Chapter #2.pptx
- 1. Chapter 2 Balance of payments
- 2. Agenda ÔÇó Definitions of Balance of payments ÔÇó Balance of Payments as a Source and Use of Funds ÔÇó Components of Balance of Payments ÔÇó Current Account and Economic Fundamentals ÔÇó Capital Account, Expectation, and Interest Rate ÔÇó U.S. Balance of Payments: Recent Evidence ÔÇó Exposure Related to Capital Account ÔÇó Exchange Rate Arrangements, Dollarization, and Peg ÔÇó Managing Balance of Payment Exposure in the Emerging Market Economies
- 3. BOP definitions ÔÇó Balance of payments (BOPs) provides a summary of all transactions involving: - Real goods, services - Financial assets (portfolio investments such as stocks, bonds and bills, etc.) - Direct investments (i.e., foreign acquisitions, joint ventures, divestitures), - Capital (import/export), and - Transfer payment in cash or in kind between any two individuals, corporations, government entities, and countries over a specific period.
- 4. Balance of Payments as a Source and Use of Funds ÔÇó BOP is virtually a source and use of fund statement as an accounting identity, where the sources of funds are those transactions that increase the purchasing power of a nation that must equal use of fund, those transactions that reduce the purchasing power of a country. ÔÇó The export of goods and services creates source of funds and the import of goods and services produces the use of funds.
- 5. Cont  The export of goods, services, and capital generates demand for the currency of the exporting country and supply of foreign currency as foreign buyers use their own currency to purchase the currency of the exporter to pay for the export.  The import of goods, services, and capital generates supply of currency of the importer and demand for foreign currency to settle transactions.  Any imbalance in the supply of and demand for the currency of the export and/or import creates temporary disequilibria and exposure to currency and interest rate risks.
- 6. COMPONENTS OF BALANCE OF PAYMENTS ÔÇó Current Account - It summarizes all transactions on the net balance of the trading of goods and services, net balance of income on direct investment and portfolio investment, and net transfer payments in cash or in kind over a specific period. ÔÇó Capital Account - It summarizes transactions on the net direct foreign investment and net portfolio investment in stocks, bonds, T-bills, and other net short- or long-term financial assets of private sector and/or government agencies over a specific period.
- 7. Cont  Official Foreign Exchange Reserve - This is the central banks portfolio holding of foreign currencies, gold, and other certificates and near money, such as special drawing rights (SDRs), issued as a form of reserve credit to members by the IMF; a member can borrow from other members up to 625 percent of the members allocation.  Statistical Discrepancy for Errors and Omissions - This category is created to balance source and use of fund statements due to transactions involving barter (i.e., an exchange of service for service) and underground economic activities (i.e., smuggling, money laundering, and other illegal transactions) where no entry is made on the port of entry as to the value of the goods over a specific period of time.
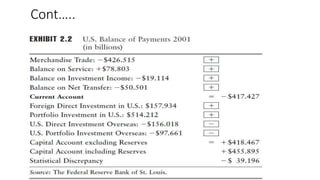
- 8. Cont.  The components of BOP that produce the balance of payments equation can be summarized as:  Current account + Capital account + Official reserve + Statistical discrepancy = 0  See exhibit 2.2:
- 10. CURRENT ACCOUNT AND ECONOMIC FUNDAMENTALS ÔÇó The current account summarizing all transactions originating in the asset markets between a countryÔÇÖs residents and the rest of the world. ÔÇó Demand for a particular good in the asset market is a function of price, income, and price of substitute goods, where the quantity demanded of a good is inversely related to its price and directly related to price of substitute goods and income. ÔÇó The same principle is applicable to the demand for imports and supply of exports originating in current account
- 11. Cont  The factors inducing change in current account can be summarized as: - Exchange rate - Income - Government - Expectations  Inflation and exchange rate affect exchange rate and consumer confidence respectively and shape individuals expectations about their own state in particular and the state of the economy in general.
- 12. Exchange Rate ÔÇó As the dollar weakens against foreign currencies, requiring more dollars to acquire foreign currency, the goods and services made in the United States become relatively more attractive to foreign buyers. ÔÇó Exports are expected to improve as the domestic goods become cheaper for foreigners to acquire and imports are expected to fall as foreign goods and services tend to be more expensive, ÔÇó Thus creating an increase and improvement in the current account balance.
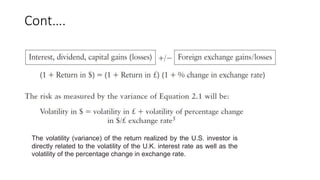
- 13. EXPOSURE RELATED TO CAPITAL ACCOUNT ÔÇó The return of the original capital and the capital gain or loss, royalties, and interest income are exposed to foreign exchange risk as well as interest rate and market risk, creating opportunities for a windfall gain as a result of favorable exchange rate movements and falling interest rates or losses stemming from unfavorable exchange rate and rising interest rates. ÔÇó Suppose a U.S. money manager invests in one-year bonds denominated in British pounds promising an 8 percent interest rate. Assume the pound appreciates by 5 percent during the year. ÔÇó What is the return to the U.S. investor?
- 14. Cont. The volatility (variance) of the return realized by the U.S. investor is directly related to the volatility of the U.K. interest rate as well as the volatility of the percentage change in exchange rate.
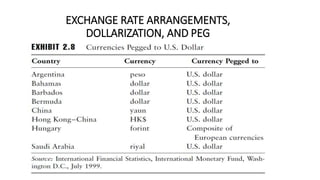
- 15. EXCHANGE RATE ARRANGEMENTS, DOLLARIZATION, AND PEG ÔÇó Free Float ÔÇó The largest number of countries, about 33, allow market forces to determine their currencyÔÇÖs value. ÔÇó Managed Float ÔÇó About 46 countries combine government intervention with market forces to set exchange rates. ÔÇó Pegged to another currency ÔÇó Such as the U.S. dollar or euro. ÔÇó No national currency ÔÇó Some countries do not bother printing their own currency. For example, Ecuador, Panama, and El Salvador have dollarized. Montenegro and San Marino use the euro.
- 16. Cont  Currency Board  Fixed exchange rates combined with restrictions on the issuing government.  Eliminates central bank functions such as monetary policy and lender of last resort (e.g., Hong Kong).  Conventional Peg  Exchange rate publicly fixed to another currency or basket of currencies.  Country buys or sells foreign exchange or uses other means to control the price of the currency (e.g., Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and Morocco).
- 17. EXCHANGE RATE ARRANGEMENTS, DOLLARIZATION, AND PEG