Chapter 4 product
Download as pptx, pdf1 like2,365 views
This document discusses products, services, and branding strategies. It defines key terms like products, consumer products, business/industrial products, and services. It classifies consumer products as convenience goods, shopping goods, specialty goods, and unsought goods. Business products are classified as raw materials, manufactured parts, installations, accessory equipment, and operating supplies. The document also discusses the core product, actual product, and augmented product. It outlines characteristics of services like intangibility, inseparability, variability, and perishability. Finally, it discusses elements of the marketing mix for services, including people, process, physical evidence, and branding strategies.
1 of 36
Downloaded 49 times


































Ad
Recommended
Introduction to Operation & production Management
Introduction to Operation & production ManagementQamar Farooq
Ěý
1. The document discusses key concepts in operations management including defining operations, the role of operations managers, types of operations, and decisions involved in system design.
2. It addresses operations in both goods-producing and service-oriented organizations and the responsibilities of operations management in planning, controlling, improving and designing systems.
3. The document provides examples of different types of operations and decision areas in system design regarding capacity, processes, layouts, work systems and facility locations.Design of Goods and Services
Design of Goods and ServicesUly Jr Maniago
Ěý
This document summarizes key concepts in production and operations management related to product development and management. It discusses that organizations exist to provide goods/services to customers and focus on core products. The product life cycle includes introduction, growth, maturity, and decline phases. It's important for operations to successfully introduce new products. Other topics covered include product strategy, design, development processes, and responding to environmental changes.MONITORING EMPLOYEES ON NETWORKS
MONITORING EMPLOYEES ON NETWORKSSinuSaji1
Ěý
This document discusses the debate around whether monitoring employee internet usage is unethical or good business. While the internet provides a valuable business tool, employees often waste time on non-work related activities. Many companies monitor employee internet usage without their knowledge to track searches, files, and activity. This raises issues around ethics versus protecting company resources and information. The document also examines different company policies regarding internet monitoring and acceptable usage of corporate networks and resources.Classification of industrial products
Classification of industrial productsvengefulwind
Ěý
1. Industrial products are goods and services used directly or indirectly in production or resale. They are classified as materials/parts, capital items, and supplies/services.
2. Materials/parts include raw materials, manufactured materials, and component parts. Capital items include heavy equipment, light equipment, and plants/buildings. Supplies/services include operational supplies and support services.
3. Industrial markets differ from consumer markets in having fewer, larger organizational buyers, more customized complex products, shorter direct distribution channels, and an emphasis on personal selling over mass promotion.Products and services
Products and servicesJeremy Paul Gecolea
Ěý
The document outlines products and services as offerings to the market, including consumer and industrial products, characterized by their classifications and attributes. It emphasizes the importance of branding, product quality, and service marketing strategies, including the service profit chain linking employee satisfaction to customer loyalty. Additionally, it addresses brand equity and strategies for successful brand positioning and sponsorship.Operations management forecasting
Operations management forecastingTwinkle Constantino
Ěý
The document summarizes key concepts about forecasting from the 8th edition of the textbook "Operations Management" by William J. Stevenson. It discusses definitions of forecasting, the importance and uses of forecasts in various business functions. Methods of forecasting include qualitative judgmental forecasts, quantitative time series analysis, and associative models using explanatory variables. Specific forecasting techniques covered include naive forecasts, moving averages, exponential smoothing, trend analysis, and regression. The document also addresses evaluating forecast accuracy and controlling forecasts.Competitiveness, strategy and productivity
Competitiveness, strategy and productivityMOHD BILAL NAIM SHAIKH
Ěý
This document discusses competitiveness, strategy, and productivity. It defines key terms like strategy, tactics, and productivity. Strategy is important for competitiveness and involves setting goals and plans to achieve an organization's mission. Operations strategy must be linked to overall organizational strategy. Time-based and quality strategies are discussed. Productivity is defined as a ratio of outputs to inputs and can be improved through methods like developing measures, determining bottlenecks, and setting reasonable goals.Production & operations management
Production & operations managementHarold B. Duran, LCB
Ěý
Production and operations management is the process of transforming inputs into outputs through the production subsystem in a controlled manner according to organizational policies. It involves the transformation of various resources into products or services. There are four main types of production systems: job shop production which involves low volume and high variety; batch production which produces limited quantities at regular intervals; mass production which uses dedicated equipment for large volume standardized output; and continuous production where materials flow automatically through dedicated equipment in a predetermined sequence.Cb introduction, scope, importance ,imp; interdisciplinary nature
Cb introduction, scope, importance ,imp; interdisciplinary natureAjay Samyal
Ěý
