C:\Fakepath\Phonetics&Phonology
- 1. Phonetics & Phonology An Introduction Sarmad Hussain Center for Research in Urdu Language Processing, NUCES, Lahore, Pakistan sarmad.hussain@nu.edu.pk
- 2. www.PANL10n.net 2 Levels of Linguistic Analysis Pragmatics Semantics Syntax Morphology Phonology Phonetics
- 4. Phonetics
- 5. www.PANL10n.net 5 What is Phonetics ? Study of human speech as a physical phenomenon Articulation Acoustics Perception
- 6. www.PANL10n.net 6 Articulatory Phonetics Study of how speech sounds are produced by human vocal apparatus Anatomy of vocal organs Air stream Mechanism Voicing Articulation
- 7. www.PANL10n.net 7 Anatomy of Vocal Organs [2]
- 9. www.PANL10n.net 9 Pulmonic Sounds Air flow is directed outwards towards the oral cavity Pressure built by compression of lungs English [p], [n], [s], [l], [e]
- 10. www.PANL10n.net 10 Glottic Egressive Sounds Air flow is directed outwards towards the oral cavity Pressure built by pushing up closed glottis Georgian [pŌĆÖ], [tŌĆÖ], [kŌĆÖ]
- 11. www.PANL10n.net 11 Glottic Ingressive Sounds Air flow is directed inwards from the oral cavity Pressure reduced by pulling down closed glottis Hausa, Sindhi [╔ō,╔Ā ]
- 12. www.PANL10n.net 12 Velaric Sounds Air flow is directed inwards from the oral cavity Pressure reduced by forming velaric and alveolar closure and pulling down tongue clicks
- 13. www.PANL10n.net 13 Articulatory Phonetics Study of how speech sounds are produced by human vocal apparatus Anatomy of vocal organs Air stream Mechanism Voicing Articulation
- 14. www.PANL10n.net 14 Bernoulli Effect Air pumped from the lungs applies pressure on closed glottis High pressure opens vocal cords High velocity air flow creates low pressure region pulling vocal cords together again Process is repeated, producing vibrations in the vocal cords [3]
- 16. www.PANL10n.net 16 Articulation Manners of Articulation Places of Articulation
- 17. www.PANL10n.net 17 Consonants ŌĆō Manners of Articulation Lateral Trill Tap mNasal jApproximant d╩Æt╩āAffricate Fricative pStop [4] Flap
- 18. www.PANL10n.net 18 Places of Articulation [2] Labial Alveolar Dental Labio- dental Palatal Velar Uvular Pharyngeal Laryngeal
- 19. www.PANL10n.net 19 Consonants ŌĆō Places of Articulation [9]
- 20. www.PANL10n.net 20 Consonants ŌĆō Places of Articulation Multiple Places of Articulation Glottal Pharyngeal Uvular Velar d╩Æ╩āPalatal Retroflex Alveolar Dental Labio-dental Bilabial [4]
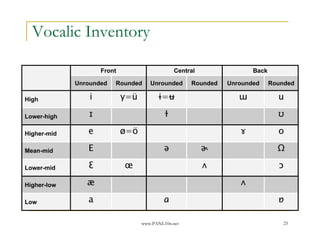
- 22. www.PANL10n.net 22 Vowel ŌĆō Features Low / High Back / Front Round Nasal Long
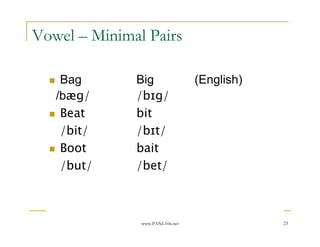
- 23. www.PANL10n.net 23 Vowel ŌĆō Minimal Pairs Bag Big (English) /b├”g/ /b╔¬g/ Beat bit /bit/ /b╔¬t/ Boot bait /but/ /bet/
- 24. www.PANL10n.net 24 /a/ Vocal Tract Outline [11]
- 27. www.PANL10n.net 27 Diphthongs Combination of two vocalic sounds English: [aj] I, eye [aj] [aw] cow [kaw]
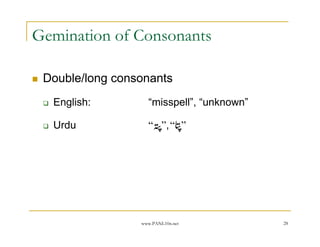
- 28. www.PANL10n.net 28 Gemination of Consonants Double/long consonants English: ŌĆ£misspellŌĆØ, ŌĆ£unknownŌĆØ Urdu ŌĆ£├¬ 6ŌĆØ,ŌĆ£ 6ŌĆØ
- 29. www.PANL10n.net 29 What is Phonetics ? Study of human speech as a physical phenomenon Articulation Acoustics Perception
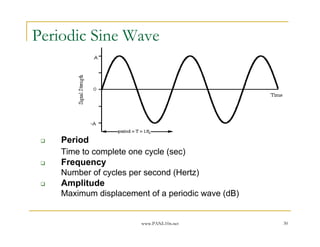
- 30. www.PANL10n.net 30 Periodic Sine Wave Period Time to complete one cycle (sec) Frequency Number of cycles per second (Hertz) Amplitude Maximum displacement of a periodic wave (dB)
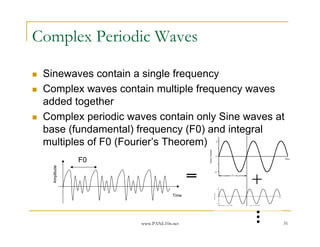
