Ch04 position analysis
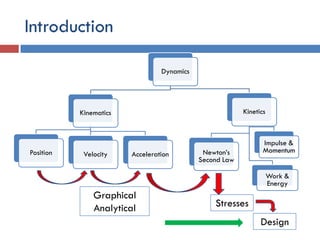
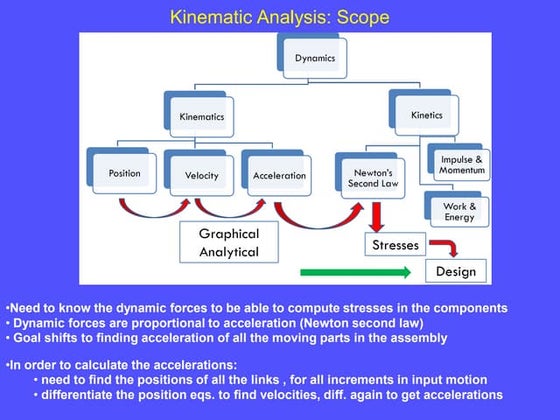
- 2. Introduction Dynamics Kinematics Position Velocity Acceleration Kinetics Newton’s Second Law Work & Energy Impulse & Momentum Stresses Design Graphical Analytical
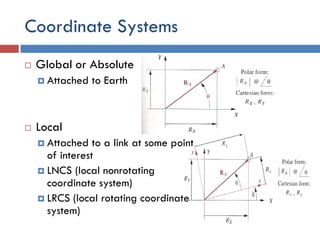
- 3. Coordinate Systems  Global or Absolute  Attached to Earth  Local  Attached to a link at some point of interest  LNCS (local nonrotating coordinate system)  LRCS (local rotating coordinate system)
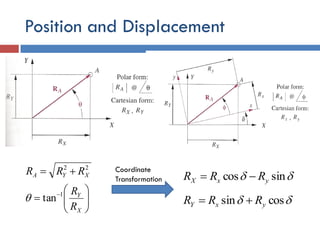
- 4. Position and Displacement 22 XYA RRR          X Y R R1 tan Coordinate Transformation  sincos yxX RRR   cossin yxY RRR 
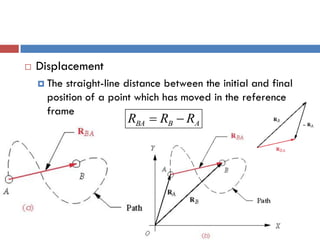
- 5.  Displacement  The straight-line distance between the initial and final position of a point which has moved in the reference frame ABBA RRR 
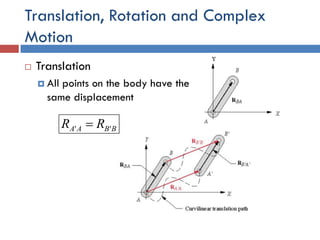
- 6. Translation, Rotation and Complex Motion  Translation  All points on the body have the same displacement BBAA RR '' 
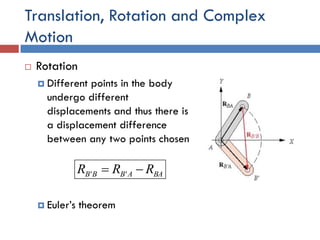
- 7. Translation, Rotation and Complex Motion  Rotation  Different points in the body undergo different displacements and thus there is a displacement difference between any two points chosen  Euler’s theorem BAABBB RRR  ''
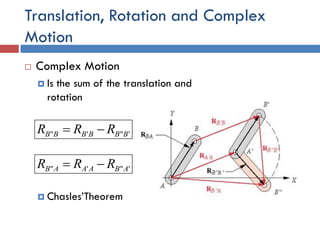
- 8. Translation, Rotation and Complex Motion  Complex Motion  Is the sum of the translation and rotation  Chasles’Theorem '"'" BBBBBB RRR  '"'" ABAAAB RRR 
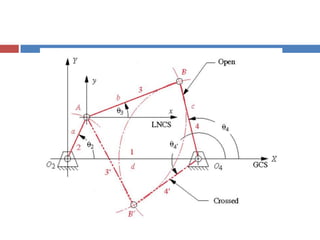
- 9. Graphical Position Analysis ÔÇ® For any one-DOF, such a fourbar, only one parameter is needed to completely define the positions of all the links. The parameter usually chosen is the angle of the input link.
