Ch23
- 1. Chapter 23 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- 2. CONTENTS CONCEPT MANAGEMENT COMPONENTS SMI MIB SNMP MESSAGES UDP PORTS SECURITY
- 3. CONCEPT 23.1
- 4. Figure 23-1 Concept
- 6. Figure 23-2 Components of network management on the Internet
- 7. SNMP defines the format of packets exchanged between a manager and an agent. It reads and changes the status (values) of objects (variables) in SNMP packets.
- 8. SMI defines the general rules for naming objects, defining object types (including range and length), and showing how to encode objects and values.
- 9. SMI defines neither the number of objects an entity should manage, nor names the objects to be managed nor defines the association between the objects and their values.
- 10. MIB creates a collection of named objects, their types, and their relationships to each other in an entity to be managed.
- 11. We can compare the task of network management to the task of writing a program. 1. Both tasks need rules. In network management this is handled by SMI. 2. Both tasks need variable declarations. In network management this is handled by MIB. 3. Both tasks have actions performed by statements.In network management this is handled by SNMP.
- 12. SMI 23.3
- 13. Figure 23-3 Object attributes
- 14. Figure 23-4 Object identifier
- 15. All objects managed by SNMP are given an object identifier. The object identifier always starts with 1.3.6.1.2.1.
- 16. Figure 23-5 Data types
- 17. Figure 23-6 Conceptual data types
- 18. Figure 23-7 Encoding format
- 19. Figure 23-8 Length format
- 20. Figure 23-9 Example 1: INTEGER 14
- 21. Figure 23-10 Example 2: OCTET STRING ŌĆ£HIŌĆØ
- 22. Figure 23-11 Example 3: ObjectIdentifier 1.3.6.1
- 23. Figure 23-12 Example 4: IPAddress 131.21.14.8
- 24. MIB 23.4
- 25. Figure 23-13 mib-2
- 26. Figure 23-14 udp group
- 27. Figure 23-15 udp variables and tables
- 28. Figure 23-16 Indexes for udpTable
- 29. Figure 23-17 Lexicographic ordering
- 30. SNMP 23.5
- 31. Figure 23-18 SNMP PDUs
- 32. Figure 23-19 SNMP PDU format
- 33. MESSAGES 23.6
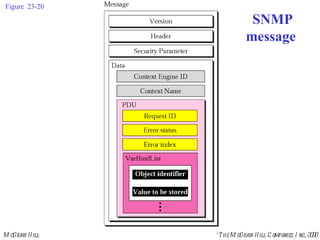
- 34. Figure 23-20 SNMP message
- 35. Figure 23-21 GetRequest message
- 36. UDP PORTS 23.7
- 37. Figure 23-22 Port numbers for SNMP
- 38. 23.8 SECURITY