮčÅčēąĖčģ 菹║ąŠą╗ąŠą│ąĖčćąĮąŠčüčéčī ąĖ ą┐čĆąĄčüčéąĖąČ.Il mio compleanno gb
Il mio compleanno gbMarisa Argentiero
╠²
Il documento riflette sulle celebrazioni del compleanno dell'autore, notando l'assurdit├Ā di festeggiare senza essere invitati. Si esprime un desiderio di connessione e riconoscimento da parte delle persone, sottolineando il significato personale della festa. L'autore invita a partecipare a una festa speciale che organizzer├Ā, sottolineando l'importanza di credere in lui.Untitled 1
Untitled 1trevondixon
╠²
Louisiana State University was founded in 1853 in Baton Rouge, Louisiana and has over 5 campuses across the state. It offers both undergraduate and graduate degrees across various colleges including Agriculture, Art & Design, Arts & Sciences, and Law. The document provides details on tuition costs, degrees offered, notable alumni, and reasons for wanting to attend LSU.More Related Content
What's hot (16)
Specialised Cells
Specialised CellsCarla Smedberg
╠²
This document discusses specialized cells and their functions. It provides examples of specialized plant cells like those with thick cell walls that allow bending as they fill with water and have large surface areas for absorbing water and minerals. Specialized animal cells discussed include cilia for moving mucus, elongated muscle cells for contraction, flat disc-shaped red blood cells for oxygen transport, and nerve cells with long axons and dendrites for transmitting electrical signals. Students are asked to order complexity from cell to organism and describe cellular adaptations and functions.6 human physiology syllabus statements
6 human physiology syllabus statementscartlidge
╠²
The document discusses several topics related to human physiology:
- Digestion and absorption in the small intestine, where villi increase surface area for absorption and different transport methods absorb nutrients.
- The blood system, including the structure and function of arteries, capillaries, and veins in circulating blood and transporting substances.
- Defense against infectious diseases, with the skin, mucous membranes, white blood cells, antibodies, and antibiotics providing protection.
- Gas exchange in the lungs, which are actively ventilated to maintain oxygen and carbon dioxide concentration gradients to enable passive exchange in alveoli.26254477 ap-biology-cells-chapter-8-the-cell-membrane-2008-teacher
26254477 ap-biology-cells-chapter-8-the-cell-membrane-2008-teacherGuruMASTURABINTIMUHA
╠²
The cell membrane controls what enters and exits the cell. It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded. Phospholipids have hydrophobic fatty acid tails and hydrophilic phosphate heads, arranging in a bilayer. Proteins allow selective permeability and perform functions like transport. Movement across the membrane includes passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion through protein channels, and active transport using protein pumps and ATP. Water moves across by osmosis, from high to low concentration areas. Cells regulate water balance in different conditions like hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic environments.Cell Theory
Cell TheoryStephen Taylor
╠²
The document discusses cell theory and provides a brief history and overview of key concepts. It states that all living things are made of cells, which are the smallest units of life. Unicellular organisms consist of single cells, while multicellular organisms have specialized cell types. Cells come only from existing cells through division.Cell Division - Mitosis
Cell Division - MitosisStephen Taylor
╠²
Eukaryotes cannot divide by binary fission like prokaryotes because they have complex internal structures that need to be divided equally. An online lab allows users to create a pie chart showing the relative lengths of the stages of mitosis. Observing an onion root tip under a microscope can also demonstrate the stages of mitosis. Mitosis ensures genetically identical daughter nuclei by equally dividing the genetic material of the parent cell between the two daughter cells during cell division.Anatomy 1 ppt
Anatomy 1 pptUPUL UDAYARAJ
╠²
This document contains a series of multiple choice questions about human anatomy from a YouTube video. It provides the questions, correct answers, and brief explanations for each answer. There are 5 sample questions covering topics like the structure of the cell membrane, characteristics of cytoplasmic organelles and exocrine glands, the number of major salivary glands in humans, and the percentage of total saliva produced by the parotid glands. The document is intended to help medical students and professionals refresh their knowledge of essential human anatomy concepts.Abstract_GDR_CellTiss_JLJ
Abstract_GDR_CellTiss_JLJSidney Perkins
╠²
1) Researchers developed a microfluidic platform to study how blood flow influences endothelial cell function and the development of atherosclerosis.