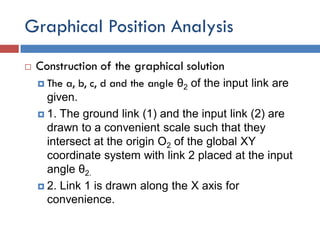
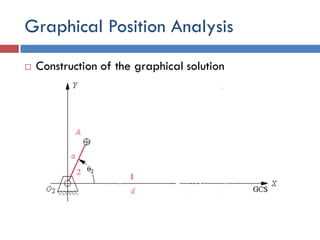
- 10. Graphical Position Analysis  Construction of the graphical solution  The a, b, c, d and the angle θ2 of the input link are given.  1. The ground link (1) and the input link (2) are drawn to a convenient scale such that they intersect at the origin O2 of the global XY coordinate system with link 2 placed at the input angle θ2.  2. Link 1 is drawn along the X axis for convenience.
- 11. Graphical Position Analysis ÔÇ® Construction of the graphical solution
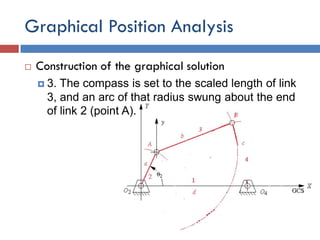
- 12. Graphical Position Analysis  Construction of the graphical solution  3. The compass is set to the scaled length of link 3, and an arc of that radius swung about the end of link 2 (point A).
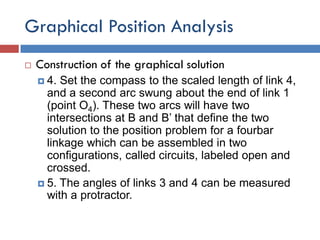
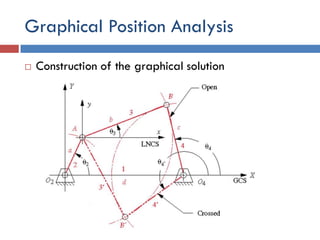
- 13. Graphical Position Analysis  Construction of the graphical solution  4. Set the compass to the scaled length of link 4, and a second arc swung about the end of link 1 (point O4). These two arcs will have two intersections at B and B’ that define the two solution to the position problem for a fourbar linkage which can be assembled in two configurations, called circuits, labeled open and crossed.  5. The angles of links 3 and 4 can be measured with a protractor.