- 31. www.PANL10n.net 31 Complex Periodic Waves Sinewaves contain a single frequency Complex waves contain multiple frequency waves added together Complex periodic waves contain only Sine waves at base (fundamental) frequency (F0) and integral multiples of F0 (FourierŌĆÖs Theorem) F0 Amplitude Time
- 32. www.PANL10n.net 32 Resonance Response of a system is not constant for signals at all frequencies. The frequency which gives largest response is called Resonance (frequency). F
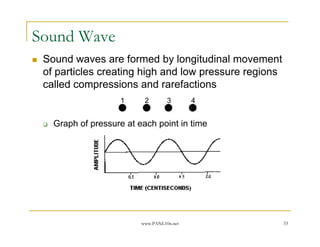
- 33. www.PANL10n.net 33 Sound Wave Sound waves are formed by longitudinal movement of particles creating high and low pressure regions called compressions and rarefactions Graph of pressure at each point in time 1 2 3 4
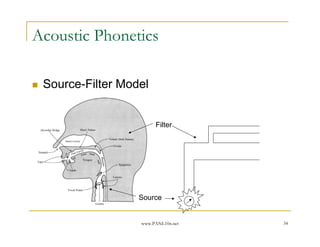
- 34. www.PANL10n.net 34 Acoustic Phonetics Source-Filter Model Source Filter
- 35. www.PANL10n.net 35 Source-Filter Theory: Filter Response curve with tongue in neutral position Resonances are called Formants (F1, F2, F3, ŌĆ”) [15] F2 F3 F1
- 36. www.PANL10n.net 36 Source-Filter Theory: Source Waveform and spectrum of the glottal pulse [15] Time Amplitude
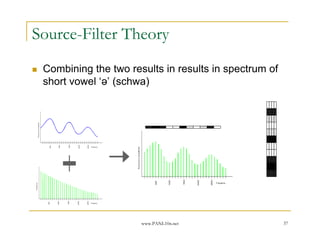
- 37. www.PANL10n.net 37 Source-Filter Theory Combining the two results in results in spectrum of short vowel ŌĆś╔ÖŌĆÖ (schwa)
- 38. www.PANL10n.net 38 Spectrogram A spectrogram is a time-frequency-amplitude graph representing sound ŌĆ£ a babŌĆØ ŌĆ£a dadŌĆØ ŌĆ£a gagŌĆØ [16]
- 40. www.PANL10n.net 40 What is Phonetics ? Study of human speech as a physical phenomenon Articulation Acoustics Perception
- 41. www.PANL10n.net 41 Speech Perception Acoustic signal is highly variable but perception is very stable (invariant) How do map physical variance to perceptual invariance? Intrinsic vs. extrinsic normalization Categorical perception Articulatory Invariance - recreation of articulatory gestures Acoustic Invariance - stable regions in speech within articulatory variability ŌĆ”?
- 42. Phonology
- 43. www.PANL10n.net 43 What is Phonology? Study of how sounds interact in various languages (phonetics conceptual representation) Segmental phenomena Phonemic Inventory and Allophony Sound-change rules and ordering Supra-segmental phenomena Syllabification Prominence Tones Intonation
- 44. www.PANL10n.net 44 Phoneme? Mental concept representing a physical sound Many to many mapping between phoneme and a phone within a language English /t/ aspirated in ŌĆ£tunafishŌĆØ unaspirated in ŌĆ£starfishŌĆØ dental before labio-dental flapped in ŌĆ£buttercupŌĆØ
- 45. www.PANL10n.net 45 Phonological Features Phoneme = set of features that are true at a given time for a particular phonemic unit (phonological features) (Auto- segmental theory) Values of features can by unary or binary ( +/- for present/absent) [18]
- 46. www.PANL10n.net 46 Phonological Features Contrastive function: Each phoneme differs from others in at least one feature Descriptive function: Accurately describes phonetic nature of a sound (may include redundant, non-contrastive features) Classificatory function: Explains and allows generalizations and common phonological processes [18]
- 47. www.PANL10n.net 47 English Consonant Features [18]
- 48. www.PANL10n.net 48 English Vowel Features [18]
- 49. www.PANL10n.net 49 Phonological Rules Humans are lazy so compromise articulation to reduce effort Compromise in Articulation changes the sound Constituents of a phonological rules are Phonemes to be modified due to a rule Conditioning context in which the rule has to be fired Change that occurs in a sound after the rule has been fired Rules are sometimes ordered in a language
- 50. www.PANL10n.net 50 Types of Phonological Rules Assimilation Addition of features due to neighboring phonemes n [+bilabial] / __ [+bilabial, +voiced, +stop] Dissimilation Deletion of features due to neighboring phonemes [7]