2) The platform allows independent control of fluid flow parameters like amplitude and direction, as well as cell shape, density, and orientation relative to flow.
3) Preliminary experiments compared calcium signaling responses in cuboidal versus elongated bovine endothelial cells under different flow conditions using the platform.Biology theory 5 (cell division in Eukaryotic cell)
Biology theory 5 (cell division in Eukaryotic cell)Dr. Shameeran Bamarni
╠²
This document provides an overview of cell division processes in eukaryotic cells, including mitosis and meiosis. It describes the key stages and outcomes of each process. Mitosis involves one nuclear division that results in two identical daughter cells. Meiosis involves two nuclear divisions that produce four haploid gametes with half the number of chromosomes, allowing for sexual reproduction. The stages of mitosis are interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Meiosis has two rounds: meiosis I which separates homologous chromosomes, and meiosis II which separates sister chromatids. Mitosis occurs in body cells for growth and repair, while meiosis occurs in sex cells and combines with fertilization to2 syllabus statements
2 syllabus statementscartlidge
╠²
This document outlines the key concepts and statements from the Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry syllabus regarding the organization of organisms. It discusses the structure and functions of plant and animal cells, including major cell organelles like the nucleus, chloroplasts, and mitochondria. It also defines the different levels of biological organization from cells to tissues to organs to organ systems. Finally, it mentions calculating magnification and sizes of biological specimens.Basic unit of life
Basic unit of life55146
╠²
This document provides an overview of cells, including their basic structures and functions. It discusses the common features of plant and animal cells, such as the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, and ribosomes. The document also notes additional structures in plant cells, like the cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuoles. It defines and provides examples of diffusion and osmosis, the processes by which substances move across cell membranes. Specialized cell types in multicellular organisms are also briefly mentioned.Primary Cells 101
Primary Cells 101allcells
╠²
This document discusses primary cells and their use in biomedical research. Primary cells are isolated directly from tissues and have important advantages over cell lines, including greater biological relevance. Primary cells are used in applications such as biomarker research, drug development, immunotherapeutics, and tissue engineering. The document reviews techniques for working with primary cells, including isolation, culture, differentiation, and characterization using methods like flow cytometry and immunoassays. Primary cells provide a more physiologically relevant model for research compared to cell lines.Cell & its organells
Cell & its organellsdinesh bawankar
╠²
The document summarizes key components and functions of the cell. It defines cells as the basic unit of life that carry out essential functions of growth, metabolism, and reproduction. The summary describes the main parts of the cell including the cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, and lysosomes. It provides a brief overview of the structure and role of each organelle in cellular processes.Isolation of pbmc