- 14. Graphical Position Analysis ÔÇ® Construction of the graphical solution
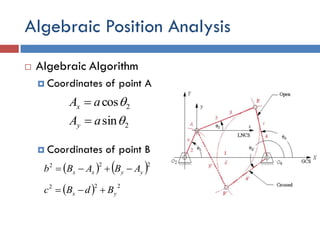
- 16. Algebraic Position Analysis  Algebraic Algorithm  Coordinates of point A  Coordinates of point B 2cosaAx  2sinaAy     222 yyxx ABABb    222 yx BdBc 
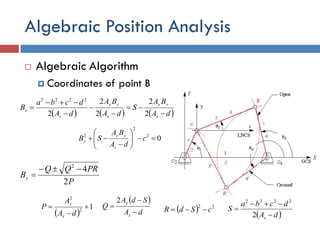
- 17. Algebraic Position Analysis  Algebraic Algorithm  Coordinates of point B      dA BA S dA BA dA dcba B x yy x yy x x        2 2 2 2 2 2222 02 2 2         c dA BA SB x yy y P PRQQ By 2 42     12 2    dA A P x y   dA SdA Q x y    2   22 cSdR   dA dcba S x    2 2222
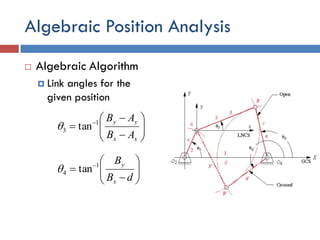
- 18. Algebraic Position Analysis  Algebraic Algorithm  Link angles for the given position           xx yy AB AB1 3 tan          dB B x y1 4 tan
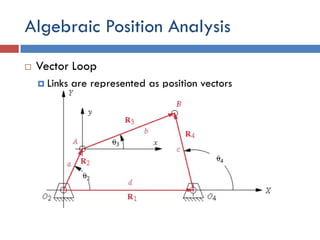
- 19. Algebraic Position Analysis  Vector Loop  Links are represented as position vectors
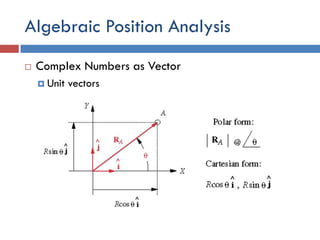
- 20. Algebraic Position Analysis  Complex Numbers as Vector  Unit vectors
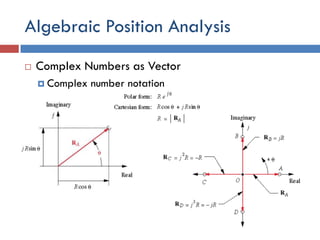
- 21. Algebraic Position Analysis  Complex Numbers as Vector  Complex number notation
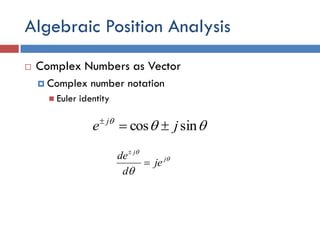
- 22. Algebraic Position Analysis  Complex Numbers as Vector  Complex number notation  Euler identity  sincos je j     j j je d de  
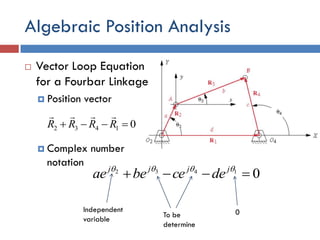
- 23. Algebraic Position Analysis  Vector Loop Equation for a Fourbar Linkage  Position vector  Complex number notation 01432  RRRR  01432   jjjj decebeae 0Independent variable To be determine
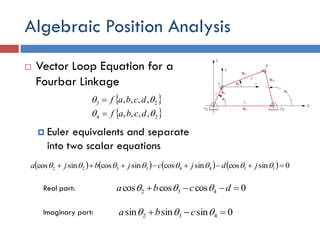
- 24. Algebraic Position Analysis  Vector Loop Equation for a Fourbar Linkage  Euler equivalents and separate into two scalar equations    24 23 ,,,, ,,,,   dcbaf dcbaf           0sincossincossincossincos 11443322   jdjcjbja Real part: 0coscoscos 432  dcba  0sinsinsin 432   cbaImaginary part:
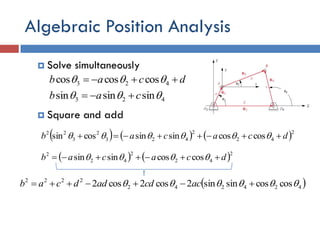
