Channel tunnel final presentation
- 1. Channel Tunnel By Group 5 Ehidame Ibazebo George Makura Isaac Addai Prashanth Akunuri
- 2. HOW DO YOU BUILD AN UNDERSEA TUNNEL TO CONNECT TWO COUNTRIES BY BRINGING TOGETHER PRIVATE FIRMS AND THE GOVERNMENTS OF THESE COUNTRIES THAT HAVE DIFFERENT LANGUAGES AND CULTURE? 2
- 3. Channel Tunnel Project keywords ’ü▒Political Support/Window of Opportunity ’ü▒Public Private Partnership ’ü▒Inter-governmental Cooperation ’ü▒Innovative Engineering 3
- 4. Agenda ’ü¼ Project Background and its context ’ü¼ Research methodology ’ü¼ Project challenges ’ü¼ Analysis of failures and success ’ü¼ Conclusions ’ü¼ Recommendations 4
- 5. Project Location 5
- 6. Project Background Previous Attempts: ’ü¼ First time idea initiated ŌĆō 1802 ŌĆō Albert Mathieu - a cross-channel tunnel proposal ’ü¼ Involvement of Britain and France ŌĆō A 1974 UK-France Governments. backed Scheme was cancelled in 1975 6
- 7. Project Background 1984 Proposals Group Proposal Details Channel Tunnel Undersea Rail ’āś 50.5km undersea Tunnel Group ’āś 4.5km span suspension Eurobridge Suspension bridge with a roadway in an Bridge enclosed tube ’āś 21km tunnel between Euroroute Tunnel artificial islands approached by bridges 7
- 8. The Eurotunnel Group 8
- 9. Project Announcement Announcement of Project ’ü▒Feb 1986. ’ü▒Treaty of Canterbury signed. 9
- 10. Project Objectives ’ü▒Undersea rail tunnel linking Folkstone in the United Kingdom with Calais in northern France. Reasons: ’ü▒Transportation ’ü▒Boost Business and Tourism ’ü▒Connect Britain with mainland Europe 10
- 11. Business Model ’ü▒Public Private Partnership ’ü▒BOOT: ’āśBuild ’āśOwn ’āśOperate ’āśTransfer 11
- 12. Cost & Finance Cost Estimates Construction costs (in ┬Ż) 2.8 billion Corporate and other costs 0.5 Provision for inflation 0.5 Net financing costs 1.0 Total ┬Ż4.8 billion Financing Plan Equity ┬Ż1.0 billion Loans ┬Ż5.0 billion Total ┬Ż6.0 billion 12
- 13. Project Stakeholders ’ü▒The government of France ’ü▒The government of Britain ’ü▒Eurotunnel Group ’ü▒Citizens of France ’ü▒Citizens of Britain 13
- 14. Organizational Breakdown Structure 14
- 15. Research Methodology Evaluation Criteria ’ü▒Project Management Knowledge Areas ’ü▒Elements of Good International Project Plan ’ü▒Success Factors for Public Private Partnerships 15
- 16. Project Challenges Impact of Challenges on Tripple Constraints 14 ’ü▒ Engineering 12 ’ü▒ Financing 10 ’ü▒ Management 8 6 ’ü▒ Political Impact of Challenges on Tripple Constraints 4 ’ü▒ Cultural 2 ’ü▒ Communication 0 16
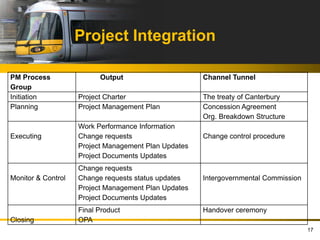
- 17. Project Integration PM Process Output Channel Tunnel Group Initiation Project Charter The treaty of Canterbury Planning Project Management Plan Concession Agreement Org. Breakdown Structure Work Performance Information Executing Change requests Change control procedure Project Management Plan Updates Project Documents Updates Change requests Monitor & Control Change requests status updates Intergovernmental Commission Project Management Plan Updates Project Documents Updates Final Product Handover ceremony Closing OPA 17
- 18. Scope & Procurement Scope Item Details Responsible Fixed price plus incentive fee Agent (50%,30%) saving, overrun Target works Tunnels TML ┬Ż699 m Lump sum Work Terminals TML ┬Ż568 m Related infrastructure Fixed equipments Electrical &mechanical works Procurement Locomotives ┬Ż113 million Items Shuttle trains TML 18
- 19. Cost Management Channel Tunnel Cost Performance 120% 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% 0% Initial Estimate Cost Overrun Total Cost 19
- 20. Human Resource Management Item English Side French Side Recruitment ’é¦ 50% travelling men ’é¦ 95% from depressed ’é¦ housed in a temporary camp region ’é¦ Recruited from depressed ’é¦ Part of employment mining regions regeneration ’é¦ Help with job at end of project Policies ’é¦ Smoking & drinking not allowed ’é¦ Smoking & drinking ’é¦ Poor safety record allowed ’é¦ More organized union structure Problems ’é¦ Senior managers did not get ’é¦ Harmonious atmosphere along 20
