Central nervous system
- 1. Central Nervous System: The Brain and The Spinal Cord
- 2. Central Nervous System The Central Nervous System (CNS) is situated centrally and is basically made up of the brain, which is housed in the skull and the spinal cord, which is in the vertebral column. This system is responsible for sending, receiving, and interpreting the nerve impulses from and to all parts of the body. As such, the CNS serves as the integrating mechanism of the entire human body Fun Fact: There are millions of nerve cells in the human body. This number even exceeds the number of stars in the Milky Way!
- 3. The Brain The brain floats on a bath of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and is protected by the skull. It is jelly-like and extra soft weighing about 1400 grams; it is often called as the “master organ”; and it is the busiest part of the body. It controls and directs all activities in the nervous system. The brain is responsible for the integration of the CNS and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). It also receives nerve impulses or message through the spinal cord, sorts them out and then releases this message to the corresponding parts of the CNS for action In humans, the right side of the brain controls the left side Fun Fact: of the body, while the left side of the brain controls the right side.
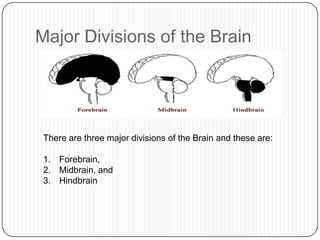
- 4. Major Divisions of the Brain There are three major divisions of the Brain and these are: 1. Forebrain, 2. Midbrain, and 3. Hindbrain
- 5. Fore Brain The Forebrain is one of the three major divisions of the brain and is further divided into three parts, the cerebrum, thalamus and hypothalamus. The cerebrum is the most complex and largest part of the brain and considered as the “seat of consciousness” and is responsible for higher mental activities like endless thinking and reasoning, memory and understanding and many other cognitive functioning. It consists of the Right and Left Cerebral Hemisphere, each subdivided into four lobes, which are the frontal, temporal, parietal and the occipital lobe. Not so Fun Fact: Neurons, which are the largest cells in the human body, do not undergo the process of mitosis.
- 6. Forebrain The thalamus is found right on top of the midbrain. This large bundle or group of nuclei serves as a relay center of the impulses being sent to the specific brain areas and is also involved in motivation. The hypothalamus is a smaller bundle of nuclei that keeps the balance of different body systems mainly because of emotion. It maintains homeostasis by its close some involuntary regulating involvement with the activities like body temperature, thirst,endocrine system. It drives as well appetite and sexual is considered as our emotional behaviours. as the seat of Not so Fun Fact: As we grow older, the brain loses a gram each year
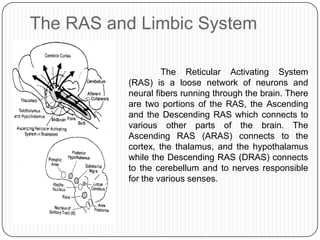
- 7. The RAS and Limbic System The Reticular Activating System (RAS) is a loose network of neurons and neural fibers running through the brain. There are two portions of the RAS, the Ascending and the Descending RAS which connects to various other parts of the brain. The Ascending RAS (ARAS) connects to the cortex, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus while the Descending RAS (DRAS) connects to the cerebellum and to nerves responsible for the various senses.
- 8. In humans, its function includes sleep and walking, eating, sex, elimination, behavioural motivation, breathing, beating of the heart and the ability to focus attention on something. The RAS is also responsible for dreaming. The RAS also dampens stimuli, so that our senses will not be overloaded. For example, when you go to a very noisy place and read a novel, you will find it hard to focus at the start but when you give it time, it would appear as if the crowd has gotten quieter. Damage on this area may induce a coma.
- 9. The limbic system is made up of complex structure located around the thalamus just beneath the cerebrum. Since this structure includes the hypothalamus, it then mediates our emotional responses. Also found here is the hippocampus (SEA HORSES), which is responsible for memories and the amygdala (ALMOND), which The disease of rabies, which affects causes aggression can irrational the hippocampus, among the rage and terror. Stimulation of some portions of the amygdala produce animals. rage reactions in animals, whereas the stimulation of other portions produce reactions interpreted as fear.