- 25. Algebraic Position Analysis  Solve simultaneously  Square and add dcab  423 coscoscos  423 sinsinsin  cab       2 42 2 423 2 3 22 coscossinsincossin dcacab      2 42 2 42 2 coscossinsin dcacab    424242 2222 coscossinsin2cos2cos2   accdaddcab
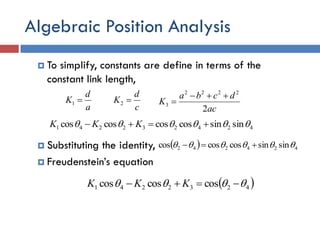
- 26. Algebraic Position Analysis  To simplify, constants are define in terms of the constant link length,  Substituting the identity,  Freudenstein’s equation a d K 1 424232241 sinsincoscoscoscos   KKK c d K 2 ac dcba K 2 2222 3     424242 sinsincoscoscos    4232241 coscoscos   KKK
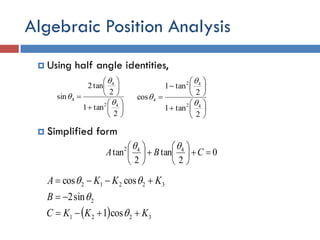
- 27. Algebraic Position Analysis  Using half angle identities,  Simplified form               2 tan1 2 tan2 sin 42 4 4                   2 tan1 2 tan1 cos 42 42 4    0 2 tan 2 tan 442             CBA    3221 2 32212 cos1 sin2 coscos KKKC B KKKA      
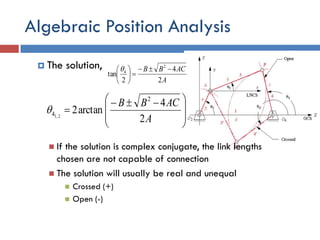
- 28. Algebraic Position Analysis  The solution,  If the solution is complex conjugate, the link lengths chosen are not capable of connection  The solution will usually be real and unequal  Crossed (+)  Open (-) A ACBB 2 4 2 tan 2 4                  A ACBB 2 4 arctan2 2 4 2,1 
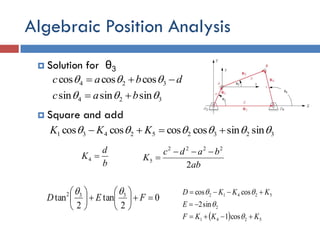
- 29. Algebraic Position Analysis  Solution for θ3  Square and add dbac  324 coscoscos  324 sinsinsin  bac  323252431 sinsincoscoscoscos   KKK b d K 4 ab badc K 2 2222 5   0 2 tan 2 tan 332             FED    5241 2 52412 cos1 sin2 coscos KKKF E KKKD      
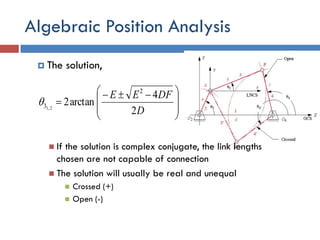
- 30. Algebraic Position Analysis  The solution,  If the solution is complex conjugate, the link lengths chosen are not capable of connection  The solution will usually be real and unequal  Crossed (+)  Open (-)           D DFEE 2 4 arctan2 2 3 2,1 
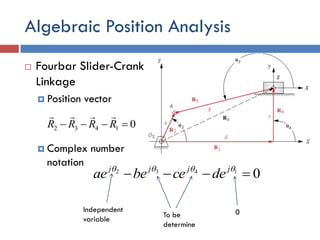