- 21. Time Management Milestone Planned Date Actual Date Project Charter (Treaty of Canterbury) 1986 Feb-86 Commencement of Tunnel Boring 1988 Jun-88 Completion of Boring 1990 1990 Opening Ceremony May-93 May-94 21
- 22. Communication Management ’ü▒Boring Phase CHAIRMAN ’āśNo Unified Structure CHIEF EXECUTIVE INTERNAL QUALITY TECHNICAL ’ü▒Fitting Phase AUDIT COMMERCIAL ASSURANCE ADVISOR TO DIRECTOR DIRECTOR DIRECTOR TML BOARD CONSTRUCTION ADMINIST- TRANSPORTATION ’āśUnified Structure FINANCE DIRECTOR MANAGING DIRECTOR LEGAL DIRECTOR RATION DIRECTOR & ENGINEERING MAN DIRECTOR TRANSPORTATION SYSTEMS & ENGINEERING GROUP FRANCE UK DIRECTOR transport system design DIRECTOR CONSTRUCTION CONSTRUCTION rolling stodk design rolling stock procurement CONSTRUCTION CONSTRUCTION transport system contracts GROUP UK GROUP FRANCE commissioning building/civils design building/civils design transport system tunnels tunnels procurement terminal terminal precast factory precast factory m & e supervison m & e supervison source: Anderson (1992) 22
- 23. Risk Management Post-mortem Risk Impact Matrix Risk Likelihood Impact Rating Engineering high High High Communication high Low medium Financial high High High Safety high High Medium Political Medium Low low 23
- 24. Quality Management Ishikawa Diagram Analysis for problems in Tunnel Environment Man Machine Lapsed Safety Measures Boring Machines Not Paying Attention Failing Causes of Issues Encountered Outdated Engineering Low Quality Material Study Material Method 24
- 25. Summary of Analysis Evaluation Based on 9 PM Knowledge Areas Knowledge Area Points Risk Management 2 Time Management 3 Scope Management 5 Cost Management 2 Human Resources Management 4 Procurement Management 5 Integration Management 5 Communication Management 2 Quality Management 4 Total Points out of 45 32 25
- 26. Summary of Analysis Evaluation Based on Good International Project Management Plan Criteria Points Organizing the project in coordination effort and flexibility 15 Highlighting areas of issues and risks 10 Building collaboration and commitment among team members 20 Communication between headquarters and local offices 10 Application of the nine knowledge areas 15.5 Total Points 70.5 Source of Criteria: PMGT 428 (Centennial College) 26
- 27. Summary of Analysis Measurement of the project against key success factors for PPPŌĆÖs Key success factors include: Channel Tunnel Grading 1. Careful planning of PPP project Ō£ö 2. Solid revenue and cost estimate x 3. User willingness to pay and communication plan x 4. Extensive feasibility study with use of PPP experts Ō£ö 5. Compliance with contractual agreement Ō£ö 6. Appropriate Legal and Regulatory Framework Ō£ö 7. Strong Institutions with appropriate resources Ō£ö 8. Competitive and transparent procurement Ō£ö 9. Mitigation and flexibility in managing macro- risks Ō£ö Source of Criteria: PMGT 428 (Centennial College) 27
- 28. What Went Wrong? ’ü▒Design problems not identified at the start ’ü▒Strict safety measures imposed by the IGC ’ü▒Dispute over costs between Eurotunnel and TML ’ü▒Delays from the parliamentary process ’ü▒Financing difficulties ’ü▒TML had clear conflicts of interest ’ü▒Eurotunnel was created late in the process ’ü▒Fragmentation of funding institutions ’ü▒Poor risk analysis 28
- 29. What Went Right? ’ü▒Strong political support by both the British and French governments ’ü▒Excellent management of cultural differences ’ü▒Strong commitment to task in terms of completing the tunnelling ’ü▒Excellent fund raising strategy to finance the project 29
- 30. Conclusions ’ü▒Political support provided a window of opportunity ’ü▒There was not enough time for risk management plan ’ü▒Risks and challenges were dealt with iteratively ’ü▒Project did well based on PPP factors ’ü▒Cost was the only hard constraint significantly affected ’ü▒Project was successful to a large extent but the cost remain to be paid 30
- 31. Recommendation for Future Projects ’ü▒Review past engineering studies ’ü▒Protect the private partner against delays in political decisions ’ü▒Use conservative forecasting approach ’ü▒Do detail risk analysis 31
- 32. Thank You Questions & Feedback are welcome Presentation template from: www.presentationmagazine.com 32