This document discusses consumer behavior and related concepts from various fields like psychology, sociology, and anthropology. It defines consumer behavior as the process people engage in to search for, select, purchase, use, and dispose of products and services. Companies need to understand factors like who their customers are, how and why they make purchases, and what influences their decisions in order to develop effective marketing strategies. The document also outlines several concepts in marketing like the production, selling, product, and marketing concepts which shifted focus over time from production to understanding customer needs.Marketing chpt 7
Marketing chpt 7Beyer_Cuesta
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts around products, services, and branding. It defines products as tangible items or services that can satisfy wants or needs, while services are intangible activities or benefits offered for sale. Market offerings often include both goods and services. Products and services can be classified based on how and when consumers purchase them, such as convenience products bought frequently in daily life. The document also covers branding, packaging, product lines, product mixes, and positioning brands through attributes, benefits and values.Operations - Managing Quality
Operations - Managing Qualitytutor2u
Ěý
This document discusses approaches to managing quality. It defines quality as meeting customer needs and expectations. Quality control focuses on inspection to detect defects, while quality assurance aims to prevent defects by building quality into processes. Total quality management (TQM) is an organization-wide approach that emphasizes continuous improvement through workforce involvement. While TQM can motivate workers and reduce waste, it also requires substantial resources and strong leadership. The document compares quality control, quality assurance, and TQM and outlines the costs of poor quality for businesses.6. process selection and facility layout
6. process selection and facility layoutSudipta Saha
Ěý
The document discusses process selection and facility layout. It describes different types of processes - job shop, batch, repetitive, continuous flow, and project - and factors like volume, variety, and flexibility that determine which type is suitable. It also covers automation levels from fixed to programmable to flexible. Facility layout depends on the process and aims to optimize efficiency, flow, and safety. Product and process layouts are introduced.Operation Process
Operation ProcessDr. Prashant Kalaskar
Ěý
The document provides an in-depth overview of operations processes and management, detailing key concepts such as process design, production types, and flow systems. It emphasizes the importance of process characteristics, including volume, variety, and flow, in achieving competitive advantages through effective resource utilization and customer involvement. Additionally, it outlines different types of production systems—continuous and intermittent flow—along with their respective requirements and applications in manufacturing and service industries.difference between product and service
difference between product and servicekpFasna
Ěý
The document discusses the key differences between products and services. It notes that products are tangible goods that can be seen and touched, while services are intangible activities or processes. The document outlines several differences in how products and services are produced, distributed, consumed and managed. It also discusses the concepts of service quality, the five gaps in service quality, and how organizations can improve service quality by closing these gaps.Process Strategy
Process StrategyTuhin Parves
Ěý
This presentation discusses different process strategies including process-focused, repetitive-focused, and product-focused strategies. It provides examples of each strategy and compares their advantages and disadvantages. A process-focused strategy uses general purpose equipment for low volume, high variety products. Repetitive-focused strategies organize facilities by modules for high volume standardized products. Product-focused strategies use specialized equipment for high volume, low variety production. Mass customization blurs the distinctions by enabling high volume, high variety production. The presentation also discusses production technologies, process redesign, and environmentally friendly processes.Productivity and operation management
Productivity and operation managementShreyas Metri
Ěý
This document discusses productivity and operation management. It defines productivity as the output of any production process per unit of input. The goal of production and operation management is to produce the right quality, quantity, and time at a pre-established cost. Productivity can be measured at the partial level looking at individual inputs like labor, capital, and materials, or at the total factor and total levels considering all inputs. Factors that affect productivity include product development, specialization, research, value analysis, process planning, and training. Improving productivity increases efficiency and leads to lower costs, higher sales, and greater profits.Business Market
Business MarketFahim Muntaha
Ěý
Business markets involve the sale of goods and services to other businesses rather than individual consumers. Business buyers face different situations like straight rebuys, modified rebuys, or new tasks. Multiple people are involved in organizational buying decisions, including users, buyers, influencers, deciders, and gatekeepers. The business buying process involves stages like problem recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. Factors like product characteristics, price, supplier service, and relationships influence business buyer decisions.1.introduction of production and operations management
1.introduction of production and operations managementAkash Bakshi
Ěý