Isolation of pbmcShreewardhan Rajopadhye
╠²
This document summarizes the process of isolating peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from whole blood. It describes that PBMCs contain lymphocytes and monocytes that are important for the immune system. The process involves layering blood on top of ficoll-hypaque, then centrifuging to separate the buffy coat containing PBMCs from other blood components. The PBMCs are then cultured for research applications such as studying HIV infection of CD4+ cells.Cell
Cellkh Ripon
╠²
The document summarizes key components and functions of eukaryotic cells. It describes the cell membrane as composed of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates that act as a selective barrier. It also discusses several intracellular organelles - the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, ribosomes, lysosomes - and their roles in processes like protein synthesis, energy production, metabolism, and waste digestion. The plasma membrane, organelles, and their specialized functions allow cells to carry out life's processes.Erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesisakash chauhan
╠²
Erythropoiesis is the process where red blood cells develop from stem cells in the bone marrow. It proceeds through several stages, starting with stem cells that differentiate into progenitor cells and then normoblasts as the cells mature. Key changes occur like decreasing size, loss of nucleus and organelles, and increasing hemoglobin content. Erythropoietin is the main hormone that stimulates and regulates red blood cell production in response to hypoxia. Other factors like iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid are also necessary for erythropoiesis.Cell culture 06
Cell culture 06Suk Namgoong
╠²
This document contains the syllabus for an advanced animal cell culture course from the Department of Animal Science at Chungbuk National University. The syllabus lists 8 topics that will be covered between September 2013 and December 2013, including introductions to cell culture and stem cells, using cell culture for antibody and protein production, transgenic and knockout animals, and genome engineering. Student groups are assigned to present on specific dates, including topics like stem cell I and II and protein production/purification. The document also includes an excerpt from the November 14th lecture on stem cell II, discussing the mechanisms of cellular reprogramming and how induced pluripotent stem cells were discovered.Viewers also liked (8)
SNAX 07
SNAX 07Sergey Kanatyev
╠²
ąöąŠą║čāą╝ąĄąĮčé ąŠą┐ąĖčüčŗą▓ą░ąĄčé ą╝čÅčüąĮčŗąĄ čüąĮąĄą║ąĖ, ą┐čĆąĄą┤ąĮą░ąĘąĮą░č湥ąĮąĮčŗąĄ ą┤ą╗čÅ ą╝čāąČčćąĖąĮ, ąĘą░ąĮąĖą╝ą░čÄčēąĖčģčüčÅ čüąĖą╗ąŠą▓čŗą╝ąĖ ą▓ąĖą┤ą░ą╝ąĖ čüą┐ąŠčĆčéą░, ą║ąŠč鹊čĆčŗąĄ ąĮčāąČą┤ą░čÄčéčüčÅ ą▓ čćąĖčüč鹊ą╝ ą▒ąĄą╗ą║ąĄ. ąŻą┐ą░ą║ąŠą▓ą║ą░ ą┤ąŠą╗ąČąĮą░ ą▒čŗčéčī ą┤ąĖąĮą░ą╝ąĖčćąĮąŠą╣ ąĖ ąŠčéą╗ąĖčćą░čéčīčüčÅ ąŠčé čéčĆą░ą┤ąĖčåąĖąŠąĮąĮčŗčģ čüąĮąĄą║ąŠą▓, ą░ č鹊čćą║ąĖ ą┐čĆąŠą┤ą░ąČąĖ ą▓ą║ą╗čÄčćą░čÄčé ą╝ą░ą│ą░ąĘąĖąĮčŗ čüą┐ąŠčĆčéąĖą▓ąĮąŠą│ąŠ ą┐ąĖčéą░ąĮąĖčÅ ąĖ ą░ą▓č鹊ą╝ą░č鹊ą▓ ą▓ čéčĆąĄąĮą░ąČąĄčĆąĮčŗčģ ąĘą░ą╗ą░čģ. ą¤čĆąŠą┤čāą║čé ą┐ąŠąĘąĖčåąĖąŠąĮąĖčĆčāąĄčéčüčÅ ą║ą░ą║ ą┐ąĖčéą░ąĮąĖąĄ ą┤ą╗čÅ čüąĖą╗čīąĮčŗčģ ą┤čāčģąŠą╝ ą╗čÄą┤ąĄą╣, čü ą░ą║čåąĄąĮč鹊ą╝ ąĮą░ čüą░ą╝ąŠčĆą░ąĘą▓ąĖčéąĖąĄ ąĖ ą▓čŗčüąŠą║čāčÄ čäąĖąĘąĖč湥čüą║čāčÄ č乊čĆą╝čā.Chem of lifea
Chem of lifeaCaroline Holmes
╠²
