Change Management Overview
- 1. Why it°Æs important to your business CHANGE MANAGEMENT
- 2. PCI Requirement on Change Management 1.1.1 A formal process for approving and testing all network connections and changes to the firewall and router configurations 6.4.5 - Change control procedures for the implementation of security patches and software modifications. Procedures must include the following: Documentation of impact Documented change approval by authorized parties Functionality testing to verify that the change does not adversely impact the security of the system Back-out procedures IT Compliance Consulting 2
- 3. What is Change Management? ITIL Definitions: Change Management ®C The process responsible for controlling the lifecycle of all changes. The primary objective of Change Management is to enable beneficial changes to be made, with minimum disruption to IT services, security standards and updating the existing ones Request For Change (RFC) ®C A formal proposal for a change to be made. An RFC includes details of the proposed change, and may be recorded on paper or electronically. The term RFC is often misused to mean a change record or the change itself IT Compliance Consulting 3
- 4. What is Change Management? ITIL Definitions: A Change ®C The addition, modification or removal of anything that could have an effect on IT services. The scope should include all IT services, configuration items, processes, documentation, etc. Change Advisory Board (CAB) ®C A group of people that advises the Change Manager in the assessment, prioritization and scheduling of changes. This board is usually made up of representatives from all areas within the IT service provider, representatives from the business and third parties such as suppliers IT Compliance Consulting 4
- 5. What is included/ in scope? Anything that is considered to be part of the production environment and within PCI scope Changes to the IT infrastructure (HW) or operating system (patches) Any software changes, be it application (bespoke/ standard) or database, new installations or upgrades Changes to LAN and WAN, data lines, configuration changes, firmware upgrades, etc. External systems such as mail servers, PBX for call centre, voice recording systems etc. Data center supporting equipment like UPS, generators, cooling units, fire suppression, etc. IT Compliance Consulting 5
- 6. Change Advisory Board (CAB) The Change Advisory Board (CAB) is a body that exists to support the authorization of changes and to assist Change Management (assessment and prioritization) with changes to LAN and WAN, data lines, configuration changes, firmware upgrades, etc. The Change Manager normally chairs the CAB, and potential member include Customer(s) Facilities/office services staff Services and operations staff User manager(s), user group representative(s) Contractor°Øs or third parties°Ø representativesOther parties Applications developers/maintainers, specialists/technical consultants IT Compliance Consulting 6
- 7. CAB Agenda The Change Management process, including any amendments made to it during the period under discussion, as well as proposed changes RFCs that have already been assessed by CAB members and were put on hold, pending additional information or testing Failed changes, unauthorized, backed-out changes, or changes applied without reference to the CAB by incident management, problem management or Change Management Outstanding changes and changes in progress RFCs to be assessed by CAB members ®C in structured and priority order Advance notice of RFCs expected for review at next CAB Review of unauthorized changes detected through Configuration Management IT Compliance Consulting 7
- 8. Emergency Change In an emergency situation it may not be possible to convene a full CAB meeting. Where CAB approval is required, this will be provided by the Emergency CAB (ECAB) Not all emergency changes will require the ECAB involvement An emergency change procedure will follow the normal change procedure except that approval will be given by the ECAB rather than waiting for the full CAB meeting The CAB should be informed of any emergency changes and/ or changes that have been implemented as a workaround All emergency changes are documented and signed off by three CAB members IT Compliance Consulting 8
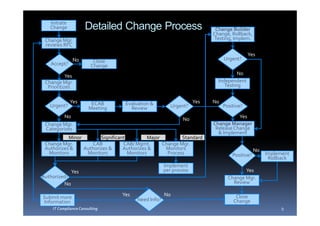
- 9. Initiate Change Detailed Change Process Change Builder Change, Rollback, Change Mgr. Testing, Implem. reviews RFC Yes No Close Urgent? Accept? Change No Yes Change Mgr. Independent Prioritizes Testing Yes ECAB Evaluation & Yes No Urgent? Meeting Review Urgent? Positive? No Yes No Change Mgr. Change Manager Categorizes Release Change & Implement Minor Significant Major Standard Change Mgr. CAB CAB/ Mgmt. Change Mgr. Authorizes & Authorizes & Authorizes & Monitors No Monitors Monitors Monitors Process Positive? Implement Rollback Implement Yes per process Yes Authorized? Change Mgr. No Review Submit more Yes No Close Information Need Info? Change IT Compliance Consulting 9
- 10. PCI Compliance Challenges Verify that the correct access rights have been given to the various roles Ensure that every week has two records of the change log ®C before and after the CAB Consistency of the data in the log e.g. approval date cannot be after the installation date, a status cannot be skipped All CAB members need to sign off on the change log as a collective endorsement of everything agreed upon during the meeting IT Compliance Consulting 10
- 11. Implementation Challenges Everything takes longer, especially in the beginning No more shortcuts by sales and management It takes time for IT staff and developers to understand what complete information on a change request means Starting with more than less, is the way to go. When people make assumptions, they are generally wrong Testing of the change AND the roll back scenario is not only required, but must be documented HR policies need to be upgraded to allow consequences when the process is not adhered to IT Compliance Consulting 11
- 12. Change Categorization Minor impact and few resources needed Change Manager evaluates and can approve autonomously Significant impact and significant resources needed CAB meeting to evaluate and approve or reject Major impact and a high level of resources needed After CAB approval, may additionally seek management approval Standard ®C pre-approved changes Change manager checks that the correct procedures are followed IT Compliance Consulting 12