This document discusses production management and the objectives of production management. It begins by defining production, operations, and production management. It then outlines the ultimate objectives of production management as producing a product at a pre-established cost, specified quality, and within a stipulated time period. The intermediate objectives are related to machinery/equipment, materials, manpower, and manufacturing services. The document concludes that the key objectives of production are to develop a high quality product, produce the correct quantity, deliver it on time, and perform these functions at the right price.Production and Operations Management
Production and Operations ManagementNishant Agrawal
Ěý
The document provides an overview of production and operations management (POM), detailing its functions, significance, historical contributions, and transformation processes involved in the production of goods and services. It outlines the importance of operations management in optimizing resource use, ensuring quality, and enhancing customer satisfaction, while also describing various manufacturing processes and operational strategies. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for effective planning, organizing, controlling, and understanding employee behavior to achieve operational efficiency.Functions of different company departments
Functions of different company departmentsIES Virgen del Carmen, Jaén
Ěý
The document outlines the main departments found in most organizations and their key functions. It discusses the production, marketing and sales, finance, human resources, and information technology departments. The production department is responsible for converting raw materials into finished goods. The human resources department handles recruiting, training, and dismissing employees. The marketing department focuses on sales, research, promotion, and distribution. Finally, the finance department manages bookkeeping, accounts, wages, financing, and providing information to managers.Quality management
Quality managementSansar Birman
Ěý
This document discusses quality management and total quality management (TQM). It defines quality as meeting customer expectations. Key aspects of TQM include top management commitment, customer focus, continuous improvement, and empowering employees. TQM aims to produce products and services that are considered best by customers by doing everything right the first time and continuously improving. Elements of a TQM system include quality design, statistical process control, supplier partnerships, and benchmarking against world-class standards. Both products and services require quality management programs to monitor and improve performance.Business Markets & Business Buyer Behaviour
Business Markets & Business Buyer BehaviourAbdul Aziz Awan
Ěý
This document discusses business markets and business buyer behavior. It defines business markets as markets where organizations purchase goods and services for resale or use in production. The key characteristics of business markets are fewer but larger buyers, demand derived from final consumer demand, more inelastic demand that fluctuates quickly. Business purchases involve multiple buyers in a formal buying process. The document outlines the business buying process and different types of buying situations. It also discusses the participants in the buying center and major influences on business buyers, including environmental, organizational, interpersonal, and individual factors. Finally, it briefly touches on institutional markets that serve organizations like hospitals and schools, as well as government markets.MIS Support to Management
MIS Support to ManagementMaria Stella Solon
Ěý
MIS uses computer technology to process and analyze large amounts of data, quickly search and retrieve information, and communicate information to users in a timely manner. It supports management functions like planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating, and controlling. MIS helps ensure the appropriate data is collected, processed, and distributed to where it is needed. It provides information to support strategic planning, management control, operational control, and transaction processing.Entrepreneurship (Introduction)
Entrepreneurship (Introduction)Mike Joseph
Ěý
The document discusses entrepreneurship, entrepreneurs, and the benefits of entrepreneurship. It defines entrepreneurship as identifying opportunities and starting new business ventures by organizing resources and taking on associated risks and rewards. Entrepreneurs take initiative, see opportunities, and create new products/services or expand markets. Benefits include job creation, economic growth through capital mobilization and tax revenue, empowering individuals, enhancing national identity, improving competition and quality of life, and equitable distribution of income and wealth. The document also categorizes different types of entrepreneurs such as solo self-employed individuals, team builders, independent innovators, and acquirers.Product And Product Lines 8
Product And Product Lines 8rajesh panda
Ěý
1. The document discusses various aspects of product planning and management, including product classification, product life cycles, and strategies for different stages of the life cycle.
2. It describes core and augmented product features, and different types of products including generic, expected, potential, consumer, and industrial products.
3. The document also covers product mix strategies, managing product lines, and discusses whether companies should focus more on designing long-lasting products that meet consistent human needs rather than frequent new launches.Marketing mix
Marketing mixdeepu2000
Ěý
The document discusses the 7Ps of marketing mix, which are a set of controllable variables that a company uses to satisfy customers better than competitors. The 7Ps include Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence. For each P, the document provides details on what they entail and how companies can implement strategies around them. It also discusses other marketing concepts like buyer behavior, assembling the marketing mix based on target customers, and how to develop a diagnostic and effective marketing plan.Unit 3 marketing lecture ppt
Unit 3 marketing lecture pptIrshad Tunio
Ěý
1. Market research is needed to identify consumer wants and determine if people will buy a product before it is produced to reduce risks of failure.