The document discusses the four major classes of chemical compounds found in living organisms: carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids. It provides examples and functions of important molecules within each class, including how they are constructed from smaller building blocks and bonded together. Key molecules like ATP store and transfer energy through bonding, while lipids like fatty acids store energy and form biological membranes.Il mio compleanno
Il mio compleanno Marisa Argentiero
╠²
Il narratore riflette sul proprio compleanno, rivelando come la celebrazione si sia trasformata in un'occasione in cui nessuno sembra ricordarsi di lui, nonostante il clamore di festeggiamenti. Egli si sente escluso e disinteressato, desiderando che le persone riconoscano il suo vero significato e la sua esistenza. Alla fine, esprime il desiderio di organizzare una festa grandiosa e invita tutti a partecipare, sottolineando l'importanza della fede.Kanatyev brief 04_revolta
Kanatyev brief 04_revoltaSergey Kanatyev
╠²
ąöąŠą║čāą╝ąĄąĮčé ąŠą┐ąĖčüčŗą▓ą░ąĄčé ą┐čĆąŠąĄą║čé čĆą░ąĘčĆą░ą▒ąŠčéą║ąĖ ą▒čĆąĄąĮą┤ąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĖčÅ ą║ąŠą╝ą┐ą░ąĮąĖąĖ ┬½revolta motors┬╗, čüą┐ąĄčåąĖą░ą╗ąĖąĘąĖčĆčāčÄčēąĄą╣čüčÅ ąĮą░ ą┐čĆąŠą┤ą░ąČąĄ 菹╗ąĄą║čéčĆąŠą╝ąŠą▒ąĖą╗ąĄą╣. ą×čüąĮąŠą▓ąĮčŗąĄ ą┐čĆąŠą▒ą╗ąĄą╝čŗ ą▓ą║ą╗čÄčćą░čÄčé čĆą░ąĘą╝čŗč鹊ąĄ ą┐ąŠąĘąĖčåąĖąŠąĮąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĖąĄ ąĖ ąĖą╝ąĄčÄčēąĖą╣čüčÅ ą┤ąĄčéčüą║ąĖą╣ čüčéąĖą╗čī ą╗ąŠą│ąŠčéąĖą┐ą░. ą¤čĆąŠąĄą║čé ą┐čĆąĄą┤ą╗ą░ą│ą░ąĄčé čĆąĄčłąĄąĮąĖąĄ ą▓ ą▓ąĖą┤ąĄ čüąŠąĘą┤ą░ąĮąĖčÅ ąŠčéą┤ąĄą╗čīąĮąŠą╣ ą║ąŠą╝ą┐ą░ąĮąĖąĖ čü čüąŠą▓čĆąĄą╝ąĄąĮąĮčŗą╝ ąĖą╝ąĖą┤ąČąĄą╝ ąĖ ą▓čŗčüąŠą║ąŠą║ą▓ą░ą╗ąĖčäąĖčåąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĮčŗą╝ąĖ čüą┐ąĄčåąĖą░ą╗ąĖčüčéą░ą╝ąĖ, ąŠčĆąĖąĄąĮčéąĖčĆąŠą▓ą░ąĮąĮąŠą╣ ąĮą░ čāčüą┐ąĄčłąĮčŗčģ ą║ą╗ąĖąĄąĮč鹊ą▓, čåąĄąĮčÅčēąĖčģ 菹║ąŠą╗ąŠą│ąĖčćąĮąŠčüčéčī ąĖ ą┐čĆąĄčüčéąĖąČ.Il mio compleanno gb
Il mio compleanno gbMarisa Argentiero
╠²
Il documento riflette sulle celebrazioni del compleanno dell'autore, notando l'assurdit├Ā di festeggiare senza essere invitati. Si esprime un desiderio di connessione e riconoscimento da parte delle persone, sottolineando il significato personale della festa. L'autore invita a partecipare a una festa speciale che organizzer├Ā, sottolineando l'importanza di credere in lui.Untitled 1
Untitled 1trevondixon
╠²
Louisiana State University was founded in 1853 in Baton Rouge, Louisiana and has over 5 campuses across the state. It offers both undergraduate and graduate degrees across various colleges including Agriculture, Art & Design, Arts & Sciences, and Law. The document provides details on tuition costs, degrees offered, notable alumni, and reasons for wanting to attend LSU.Nutrition digestion
Nutrition digestionCaroline Holmes
╠²
This document discusses the human digestive system and nutrient absorption. It describes the key functions of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, small intestine and large intestine. The mouth mechanically breaks down food and adds saliva. The stomach initiates protein digestion with hydrochloric acid and pepsin. The liver and pancreas produce bile salts and digestive enzymes that aid in digestion in the small intestine, where most nutrients are absorbed. The large intestine absorbs water and hosts bacterial fermentation.Classical conditioning
Classical conditioningmthies555
╠²
