Chapter 12 - Activity Intent
- 2. [Recap] What is Ac#vity? Ac$vity Ac$vity class takes care of crea$ng a window for you in which you can place your UI
- 3. Introduc#on to Ac#vity ŌĆóŌĆ» Ac$vity is one of the core and key system in Android ŌĆóŌĆ» Very important, you canŌĆÖt just know about it, you have to MASTER at it ŌĆóŌĆ» Key message to fully understand: ŌĆóŌĆ» Lifecycle
- 4. Play around: Hide The Title Bar 1)ŌĆ» Hide by Code 2)ŌĆ» Hide by Style Why do we hide it? Live DemoCustom Title Bar No Title Bar at all
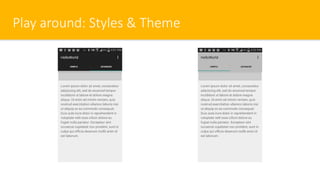
- 5. Play around: Styles & Theme
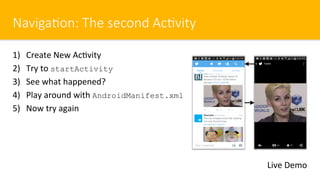
- 6. Naviga#on: The second Ac#vity 1)ŌĆ» Create New Ac$vity 2)ŌĆ» Try to startActivity 3)ŌĆ» See what happened? 4)ŌĆ» Play around with AndroidManifest.xml 5)ŌĆ» Now try again Live Demo
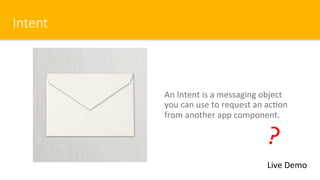
- 7. Intent An Intent is a messaging object you can use to request an ac$on from another app component. Live Demo ?
- 8. Lab: Intent & Bundle Q: Why we need to send data through Intent? A: Because Ac)vity is independent to each other ŌĆ” Play Play Play ŌĆ”
- 9. Understand how Android OS works ŌĆóŌĆ» Secret: Actually Launcher (Home Screen) is also an Ac$vity ! ŌĆóŌĆ» And launcher also launch our applica$on through Intent and startActivity Live Demo
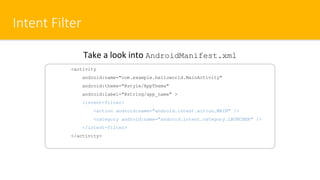
- 10. Intent Filter <activity android:name="com.example.helloworld.MainActivity" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> Take a look into AndroidManifest.xml
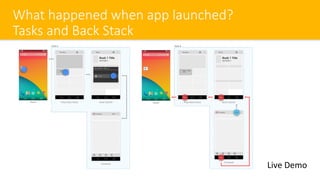
- 11. What happened when app launched? Tasks and Back Stack Live Demo
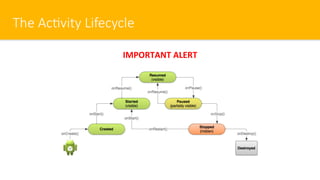
- 12. The Ac#vity Lifecycle IMPORTANT ALERT
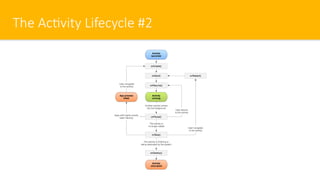
- 13. The Ac#vity Lifecycle #2
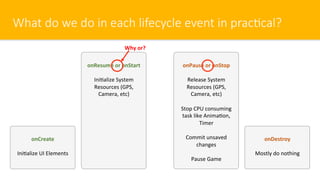
- 14. What do we do in each lifecycle event in prac#cal? onCreate Ini$alize UI Elements onResume or onStart Ini$alize System Resources (GPS, Camera, etc) onDestroy Mostly do nothing onPause or onStop Release System Resources (GPS, Camera, etc) Stop CPU consuming task like Anima$on, Timer Commit unsaved changes Pause Game Why or?