2. There are two main types of market research: primary research involves direct contact with customers through surveys, interviews, and experiments. Secondary research uses already collected data from internal sources like sales records or external sources like reports.
3. Primary research methods include questionnaires, interviews, observation, and experiments, each with advantages and disadvantages. Secondary research sources data from within the business or externally from the internet, trade groups, and reports.Operations Management Presentation
Operations Management PresentationPatrick Rubix
Ěý
Operations management aims to produce the right quality of goods and services as quickly as possible and as cheaply as possible. However, achieving all three goals simultaneously can be difficult. Operations managers must decide on production location, scale, methods, and material supplies to balance quality, speed, and cost in an efficient manner. Changing production methods can lower costs per unit but may also reduce flexibility and customization.Marketing Mix / 7 P's of marketing / Meaning of marketing mix
Marketing Mix / 7 P's of marketing / Meaning of marketing mixheenam8
Ěý
The marketing mix, initially defined by Neil Borden and later expanded by E. Jerome McCarthy to include the 7 P's (product, price, place, promotion, people, process, physical evidence), remains a fundamental concept in marketing despite the evolution of theories over nearly 70 years. Each component of the marketing mix plays a crucial role in satisfying consumer needs and achieving organizational objectives while adapting to various market conditions. Understanding and strategically implementing these elements can enhance consumer satisfaction and differentiate a business in competitive markets.Chapter 6
Chapter 6herbison
Ěý
1. The document defines marketing and distinguishes between consumer and industrial products and services.
2. It discusses methods of pricing products and services including cost-plus pricing and penetration pricing.
3. The document outlines different promotion techniques including personal selling, advertising, sales promotions, and public relations.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Cb introduction, scope, importance ,imp; interdisciplinary nature
Cb introduction, scope, importance ,imp; interdisciplinary natureAjay Samyal
Ěý
This document discusses consumer behavior and related concepts from various fields like psychology, sociology, and anthropology. It defines consumer behavior as the process people engage in to search for, select, purchase, use, and dispose of products and services. Companies need to understand factors like who their customers are, how and why they make purchases, and what influences their decisions in order to develop effective marketing strategies. The document also outlines several concepts in marketing like the production, selling, product, and marketing concepts which shifted focus over time from production to understanding customer needs.Marketing chpt 7
Marketing chpt 7Beyer_Cuesta
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts around products, services, and branding. It defines products as tangible items or services that can satisfy wants or needs, while services are intangible activities or benefits offered for sale. Market offerings often include both goods and services. Products and services can be classified based on how and when consumers purchase them, such as convenience products bought frequently in daily life. The document also covers branding, packaging, product lines, product mixes, and positioning brands through attributes, benefits and values.Operations - Managing Quality
Operations - Managing Qualitytutor2u
Ěý
This document discusses approaches to managing quality. It defines quality as meeting customer needs and expectations. Quality control focuses on inspection to detect defects, while quality assurance aims to prevent defects by building quality into processes. Total quality management (TQM) is an organization-wide approach that emphasizes continuous improvement through workforce involvement. While TQM can motivate workers and reduce waste, it also requires substantial resources and strong leadership. The document compares quality control, quality assurance, and TQM and outlines the costs of poor quality for businesses.6. process selection and facility layout
6. process selection and facility layoutSudipta Saha
Ěý
The document discusses process selection and facility layout. It describes different types of processes - job shop, batch, repetitive, continuous flow, and project - and factors like volume, variety, and flexibility that determine which type is suitable. It also covers automation levels from fixed to programmable to flexible. Facility layout depends on the process and aims to optimize efficiency, flow, and safety. Product and process layouts are introduced.Operation Process
Operation ProcessDr. Prashant Kalaskar
Ěý
The document provides an in-depth overview of operations processes and management, detailing key concepts such as process design, production types, and flow systems. It emphasizes the importance of process characteristics, including volume, variety, and flow, in achieving competitive advantages through effective resource utilization and customer involvement. Additionally, it outlines different types of production systems—continuous and intermittent flow—along with their respective requirements and applications in manufacturing and service industries.difference between product and service
difference between product and servicekpFasna
Ěý
The document discusses the key differences between products and services. It notes that products are tangible goods that can be seen and touched, while services are intangible activities or processes. The document outlines several differences in how products and services are produced, distributed, consumed and managed. It also discusses the concepts of service quality, the five gaps in service quality, and how organizations can improve service quality by closing these gaps.Process Strategy
Process StrategyTuhin Parves
Ěý
This presentation discusses different process strategies including process-focused, repetitive-focused, and product-focused strategies. It provides examples of each strategy and compares their advantages and disadvantages. A process-focused strategy uses general purpose equipment for low volume, high variety products. Repetitive-focused strategies organize facilities by modules for high volume standardized products. Product-focused strategies use specialized equipment for high volume, low variety production. Mass customization blurs the distinctions by enabling high volume, high variety production. The presentation also discusses production technologies, process redesign, and environmentally friendly processes.Productivity and operation management