This document defines learning and discusses classical conditioning. It provides examples of classical conditioning, such as feeling nauseous every time entering a math classroom due to previous negative experiences. The document outlines Pavlov's classic experiment with dogs, where he conditioned them to salivate in response to a bell by pairing the bell with food. It discusses key aspects of classical conditioning, including unconditioned stimulus/response and conditioned stimulus/response.Ad
Similar to Cell transport 2011a (20)
Cell-Transport-Powerpoint_Bio chem 10001
Cell-Transport-Powerpoint_Bio chem 10001BgDueas
╠²
The document provides an overview of cellular transport mechanisms, detailing key terms such as concentration, solute, and solution. It differentiates between passive transport (e.g., diffusion and osmosis) and active transport (e.g., endocytosis and exocytosis), explaining how cells regulate the movement of substances across their membranes. Additionally, it discusses osmotic pressure and how various organisms adapt to different osmotic conditions.Cell Membrane And Cell Transport Notes New
Cell Membrane And Cell Transport Notes NewFred Phillips
╠²
The document discusses cellular transport and the cell membrane. It explains that the cell membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell to maintain homeostasis. There are two main types of transport - passive transport which doesn't require energy, and active transport which does. Passive transport includes diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. Active transport uses protein pumps and transports molecules against their concentration gradient.cell.transport..pptx
cell.transport..pptxssuser749fb9
╠²
The cell membrane separates a cell from its environment and regulates what passes in and out through selective permeability. It is a phospholipid bilayer with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails. Passive transport uses diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis to move molecules from high to low concentration without energy. Active transport moves molecules from low to high concentration by using protein pumps and requires energy in the form of ATP. Homeostasis is maintained through these transport processes.Cells 2 homeostasis
Cells 2 homeostasisRobin Seamon
╠²
1) Protists maintain homeostasis through various transport mechanisms across their cell membranes, including passive transport like diffusion and osmosis, as well as active transport powered by ATP.
2) Examples of protists like Paramecium, Amoeba, and Euglena demonstrate different modes of movement, feeding, waste removal, and reproduction to regulate their internal environments.
3) Paramecium uses cilia to sweep in food and remove wastes, Amoeba forms pseudopods for movement and surrounds prey, and Euglena uses flagella and chloroplasts depending on light levels for photosynthesis or absorbing nutrients.Cell_Membrane_Transport.ppt
Cell_Membrane_Transport.ppthaimn
╠²
The document discusses various mechanisms of transport across cell membranes:
1) Diffusion and facilitated diffusion allow small, nonpolar molecules and ions to passively move across the phospholipid bilayer down their concentration gradients.
2) Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a partially permeable membrane down its water potential gradient.
3) Active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradients by using energy in the form of ATP. The sodium-potassium pump is given as an example.