- 31. Algebraic Position Analysis ÔÇ® Fourbar ∫›∫›fl£r-Crank Linkage Ôǧ Position vector Ôǧ Complex number notation 01432 ÔÄΩÔÄ≠ÔÄ≠ÔÄ≠ RRRR ÔÅ≤ÔÅ≤ÔÅ≤ÔÅ≤ 01432 ÔÄΩÔÄ≠ÔÄ≠ÔÄ≠ ÔűÔűÔűÔű jjjj decebeae 0Independent variable To be determine
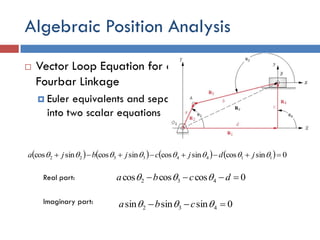
- 32. Algebraic Position Analysis  Vector Loop Equation for a Fourbar Linkage  Euler equivalents and separate into two scalar equations         0sincossincossincossincos 11443322   jdjcjbja Real part: 0coscoscos 432  dcba  0sinsinsin 432   cbaImaginary part:
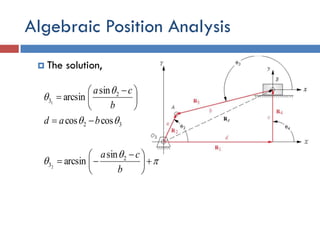
- 33. Algebraic Position Analysis  The solution, 32 2 3 coscos sin arcsin1    bad b ca                     b ca 2 3 sin arcsin2
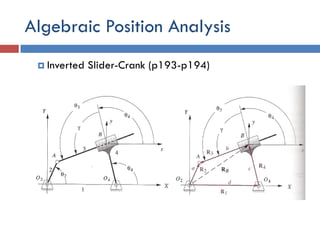
- 34. Algebraic Position Analysis Ôǧ Inverted ∫›∫›fl£r-Crank (p193-p194)
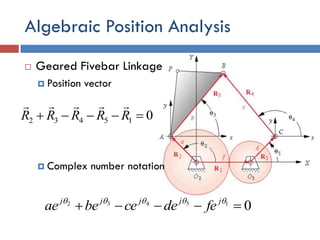
- 35. Algebraic Position Analysis  Geared Fivebar Linkage  Position vector  Complex number notation 015432  RRRRR  015432   jjjjj fedecebeae
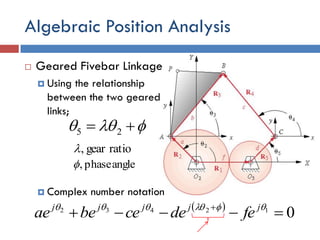
- 36. Algebraic Position Analysis  Geared Fivebar Linkage  Using the relationship between the two geared links;  Complex number notation   25   012432    jjjjj fedecebeae ratiogear, anglephase,
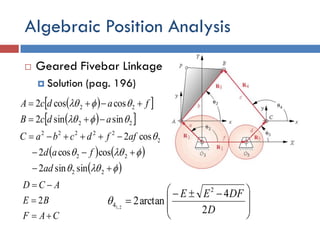
- 37. Algebraic Position Analysis  Geared Fivebar Linkage  Solution (pag. 196)           D DFEE 2 4 arctan2 2 4 2,1                       22 22 2 22222 22 22 sinsin2 coscos2 cos2 sinsin2 coscos2 ad fad affdcbaC adcB fadcA CAF BE ACD    2
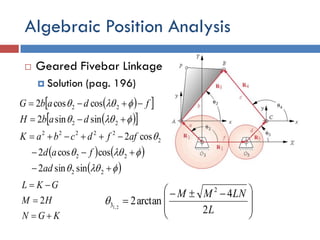
- 38. Algebraic Position Analysis  Geared Fivebar Linkage  Solution (pag. 196)           L LNMM 2 4 arctan2 2 3 2,1                       22 22 2 22222 22 22 sinsin2 coscos2 cos2 sinsin2 coscos2 ad fad affdcbaK dabH fdabG KGN HM GKL    2
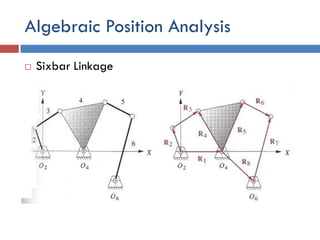
- 39. Algebraic Position Analysis ÔÇ® Sixbar Linkage
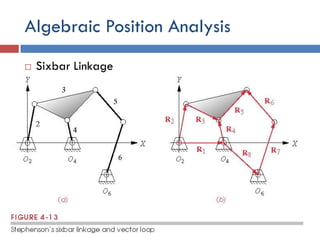
- 40. Algebraic Position Analysis ÔÇ® Sixbar Linkage