Productivity and operation managementShreyas Metri
Ěý
This document discusses productivity and operation management. It defines productivity as the output of any production process per unit of input. The goal of production and operation management is to produce the right quality, quantity, and time at a pre-established cost. Productivity can be measured at the partial level looking at individual inputs like labor, capital, and materials, or at the total factor and total levels considering all inputs. Factors that affect productivity include product development, specialization, research, value analysis, process planning, and training. Improving productivity increases efficiency and leads to lower costs, higher sales, and greater profits.Business Market
Business MarketFahim Muntaha
Ěý
Business markets involve the sale of goods and services to other businesses rather than individual consumers. Business buyers face different situations like straight rebuys, modified rebuys, or new tasks. Multiple people are involved in organizational buying decisions, including users, buyers, influencers, deciders, and gatekeepers. The business buying process involves stages like problem recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. Factors like product characteristics, price, supplier service, and relationships influence business buyer decisions.1.introduction of production and operations management
1.introduction of production and operations managementAkash Bakshi
Ěý
This document discusses production management and the objectives of production management. It begins by defining production, operations, and production management. It then outlines the ultimate objectives of production management as producing a product at a pre-established cost, specified quality, and within a stipulated time period. The intermediate objectives are related to machinery/equipment, materials, manpower, and manufacturing services. The document concludes that the key objectives of production are to develop a high quality product, produce the correct quantity, deliver it on time, and perform these functions at the right price.Production and Operations Management
Production and Operations ManagementNishant Agrawal
Ěý
The document provides an overview of production and operations management (POM), detailing its functions, significance, historical contributions, and transformation processes involved in the production of goods and services. It outlines the importance of operations management in optimizing resource use, ensuring quality, and enhancing customer satisfaction, while also describing various manufacturing processes and operational strategies. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for effective planning, organizing, controlling, and understanding employee behavior to achieve operational efficiency.Functions of different company departments
Functions of different company departmentsIES Virgen del Carmen, Jaén
Ěý
The document outlines the main departments found in most organizations and their key functions. It discusses the production, marketing and sales, finance, human resources, and information technology departments. The production department is responsible for converting raw materials into finished goods. The human resources department handles recruiting, training, and dismissing employees. The marketing department focuses on sales, research, promotion, and distribution. Finally, the finance department manages bookkeeping, accounts, wages, financing, and providing information to managers.Quality management
Quality managementSansar Birman
Ěý
This document discusses quality management and total quality management (TQM). It defines quality as meeting customer expectations. Key aspects of TQM include top management commitment, customer focus, continuous improvement, and empowering employees. TQM aims to produce products and services that are considered best by customers by doing everything right the first time and continuously improving. Elements of a TQM system include quality design, statistical process control, supplier partnerships, and benchmarking against world-class standards. Both products and services require quality management programs to monitor and improve performance.Business Markets & Business Buyer Behaviour
Business Markets & Business Buyer BehaviourAbdul Aziz Awan
Ěý
This document discusses business markets and business buyer behavior. It defines business markets as markets where organizations purchase goods and services for resale or use in production. The key characteristics of business markets are fewer but larger buyers, demand derived from final consumer demand, more inelastic demand that fluctuates quickly. Business purchases involve multiple buyers in a formal buying process. The document outlines the business buying process and different types of buying situations. It also discusses the participants in the buying center and major influences on business buyers, including environmental, organizational, interpersonal, and individual factors. Finally, it briefly touches on institutional markets that serve organizations like hospitals and schools, as well as government markets.MIS Support to Management
MIS Support to ManagementMaria Stella Solon
Ěý
MIS uses computer technology to process and analyze large amounts of data, quickly search and retrieve information, and communicate information to users in a timely manner. It supports management functions like planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating, and controlling. MIS helps ensure the appropriate data is collected, processed, and distributed to where it is needed. It provides information to support strategic planning, management control, operational control, and transaction processing.Entrepreneurship (Introduction)
Entrepreneurship (Introduction)Mike Joseph
Ěý
The document discusses entrepreneurship, entrepreneurs, and the benefits of entrepreneurship. It defines entrepreneurship as identifying opportunities and starting new business ventures by organizing resources and taking on associated risks and rewards. Entrepreneurs take initiative, see opportunities, and create new products/services or expand markets. Benefits include job creation, economic growth through capital mobilization and tax revenue, empowering individuals, enhancing national identity, improving competition and quality of life, and equitable distribution of income and wealth. The document also categorizes different types of entrepreneurs such as solo self-employed individuals, team builders, independent innovators, and acquirers.Product And Product Lines 8
Product And Product Lines 8rajesh panda
Ěý
1. The document discusses various aspects of product planning and management, including product classification, product life cycles, and strategies for different stages of the life cycle.