4) Bulk transport involves vesicle-mediated endocytosis and exocytosis to transport larger particles and molecules into and out of cells.cellular transport.pdf
cellular transport.pdfImtiyaz60
╠²
The cell membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell through selective permeability. Small, uncharged molecules can pass through the phospholipid bilayer via diffusion. Larger or charged molecules require transport proteins to cross via facilitated diffusion. Water moves in and out of cells through osmosis in order to balance solute concentrations; it will diffuse into areas of higher solute concentration. The membrane also uses active transport and bulk transport like exocytosis and endocytosis to move molecules against gradients or transport larger particles, requiring energy in the form of ATP.Cellulartransportpowerpoint
Cellulartransportpowerpointceciliaadem
╠²
The cell membrane separates the components of a cell from its environment and regulates what passes in and out through passive and active transport. Passive transport includes diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis, and moves particles from high to low concentration without energy. Active transport requires energy to move particles from low to high concentration against the gradient. Some cells also have a cell wall providing structure and protection to plant, fungi, and bacteria cells.Cell transport Biotech
Cell transport Biotech Darrell Morales
╠²
The cell membrane separates the components of a cell from its environment and regulates what passes in and out through passive and active transport. Passive transport includes diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis, and moves particles from high to low concentration without energy. Active transport requires energy to move particles from low to high concentration against the gradient. Some cells also have a cell wall providing structure and protection to plant, fungi, and bacteria cells.new bacterial cell membrane transport.14.pptx
new bacterial cell membrane transport.14.pptxpalashmahmudg
╠²
The cell membrane, composed of a phospholipid bilayer, acts as a gatekeeper, regulating the flow of materials to maintain homeostasis within the cell. It facilitates both passive transport (e.g., diffusion and osmosis) without energy and active transport, which requires energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient. Homeostasis involves balancing pH, temperature, and solute concentrations, affecting cellular functions.membrane transport AIMC
membrane transport AIMCShamim Akram
╠²
Membrane transport can occur passively through diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion which do not require energy, or actively through processes like ion pumps, cotransporters, and endocytosis/exocytosis which do require energy. Passive transport moves molecules along concentration gradients while active transport moves molecules against gradients using cellular energy from ATP. Cell membranes regulate the passage of substances in and out of cells through selective permeability and various transport mechanisms.Plasma Membrane.pptx22222222222222222222
Plasma Membrane.pptx22222222222222222222KelfalaHassanDawoh
╠²
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the plasma membrane, highlighting its structure, functions, and mechanisms of transport. It explains the fluid mosaic model, the selective permeability of the membrane, and various processes such as diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. Additionally, it describes endocytosis and exocytosis, detailing how cells take in and expel larger molecules.cellulartransportpowerpoint.pptx pharmacology
cellulartransportpowerpoint.pptx pharmacologysyamjith2019
╠²
The document outlines the structure and function of cell membranes, emphasizing their role as gatekeepers that regulate material flow and maintain homeostasis. It discusses passive transport mechanisms like diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis, as well as active transport that requires energy to move substances against the concentration gradient. Additionally, it explains the concepts of hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions, and the processes of endocytosis and exocytosis for transporting large molecules.Transport across cell membrane
Transport across cell membraneZENITH PARMAR
╠²
Transport of substances across cell membranes is necessary for cellular functioning. Passive transport mechanisms like diffusion and osmosis move substances down concentration gradients without energy expenditure. Active transport mechanisms like the sodium-potassium pump and calcium pump move substances against concentration gradients by utilizing energy from ATP hydrolysis. Vesicular transport uses endocytosis and exocytosis to transport larger molecules into and out of cells.Chapter 4 notes new