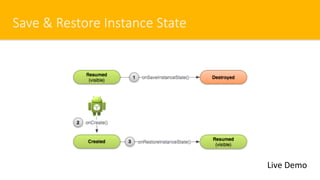
- 15. Save & Restore Instance State Live Demo
- 16. You will a liOle bit confuse now But it will be be^er when you prac$ce more (and more) (and more) (and more)
- 17. Best Prac#ces: Ac#vity Code Structure ŌĆóŌĆ» In The Android Cheese Sheet
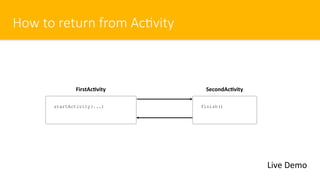
- 18. How to return from Ac#vity Live Demo finish() FirstAc)vity startActivity(...) SecondAc)vity
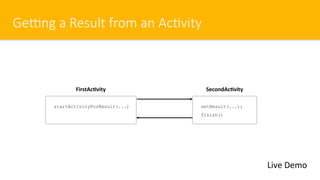
- 19. GeRng a Result from an Ac#vity Live Demo setResult(...); finish() FirstAc)vity startActivityForResult(...) SecondAc)vity
- 20. The Screen Orienta#on android:screenOrientation=["unspecified" | "behind" | "landscape" | "portrait" | "reverseLandscape" | "reversePortrait" | "sensorLandscape" | "sensorPortrait" | "userLandscape" | "userPortrait" | "sensor" | "fullSensor" | "nosensor" | "user" | "fullUser" | "locked"] Live Demo You can ’¼üx the Ac$vityŌĆÖs orienta$on in AndroidManifest.xml Sugges$on: Fix Orienta$on to portrait at the beginning (why?)
- 21. SoS Keyboard Mode android:windowSoftInputMode=["stateUnspecified", "stateUnchanged", "stateHidden", "stateAlwaysHidden", "stateVisible", "stateAlwaysVisible", "adjustUnspecified", "adjustResize", "adjustPan"] Live Demo You can change behavior of sod keyboard in Ac$vity through AndroidManifest.xml
- 22. Ac#vity Transi#on ŌĆóŌĆ» Basically transi$on will be done by default seengs ŌĆóŌĆ» But you can override it (but not so recommend unless it is by design) ŌĆóŌĆ» Example: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <alpha xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator" android:fromAlpha="0.0" android:toAlpha="1.0" android:duration="2000" /> res/anim/fade_in.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <alpha xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator" android:fromAlpha=ŌĆ£1.0" android:toAlpha=ŌĆ£0.0" android:duration="2000" /> res/anim/fade_out.xml overridePendingTransition(R.anim.fade_in, R.anim.fade_out);
- 23. Recap ŌĆóŌĆ» Every$me you create a new Ac$vity, declare in AndroidManifest.xml immediately ŌĆóŌĆ» Ac)vity Lifecycle is very very very important ŌĆóŌĆ» In can e’¼Ćect your lifecycle as an Android App Developer as well ŌĆóŌĆ» Most of the Android Developer doesnŌĆÖt know about Lifecycle clearly and that lead to appŌĆÖs quality problem ŌĆóŌĆ» Crash ŌĆóŌĆ» Malfunc$onal
- 24. Ac#vity Types Ac$vity ListAc$vity PreferenceAc$vity LauncherAc$vity FragmentAc$vity Ac$onBarAc$vity AppCompatAc$vity ŌĆ”

![[Recap] What is Ac#vity?
Ac$vity
Ac$vity class takes care of crea$ng a
window for you in which you can place
your UI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-12-activity-intent-160218014124/85/Chapter-12-Activity-Intent-2-320.jpg)




![The Screen Orienta#on
android:screenOrientation=["unspecified" | "behind" |
"landscape" | "portrait" |
"reverseLandscape" | "reversePortrait" |
"sensorLandscape" | "sensorPortrait" |
"userLandscape" | "userPortrait" |
"sensor" | "fullSensor" | "nosensor" |
"user" | "fullUser" | "locked"]
Live Demo
You can ’¼üx the Ac$vityŌĆÖs orienta$on in AndroidManifest.xml
Sugges$on: Fix Orienta$on to portrait at the beginning
(why?)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-12-activity-intent-160218014124/85/Chapter-12-Activity-Intent-20-320.jpg)
![SoS Keyboard Mode
android:windowSoftInputMode=["stateUnspecified",
"stateUnchanged",
"stateHidden",
"stateAlwaysHidden",
"stateVisible",
"stateAlwaysVisible",
"adjustUnspecified",
"adjustResize",
"adjustPan"]
Live Demo
You can change behavior of sod keyboard in Ac$vity through
AndroidManifest.xml](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-12-activity-intent-160218014124/85/Chapter-12-Activity-Intent-21-320.jpg)