- 51. www.PANL10n.net 51 Types of Phonological Rules Insertion / Deletion Addition or deletion of an entire phone Metathesis Change order of phonemes prescribe => perscribe ask => aks [7]
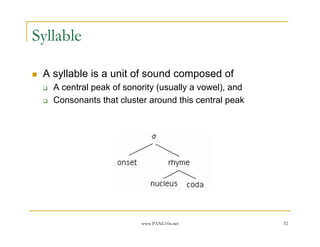
- 52. www.PANL10n.net 52 Syllable A syllable is a unit of sound composed of A central peak of sonority (usually a vowel), and Consonants that cluster around this central peak
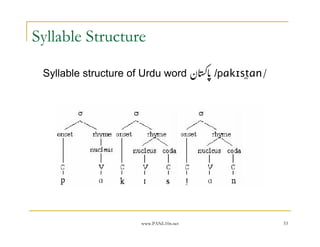
- 53. www.PANL10n.net 53 Syllable Structure Syllable structure of Urdu word ŌĆ½┘åŌĆ¼ ŌĆĀ /p╔æk╔¬st╠¬╔æn/
- 54. www.PANL10n.net 54 Syllabification Syllabification is the process of dividing words into syllables Nuclear Projection Maximal Onset Principle Sonority Sequencing Principle Template based Matching Templates: V, CV, CVC, CVCC Direction of largest template application: RTL, LTR
- 55. www.PANL10n.net 55 Prominence Syllable(s) in a word may be more prominent than others Prominence can change meaning Spanish: t├®rmino, 'end' (noun), term├Łno, 'I'm finishing' termin├│, 'she/he finishedŌĆÖ English ŌĆśob.ject, ob.ŌĆÖject ŌĆścon.tent, con.ŌĆÖtent Syllable vs. stress timed languages Final heavy syllable is stressed, no secondary stress Sensitive to segmental ŌĆ£quantityŌĆØ or moras Every odd syllable is stress, First has primary stress
- 56. www.PANL10n.net 56 Intonation You are going! You are going. You are going? Intonation carries linguistic meaning, e.g. emotion, intention, etc. Realized primarily through variation of F0 over a sentence Multiple theories of how intonation is computed and realized, e.g. Pierrehumbert (TOBI), IPO, Fujisaki, etc.
- 57. www.PANL10n.net 57 Computational Phonology Letter-to-sound rules (?) Regular, heuristic, statistical Sound change rules FST Rule base Syllabification algorithm Template or sonority based algorithm Stress-assignment algorithm Stress-assignment algorithm Intonation assignment algorithm Rule-based algorithm ŌĆō based on syntactic parse (?) Corpus based (Machine Learning) algorithm Other corpus based approaches
- 58. Thank you
- 59. www.PANL10n.net 59 References 1. http://www.mapsofworld.com/world-language-map.htm 2. http://www.ling.upenn.edu/courses/Spring_2001/ling001/phonetics.html 3. http://www.umanitoba.ca/faculties/arts/linguistics/russell/138/sec5/phonatio .htm 4. http://web.uvic.ca/ling/resources/ipa/ 5. http://www.ling.mq.edu.au/speech/phonetics/phonetics/airstream_laryngeal /vot.html 6. http://www.indiana.edu/~hlw/PhonUnits/consonants2.html 7. http://www.ling.ohio-state.edu/~xflu/201/phonology.pdf 8. http://encyclopedia.thefreedictionary.com/IPA%20in%20Unicode 9. http://www.ling.upenn.edu/courses/Summer_2003/ling001/lecture4.html 10. http://encyclopedia.thefreedictionary.com/International%20Phonetic%20Al phabet
- 60. www.PANL10n.net 60 References 11. http://www.haskins.yale.edu/Haskins/MISC/ASY/VOWELS/ah.html 12. http://www.sil.org/mexico/ling/glosario/E005ei-VowelsChart.htm 13. http://people.deas.harvard.edu/~jones/cscie129/nu_lectures/lecture3%20/ formants1.gif 14. http://www.umanitoba.ca/faculties/arts/linguistics/russell/138/sec4/formant s.htm 15. http://www.umanitoba.ca/faculties/arts/linguistics/russell/138/sec4/src- filt.htm 16. A Course in Phonetics by Peter Ladefoged http://hctv.humnet.ucla.edu/departments/linguistics/VowelsandConsonant s/course/contents.html 17. http://web.uvic.ca/ling/resources/ipa/ 18. Introduction to Phonetics and Phonology by Clark and Yallop http://ifla.uni-stuttgart.de/~jilka/teaching/intro1/i3_features.pdf






