Chapter 25 lc harris
- 1. LC Liquid Chromatography • Mobile phase: liquid • Stationary phase: liquid or solid • Solute: liquid • Mechanism: stronger ads. longer tr 1. Classical Liquid Chromatography 2. High Performance Liquid Chromatography http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kz_egMtdnL4
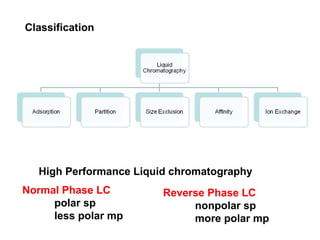
- 2. High Performance Liquid chromatography Normal Phase LC polar sp less polar mp Reverse Phase LC nonpolar sp more polar mp Classification
- 3. A. Classical Liquid Chromatography Column: glass tube (1-5 cm dia, 50-100 cm length) sp: solid particles (150-200 µm dia) mp: liquid, gravity fed Limitations: Slow flow rates Long separation times Resolution not great Use: preparative chemistry/biochemistry
- 4. Smaller particle size  narrower peaks
- 5. Smaller particle size  small H
- 7. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Instrument 1. Solvent delivery system 2. Pump 3. precolumn 4. Injection valve 5. Column 6. Detector
- 8. High Performance Liquid Chromatography 1. Solvent Reservoirs Isocratic: single solvent Gradient elution: vary ratio of solvents 2. Pump Steady, reproducible, constant
- 9. 3. Precolumn (Guard Column) Protect more expensive analytical column Identical to analytical column Helps avoid stripping stationary phase from analytical column
- 11. 5. Analytical Column A. Stationary phase • Liquid on solid surface High Performance Liquid Chromatography
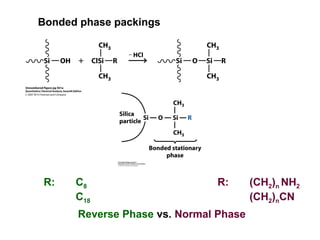
- 12. Bonded phase packings R: C8 C18 R: (CH2)n NH2 (CH2)nCN Reverse Phase vs. Normal Phase
- 14. Normal Phase Chromatography sp: polar mp: less polar Increase solvent strength: add more polar solvent Reverse Phase Chromatography sp: nonpolar mp: more polar Increase solvent strength: add more nonpolar solvent High Performance Liquid Chromatography
- 16. General Elution Problem in Chromatography Much shorter time
- 17. High Performance Liquid Chromatography Detectors Sensitive Linear response Small volume cells Insensitive to changes in T, solvent
- 19. A. UV-Vis Must absorb radiation
- 20. B. Refractive Index Universal Less sensitive T, P solvent sensitive
- 21. C. Electrochemical Must be able to be reduced/oxidized Selective D. Fluorescence Very sensitive Selective Derivatization
- 22. High Performance Liquid Chromatography 5. Detectors - Comparison Detector Detection limits, ng UV 0.1-1 RI 100-1000 Echem 0.01-1 Fluorescence0.001-0.01
- 24. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis Quantitative Peak height Peak area Calibration with standards Internal standard method Qualitative Limited # of components Absence of component Use hyphenated techniques
- 25. From Skoog, West, Holler,