Ch ammonia
- 1. YOU TUBE CHANNEL: KNOW THE CHEMISTRY BY RAJIV JAIN
- 2. THOUGHT FOR THE SESSION
- 3. THOUGHT FOR THE SESSION
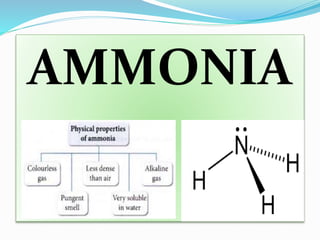
- 4. AMMONIA
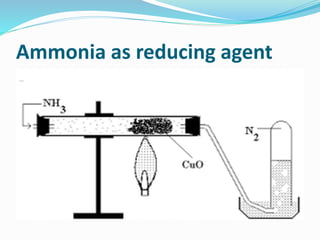
- 9. Ammonia as reducing agent
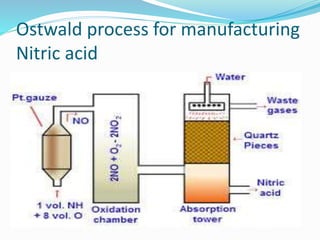
- 11. Ostwald process for manufacturing Nitric acid
- 13. Reactions of ammonia with mineral acids
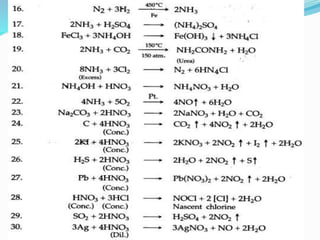
- 16. Important reactions in ammonia
- 18. TEST FOR AMMONIA ïMoist red LITMUS blue / INIDCATOR/ pH test ïPungent smell ïDense white fumes with HCl ïIt turns colorless nesslerâs reagent to brown
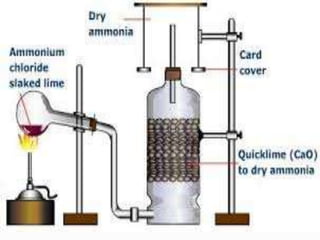
- 19. Q1. The gas used as reducing agent in reducing copper oxide to copper. Ans1. Ammonia Q2. Write balanced chemical equations: Lab preparation of ammonia from ammonium salts. ANS 2. NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 ï CaCl2 + NH3 + 2H2O
- 20. (II)Reaction of ammonia with excess chlorine. ANS 2(II) 3Cl2 (excess) + NH3 ï NCl3 + 3 HCl
- 21. (III) Reaction of ammonia with sulphuric acid. ANS2 (III) 2 NH3 + H2SO4 ï (NH4)2SO4 (IV) Action of warm water on magnesium nitride. ANS (IV) Mg3N2 + 6 H2O ï 3Mg(OH)2 + 2NH3
- 22. Q3. (i) Ammonium nitrate is not used in the preparation of ammonia because ANS3 (I) It is explosive in nature (ii) drying agent during the process. ANS3 (II) Calcium oxide
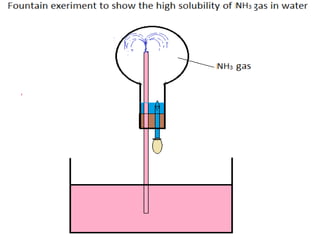
- 23. (iii) How is ammonia gas collected? Ans 3(IV) Downward displacement of air. (iv) Explain why it is not collected over water. ANS3(IV) Because it is highly soluble in water.
- 24. Q4. The diagram shows an experimental set up for the lab preparation of a pungent smelling gas. The gas is alkaline in nature. (i) Name the gas collected in the jar. ANS 4. ammonia (ii) Write the balanced equation for the above preparation. Ans 4 (ii) NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 ï CaCl2 + NH3 + 2H2O
- 25. Q4How is the gas being collected? ANS4(iii). Downward displacement of air. (iv)Name the drying agent used. ANS 4(iv). Quick lime (v) How will you find that the jar is full of gas? ANS 4 (v) Bring a rod dipped in hydrogen chloride. Dense white fumes gives white ppt.
