cervical vertebrae presentation by Dr Ela kinra
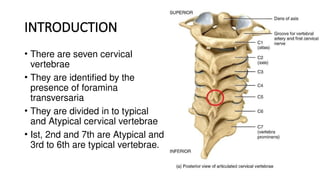
- 2. INTRODUCTION • There are seven cervical vertebrae • They are identified by the presence of foramina transversaria • They are divided in to typical and Atypical cervical vertebrae • Ist, 2nd and 7th are Atypical and 3rd to 6th are typical vertebrae.
- 4. TYPICAL CERVICAL VERTEBRAE • Body • Vertebral foramen • Vertebral arch
- 5. BODY Small & broader Concave superior surface with upward projecting lip Anterior surface is beveled • Inferior surface is saddle shaped • Anterior border proiects downward & hide intervertebral disc • Inter vertebral foramina • (superior /inferior vertebral notches in pedicle)
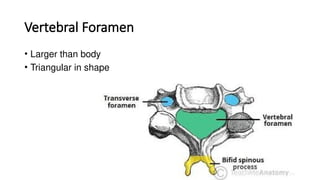
- 6. Vertebral Foramen • Larger than body • Triangular in shape
- 7. VERTEBRAL ARCH • Pedicles are directed backwards and laterally • Superior and inferior notches are of equal sizes • Laminae are relatively long and narrow, thinner above than below • superior & inferior articular processes - form articular pillars, project laterally at the junction of pedicle and the lamina
- 8. TRANSVERSE PROCESS • Transverse process: • Pierced bv Foramen transversaria • Each TP has two roots- ends as tubercle - ant & post tubercle • Joined by costotransverse bar • Costal element = tubercles + CT bar • Site for articulation with ribs • Ant tubercle of 6th CV is large • carotid tubercle
- 9. • Spine - short & bifid • Notch is filled by ligamentum nuchae • Gives origin to deep muscles of the back of the neck
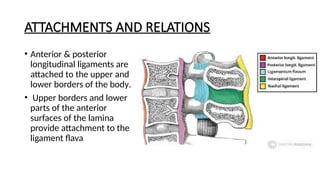
- 10. ATTACHMENTS AND RELATIONS • Anterior & posterior longitudinal ligaments are attached to the upper and lower borders of the body. • Upper borders and lower parts of the anterior surfaces of the lamina provide attachment to the ligament flava
- 11. FORAMEN TRANSVERSARIUM • Foramen transversarium • Vertebral artery • Vertebral veins • Branch of inferior cervical ganglion
- 12. • Anterior tubercle: scalenus anterior, longus capitis oblique part of the longus colli • Posterior tubercle- scalenus medius, scalenu posterior, levator scapula splenius cervicis longissimus cervicis,iliocostalis cervic • Costotransverse bar- Ant. Primary Rami of the Corresponding cervical nerve.
- 13. FIRST CERVICAL VERTEBRAE / ATLAS • Ring shaped • No body • No spine • Short ant arch • Long posterior arch • Rt & Lt masses • Transverse process
- 14. • Posterior arch - longer than ant arch • Median posterior tubercle • Lateral mass: superior articular facet, groove • Atlanto-occipital joint
- 15. • Inferior surface : inferior articular facet, circular, more or less flat, directed downward , medially and backward • Articulates with corresponding axis vertebra to form atlanto-axial joint • Medial surface has a roughened tubercle- transverse ligament transverse process projects laterally from lateral mass - long, acts as lever for rotatory movements of head , pierced by foramen transversarium
- 16. ATTACHMENTS OF ATLAS VERTEBRAE • Anterior tubercle- anterior longitudinal ligament • On each side - longus colli • Upper border of the anterior arch gives attachment to the anterior atlanto-occipital membrane • Posterior tubercle provides attachment to the ligamentum nuchae in the median plane and gives origin to the rectus capitis posterior minor on each side
- 17. Groove on the upper surface of the posterior arch is occupied by the vertebral artery and by the first cervical nerve.
- 18. • Transverse process- rectus capitus Iteralis, superior oblique, inferior oblique , levator scapulae, splenius cervicis, scalenius medius
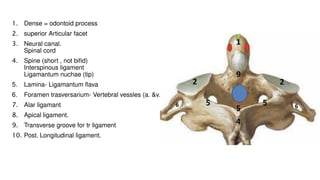
- 19. 1. Ant. Arch Ant. atlanto-occipital membrane, 2. Post. Arch Post. atlanto-occipital membrane 3. Transverse process. 4. superior articular facet 5. Neural canal. Spinal cord 6. Foramen transversarium- Vertebral vessles 7. Groove for vertebral a. 8. Tubercle for tr. Ligament. 9. Facet for dense of axis 10.Post. Tubercle LIgamantum nuchao 11.Ant. Tubercle Ant. Longitudinal ligament
- 20. SECOND CERVICAL VERTEBRAE / AXIS • Identified by the presence of dens or odontoid process (strong tooth like process projecting upwards from the body) • Superior surface of the body- fused with Dens • Dens articulates anteriorly with ant arch of atlas, posteriorly with transverse ligament of atlas • Superior articular facets • Inferior surface - prominent ant margin which projects downwards
- 21. VERTEBRAL ARCH • Pedicle- superior articular facet (circular directed upward and laterally) • Inferior surface - deep wide inf vertebral notch • Lamina- superior vertebral notch behind the sup articular process • Lamina - thick & strong
- 22. • Transverse process • Spine : large , thick, very strong, grooved inferiorly, bifid
- 23. ATTACHMENTS • Ant surface of body- longus coli, ant longitudinal ligament • Post surface of body-post longitudinal ligament, cruciate ligament, membrana tectoria • Tip of transverse process- levatoor scapulae, sclenus medius • Spine - ligamentum nuchae, vertebral muscles
- 24. 1. Dense = odontoid process 2. superior Articular facet 3. Neural canal. Spinal cord 4. Spine (short , not bifid) Interspinous ligament Ligamantum nuchae (tip) 5. Lamina- Ligamantum flava 6. Foramen trasversarium- Vertebral vessles (a. &v.) 7. Alar ligamant 8. Apical ligament. 9. Transverse groove for tr ligament 10. Post. Longitudinal ligament.
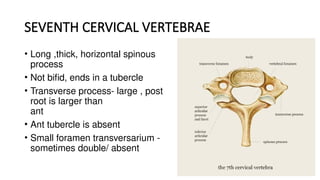
- 25. SEVENTH CERVICAL VERTEBRAE • Long ,thick, horizontal spinous process • Not bifid, ends in a tubercle • Transverse process- large , post root is larger than ant • Ant tubercle is absent • Small foramen transversarium - sometimes double/ absent
- 26. ATTACHMENTS • Spine - ligamentum nuchae, trapezius, rhomboideus minor, serratus posterior superior, splenius capitus, semispinalis thoracis , spinalis cervicis, multifundus • Transverse foramen: accessory vertebral vein, • Posterior tubercle- suprapleural membrane • > Lower border- levator costarum
- 27. 1. Body Intervertebral disc 2. Transverse process 3. foramen transversarium Vertebral vein only 4. superior Articular facet 5. post. Lamina Ligamentum flava 6. Pedicle 7. Spine (long & not bifid) Interspinous ligament Ligamantum nuchae (tip) 8. Vertebral canal Spinal cord