![www.PANL10n.net 7
Anatomy of Vocal Organs
[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-7-320.jpg)

![www.PANL10n.net 9
Pulmonic Sounds
Air flow is directed outwards towards the oral
cavity
Pressure built by compression of lungs
English [p], [n], [s], [l], [e]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-9-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 10
Glottic Egressive Sounds
Air flow is directed outwards towards the oral
cavity
Pressure built by pushing up closed glottis
Georgian [pŌĆÖ], [tŌĆÖ], [kŌĆÖ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-10-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 11
Glottic Ingressive Sounds
Air flow is directed inwards from the oral
cavity
Pressure reduced by pulling down closed
glottis
Hausa, Sindhi [╔ō,╔Ā ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-11-320.jpg)


![www.PANL10n.net 14
Bernoulli Effect
Air pumped from the lungs applies pressure on closed glottis
High pressure opens vocal cords
High velocity air flow creates low pressure region pulling vocal
cords together again
Process is repeated, producing vibrations in the vocal cords
[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-14-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 15
Voicing
Whisper
Creak
bhBreathy Voice
ph
Aspirated
bVoice
pVoicelessness
[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-15-320.jpg)

![www.PANL10n.net 17
Consonants ŌĆō Manners of Articulation
Lateral
Trill
Tap
mNasal
jApproximant
d╩Æt╩āAffricate
Fricative
pStop
[4]
Flap](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-17-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 18
Places of Articulation
[2]
Labial
Alveolar
Dental
Labio-
dental
Palatal
Velar
Uvular
Pharyngeal
Laryngeal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-18-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 19
Consonants ŌĆō Places of Articulation
[9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-19-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 20
Consonants ŌĆō Places of Articulation
Multiple Places of Articulation
Glottal
Pharyngeal
Uvular
Velar
d╩Æ╩āPalatal
Retroflex
Alveolar
Dental
Labio-dental
Bilabial
[4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-20-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 21
Consonantal Sounds
[10]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-21-320.jpg)

![www.PANL10n.net 24
/a/ Vocal Tract Outline
[11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-24-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 26
Vocalic Quadrilateral
[12]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-26-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 27
Diphthongs
Combination of two vocalic sounds
English: [aj] I, eye [aj]
[aw] cow [kaw]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-27-320.jpg)


![www.PANL10n.net 35
Source-Filter Theory: Filter
Response curve with tongue in neutral position
Resonances are called Formants (F1, F2, F3, ŌĆ”)
[15]
F2
F3
F1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-35-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 36
Source-Filter Theory: Source
Waveform and spectrum of the glottal pulse
[15]
Time
Amplitude](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-36-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 38
Spectrogram
A spectrogram is a time-frequency-amplitude graph
representing sound
ŌĆ£ a babŌĆØ ŌĆ£a dadŌĆØ ŌĆ£a gagŌĆØ
[16]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-38-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 39
Spectrogram
[17][16]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-39-320.jpg)





![www.PANL10n.net 45
Phonological Features
Phoneme = set of features that are true at a given time for a
particular phonemic unit (phonological features) (Auto-
segmental theory)
Values of features can by unary or binary ( +/- for
present/absent)
[18]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-45-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 46
Phonological Features
Contrastive function:
Each phoneme differs from others in at least one
feature
Descriptive function:
Accurately describes phonetic nature of a sound
(may include redundant, non-contrastive features)
Classificatory function:
Explains and allows generalizations and common
phonological processes
[18]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-46-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 47
English Consonant Features
[18]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-47-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 48
English Vowel Features
[18]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-48-320.jpg)

![www.PANL10n.net 50
Types of Phonological Rules
Assimilation
Addition of features due to neighboring phonemes
n [+bilabial] / __ [+bilabial, +voiced, +stop]
Dissimilation
Deletion of features due to neighboring phonemes
[7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-50-320.jpg)
![www.PANL10n.net 51
Types of Phonological Rules
Insertion / Deletion
Addition or deletion of an entire phone
Metathesis
Change order of phonemes
prescribe => perscribe
ask => aks
[7]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathphoneticsphonology-100501165748-phpapp02/85/C-Fakepath-Phonetics-amp-Phonology-51-320.jpg)