Chapter 4 notes newjalex1966
╠²
This document summarizes different types of transport across cell membranes, including passive transport mechanisms like diffusion and osmosis, as well as active transport processes that require energy. Passive transport includes diffusion of substances down their concentration gradient and osmosis, where water diffuses through selectively permeable membranes. Active transport moves substances against their concentration gradient using cellular energy in the form of ATP. It discusses specific examples of active transport like the sodium-potassium pump and endocytosis/exocytosis for larger molecules.P.mauri membrane transport
P.mauri membrane transportmastx
╠²
The document summarizes the structure and functions of the cell membrane. It discusses that the cell membrane is made up of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. It selectively controls the movement of substances in and out of cells using both passive transport mechanisms like diffusion and facilitated diffusion, as well as active transport processes that require cellular energy. The different types of cellular transport mechanisms allow cells to maintain homeostasis.cellular transport powerpoint presentation
cellular transport powerpoint presentationRosalynMarieSugay
╠²
The document focuses on cellular transport, detailing the structure and function of cells, tissues, organs, and systems. It explains concepts such as passive and active transport, osmosis, and the effects of different solutions on cells. Key terms include concentration gradient, solute, and the role of cell membranes in regulating nutrient intake and waste removal.Cell membranes and transport
Cell membranes and transportteddybarber17
╠²
The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that surrounds cells and controls what enters and leaves. It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Transport across the membrane can occur passively via diffusion or facilitated diffusion, or actively via protein transporters that require energy. Passive transport moves molecules down their concentration gradient without energy expenditure, while active transport moves molecules against their gradient by using ATP. Endocytosis and exocytosis involve vesicles budding inward or outward to transport larger cargo. The membrane plays key roles in homeostasis, signaling, anchoring, and compartmentalization within cells.Transport__Across__Cell__Membranes_.pptx
Transport__Across__Cell__Membranes_.pptxSachin Teotia
╠²
The document summarizes various methods of transport across the cell membrane, including passive transport mechanisms like diffusion and facilitated diffusion, as well as active transport mechanisms like primary active transport, secondary active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis. It discusses the roles of carrier proteins and concentration gradients in different transport processes and provides examples of glucose, ion, and molecule transport across the membrane.Cell homeostatis
Cell homeostatisManju Chhetri
╠²
This document discusses cellular homeostasis and the role of the cell membrane in maintaining homeostasis. It begins by defining homeostasis as the ability to maintain stable internal conditions despite external fluctuations. It then discusses how homeostasis operates at the whole body, tissue, and cellular levels. The document focuses on the cellular level and the cell membrane's role in regulating transport using channel, carrier, and active transport proteins. It describes different types of cellular transport including passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport processes like endocytosis and exocytosis. The document emphasizes how these transport mechanisms help cells regulate conditions to survive in varying external environments.Ad
Cell transport 2011a
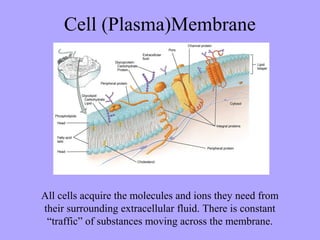
- 1. Cell (Plasma)Membrane All cells acquire the molecules and ions they need from their surrounding extracellular fluid. There is constant ŌĆ£trafficŌĆØ of substances moving across the membrane.
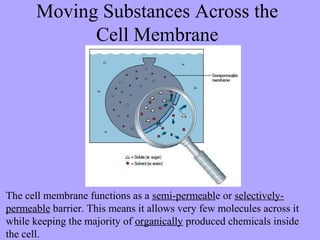
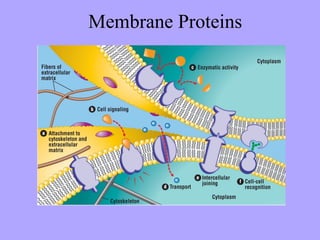
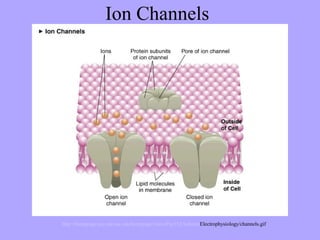
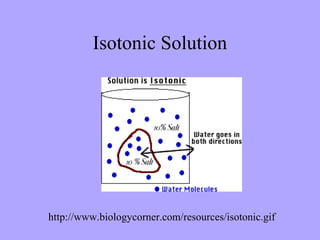
- 2. Moving Substances Across the Cell Membrane The cell membrane functions as a semi-permeable or selectively- permeable barrier. This means it allows very few molecules across it while keeping the majority of organically produced chemicals inside the cell.