- 26. Q5. Ammonia can be obtained by adding water to: (A) Ammonium chloride. (B) Ammonium nitrate. (C) Magnesium nitride. (D) Magnesium nitrate. ANS5 (d). Magnesium nitride. Q6. Identify the following substances: (i) An alkaline gas A, which gives dense white fumes with hydrogen chloride. ANS 6 (i) Ammonia
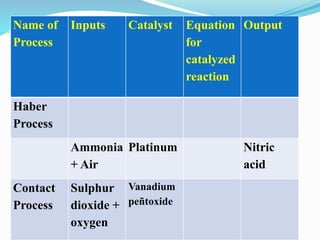
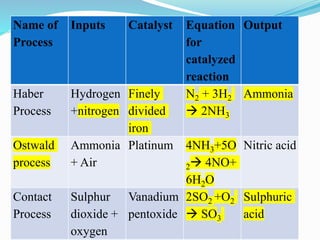
- 27. Q7. Copy and complete the following table relating to important industrial processes. Output refers to the product of the process not the intermediate steps.
- 28. Name of Process Inputs Catalyst Equation for catalyzed reaction Output Haber Process Ammonia + Air Platinum Nitric acid Contact Process Sulphur dioxide + oxygen Vanadium peÃątoxide
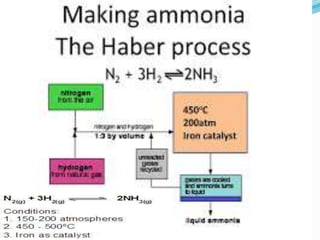
- 29. Name of Process Inputs Catalyst Equation for catalyzed reaction Output Haber Process Hydrogen +nitrogen Finely divided iron N2 + 3H2 ï 2NH3 Ammonia Ostwald process Ammonia + Air Platinum 4NH3+5O 2ï 4NO+ 6H2O Nitric acid Contact Process Sulphur dioxide + oxygen Vanadium pentoxide 2SO2 +O2 ï SO3 Sulphuric acid
- 30. Q8. Write a balanced equation in which ammonia is oxidised by: (i) A metal oxide; (reducing agent property of ammonia) 3CuO + 2NH3 ï 3 Cu + N2 + 3H2O (ii) A gas which is not oxygen. 3Cl2 (excess) +8NH3 ï 6 NH4Cl + N2
- 31. Q9. (i) Name the substance used for drying ammonia. ANS 9. Calcium oxide or lime (ii) Write an equation to illustrate the reducing nature of ammonia. Ans 9(ii) 3CuO + 2NH3 ï 3 Cu + N2 + 3H2O Copper oxide (black) is reduced to copper (brown color metallic copper)
- 32. Q9. With reference to Haberâs process for the preparation of ammonia, write the equation and the conditions required. ANS. N2 + 3H2 ï 2NH3 T= 450 0C, 200 atm, finely divided iron Prmoter: molybdenum
- 33. Q10. Write the balanced chemical equation: (i) A mixture of ammonium chloride and slaked lime is heated. NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 ï CaCl2 + NH3 + 2H2O (ii) Aluminium nitride and water. AlN + 3 H2O ï Al(OH)3 + NH3
- 34. Q11. The following reaction is carried out: A: Nitrogen + metal ï compound X B: X + water ï ammonia + other compound. C: Ammonia + metal oxide ï metal + water + N2 The one metal which can be used in reaction A is Ans. Magnesium.
- 35. Q11b . The following reaction is carried out: A: Nitrogen + metal ï compound X B: X + water ï ammonia + other compound. C: Ammonia + metal oxide ï metal + water + N2 (a)State the condition for the reaction Ans red hot / high temperature (b) write the formula of the compound X. Heating Ans Magnesium hydroxide (c) What property is demonstrated by reaction C. Ans. Reducing agent
- 36. Q12. Write equations for the following reactions: (i) Burning of ammonia in oxygen Ans. 4NH3 + 3O2 ï 2N2 + 6H2O (ii) Catalytic oxidation of ammonia Ans. 4NH3+5O2 Pt ï 4NO+ 6H2O
- 37. Q13.(i) What do you observe when ammonia reacted with oxygen in absence of catalyst? Ans. Greenish yellow flame (ii) Name the catalyst used. Ans. platinum (iii) In the reaction, the catalyst glows red hot. Why ? Ans. because reaction takes place at high temperature. (iv) What is the name of the industrial process? Ans. Ostwald process
- 38. Q14. What do you observe when ammonia gas is bubbled through red litmus solution? Ans14. Red litmus solution changes to blue. Q15. Write a balanced chemical equation when solution of ammonium chloride and sodium hydroxide are mixed and heated. Ans15. NH4Cl + NaOH ï NaCl + H2O + NH3
- 40. Please share and subscribe to gain knowledge from more videos âĶ. Facebook page and You tube channel: Know the Chemistry by Rajiv Jain