- 10. Midbrain The smallest region of the brain, the Midbrain, serves as a bridge between the hindbrain and the forebrain. It is responsible in linking the sensory and motor pathways between the upper and lower parts of the nervous system. The midbrain also has visual and auditory function. Despite its small size, it is one of the major divisions of the brain because it acts as a switchboard of receiving nerve impulses all over the body, sorts them out and send them to higher brain centers.
- 11. Hindbrain The hindbrain is located at the bottom of the cerebrum and the midbrain. It is connected to the spinal cord. It is further divided into three parts, the pons, medulla oblongata, and the Pons cerebellum. - Located in front of the cerebellum, it is made up mostly of the nerve fibers running from one part of the brain to the others. (Functions: Arousal, Controlling Autonomic Functions, Relaying sensory information Between the Cerebrum and Cerebellum, Sleep) Medulla Oblongata - Just above the spinal cord is a 1-inch-long organ, is the Medulla Oblongata. (Functions: Involuntary movements, e.g. breathing, heartbeat, peristalsis) Cerebellum - Also called the “little brain” , it has two hemispheres and connected to the back of the brain stem. (Functions: Coordination of voluntary motor activities, Balance and Posture, Learning of habits and skills, Regulates tongue and jaw
- 12. Spinal Cord The spinal cord, a long and stem- like structure running down the vertebral column., is composed of nerves that lead to and from the brain and nerves that are distributed in the body region. The two main function of the spinal cord are to provide connector mechanisms for reflex reactions, and to transmit messages to and from the brain. These two functions is made possible thanks to the grey matter, which contains connector cells responsible for reflex reactions, and the white matter, which consists of ascending and descending nerve fibers.
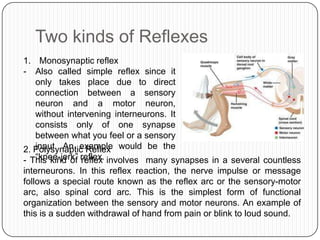
- 13. Two kinds of Reflexes 1. Monosynaptic reflex - Also called simple reflex since it only takes place due to direct connection between a sensory neuron and a motor neuron, without intervening interneurons. It consists only of one synapse between what you feel or a sensory 2. Polysynaptic Reflex would be the input. An example “knee-jerk” reflex - This kind of reflex. involves many synapses in a several countless interneurons. In this reflex reaction, the nerve impulse or message follows a special route known as the reflex arc or the sensory-motor arc, also spinal cord arc. This is the simplest form of functional organization between the sensory and motor neurons. An example of this is a sudden withdrawal of hand from pain or blink to loud sound.
- 14. Additional Information Basal Ganglia - They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including voluntary motor control, procedural learning relating to routine behaviours or “habits” such as bruxism, eye movements, and cognitive, emotional functions. This is just as essential as the ones given before.
- 15. References ÔÇó http://www.pennmedicine.org/encyclopedia/ency_images/encymulti/images/ en/19588.jpg ÔÇó http://biology.about.com/od/organsystems/ss/central-nervous-system.htm ÔÇó http://mybrainnotes.com/forebrain-midbrain-hindbrain.gif ÔÇó http://www.buzzle.com/articles/interesting-facts-about-nervous-system.html ÔÇó http://files.abovetopsecret.com/uploads/ats37552_forebrain1.gif ÔÇó http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-the-reticular-activating-system.htm ÔÇó http://www.benbest.com/science/anatmind/anatmd2.html ÔÇó http://0.tqn.com/d/psychology/1/0/E/midbrain.jpg ÔÇó http://biology.about.com/od/anatomy/p/pons.htm ÔÇó http://t2.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcTd6N4szebwo7cU- na8mGQvESLsLzXZ4n8TIG0rGg-JGnaVVqAL&t=1 ÔÇó http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/1b/Basal_Ganglia_ and_Related_Structures.svg/250px- Basal_Ganglia_and_Related_Structures.svg.png ÔÇó Introduction to Psychology 2011 ed., by Aguirre, Felisa Ph.D, Monce, Ma. Rosaria Ph.D, and Dy, Gary Ed.D.
Editor's Notes
- . Some significant areas are found in the different lobes of the brain like those of the sensory functions for vision, hearing and feeling. Also the motor functions have their own corresponding area just like the association functions. The retraining, integrating and interpretative functions make up together the association functions.