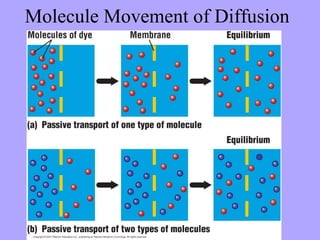
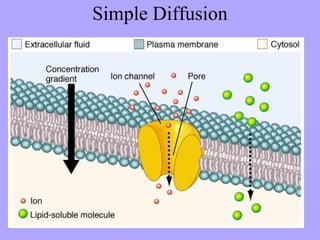
- 4. Diffusion
- 5. Molecule Movement of Diffusion
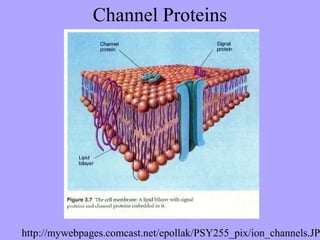
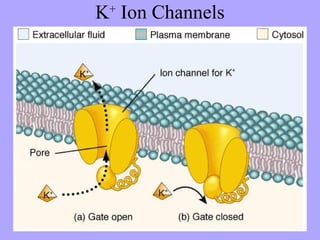
- 11. K+ Ion Channels
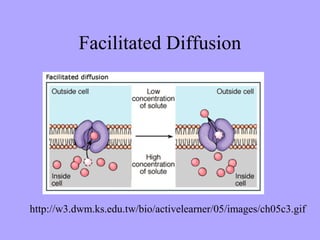
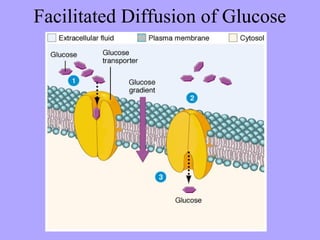
- 12. Facilitated Diffusion of Glucose
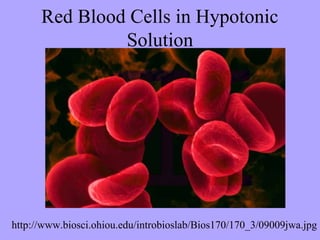
- 17. Red Blood Cells in Hypotonic Solution http://www.biosci.ohiou.edu/introbioslab/Bios170/170_3/09009jwa.jpg
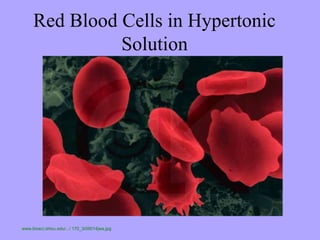
- 18. Red Blood Cells in Hypertonic Solution www.biosci.ohiou.edu/.../ 170_3/09014jwa.jpg
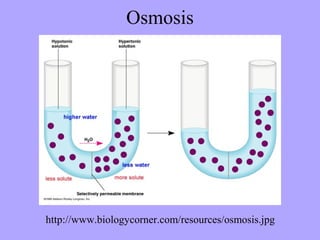
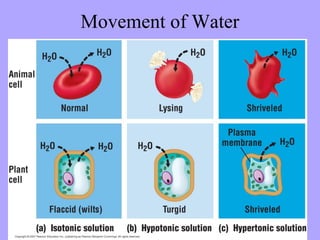
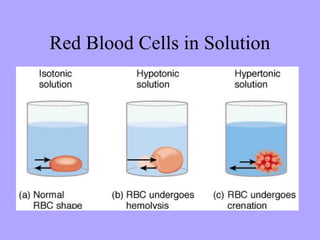
- 20. Red Blood Cells in Solution
- 21. Plant Cells in Solution Turgid Elodea Plasmolyzed Elodea
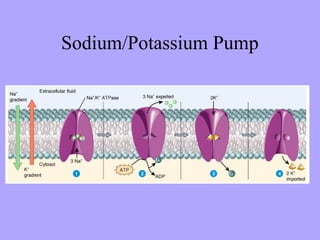
- 22. Active Transport ŌĆó Movement of molecules across the cell membrane that requires energy. ŌĆó Source of energy: ATP
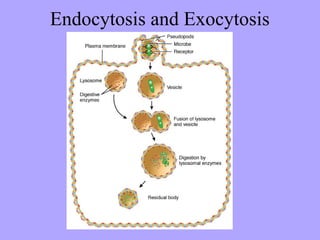
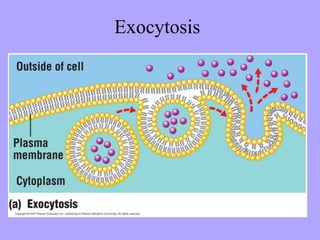
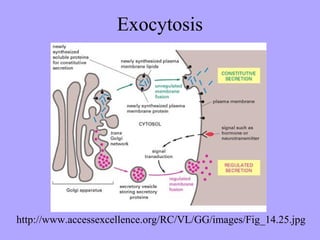
- 25. Exocytosis
Editor's Notes
- #21: Hemolysis: release of hemoglobin into fluid after lysing of RBCs Crenation: formation of abnormal indentation into cell membrane
