Chapter 36 presentation
- 1. DECISION TREES Logical approach to decision making
- 2. DECISION TREE A diagram that sets out the options connected with a decision and the outcomes and economic returns that may result
- 3. Four main features of a bussiness decision All of the option open to a manager The different possible outcomes The chances of these outcomes occurring The economic return from these outcomes
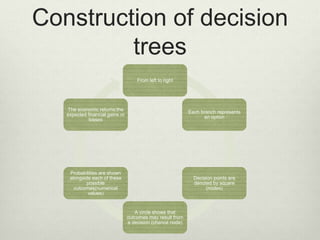
- 4. Construction of decision trees From left to right Each branch represents an option Decision points are denoted by square (nodes) A circle shows that outcomes may result from a decision (chance node) Probabilities are shown alongside each of these possible outcomes(numerical values) The economic returns:the expected financial gains or losses
- 5. Expected value  The likely financial result of an outcome obtained by multiplying the probability of an event occurring by the forecast economic return if it does occur.
- 6. Main advantages of decision trees They force the decision marker to consider all of the options and variables related to a decision An easy to follow diagram allows for numerical consideration of risk and economic returns to be included Encourages logical thinking and discussion amongst managers
- 7. Evaluation of decision trees: limitations The accuracy of the data used: Probabilities may be based on past data, but circumstances may change Decision trees cannot replace the consideration of risk or the impact of non numerical qualitative factors The expected values are averages returns.
Editor's Notes
- #4: By comparing the likely financial results from each option, the manager can minimise the risks involved
- #6: Leer ejemplo de la moneda pag 637
- #8: 1-Estimated economic returns may be accurate concerning projects where experience has be gained from similar decisions but in other cases the may bases on forecast or gesstimates resulting in inaccuracy. 2-A succesful buiseness in the past can have more competion in another place. 3for example the impact on the enviroment the attiude of the workforce and the approach to risk taken by the managers and owners of the business. 4- the avarge will not be the final result