Chapter 2 process skills
- 1. Process SkillsSCED 570, Fall 2011 Chap2.
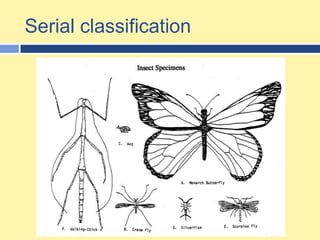
- 2. Classification Process of grouping Binary classification: Sorting objects into 2 groups based on a particular propertyMultistage classification Serial classification: sorting objects in a logical order on the basis of the extent or degree to which they demonstrate a common attribute Dichotomous key: a tool that scientists can use to help identify a particular specimen
- 5. Measurement Quantify variables using a variety of instruments and nonstandard/standard unitsNonstandard units: it is difficult to consistently compare objects that cannot be held side by sideStandard units: enable consistent descriptions and comparisons of measured objects that are not side by side and cannot be directly compared
- 6. CommunicationConvey information from one part to another Record data in multiple ways and present them to others
- 7. Inference Interpretation of observationDraw a tentative conclusion about objects, organism, or events base on observation and prior knowledge
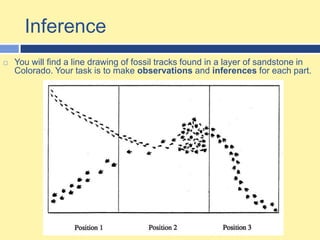
- 8. Inference You will find a line drawing of fossil tracks found in a layer of sandstone in Colorado. Your task is to make observations and inferences for each part.Prediction Statements of future observation Make a forecast of a possible outcome of an investigation based on known patters in data Interpolation: between available data points p.39Extrapolation: outside the collected data points p.40