2. It describes core and augmented product features, and different types of products including generic, expected, potential, consumer, and industrial products.
3. The document also covers product mix strategies, managing product lines, and discusses whether companies should focus more on designing long-lasting products that meet consistent human needs rather than frequent new launches.Marketing mix
Marketing mixdeepu2000
Ěý
The document discusses the 7Ps of marketing mix, which are a set of controllable variables that a company uses to satisfy customers better than competitors. The 7Ps include Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence. For each P, the document provides details on what they entail and how companies can implement strategies around them. It also discusses other marketing concepts like buyer behavior, assembling the marketing mix based on target customers, and how to develop a diagnostic and effective marketing plan.Unit 3 marketing lecture ppt
Unit 3 marketing lecture pptIrshad Tunio
Ěý
1. Market research is needed to identify consumer wants and determine if people will buy a product before it is produced to reduce risks of failure.
2. There are two main types of market research: primary research involves direct contact with customers through surveys, interviews, and experiments. Secondary research uses already collected data from internal sources like sales records or external sources like reports.
3. Primary research methods include questionnaires, interviews, observation, and experiments, each with advantages and disadvantages. Secondary research sources data from within the business or externally from the internet, trade groups, and reports.Operations Management Presentation
Operations Management PresentationPatrick Rubix
Ěý
Operations management aims to produce the right quality of goods and services as quickly as possible and as cheaply as possible. However, achieving all three goals simultaneously can be difficult. Operations managers must decide on production location, scale, methods, and material supplies to balance quality, speed, and cost in an efficient manner. Changing production methods can lower costs per unit but may also reduce flexibility and customization.Similar to Chapter 4 product (20)
Marketing Mix / 7 P's of marketing / Meaning of marketing mix
Marketing Mix / 7 P's of marketing / Meaning of marketing mixheenam8
Ěý
The marketing mix, initially defined by Neil Borden and later expanded by E. Jerome McCarthy to include the 7 P's (product, price, place, promotion, people, process, physical evidence), remains a fundamental concept in marketing despite the evolution of theories over nearly 70 years. Each component of the marketing mix plays a crucial role in satisfying consumer needs and achieving organizational objectives while adapting to various market conditions. Understanding and strategically implementing these elements can enhance consumer satisfaction and differentiate a business in competitive markets.Chapter 6
Chapter 6herbison
Ěý
1. The document defines marketing and distinguishes between consumer and industrial products and services.
2. It discusses methods of pricing products and services including cost-plus pricing and penetration pricing.
3. The document outlines different promotion techniques including personal selling, advertising, sales promotions, and public relations.Products, services and brands building customer value
Products, services and brands building customer valueFahad Aziz
Ěý
This document contains questions and answers about products, services, and brands. It discusses:
1. The three levels of products - core, actual, and augmented products. Core products address customer needs, actual products deliver core benefits, and augmented products offer additional services.
2. The four types of consumer products - convenience, shopping, specialty, and unsought - with examples like toothpaste, appliances, and luxury watches.
3. The three groups of industrial products - materials and parts, capital items, and supplies and services - with examples like raw materials, buildings, and operating supplies.
4. Individual product decisions around attributes, branding, packaging, labeling, style, quality, features, and supportProduct management
Product managementSagar Gadekar
Ěý
The document discusses the concept of products. It defines a product as anything that can be offered to satisfy a want or need, including physical goods, services, ideas, and experiences. It then discusses the meaning, features, levels, and classification of products. It also defines services and discusses the nature and characteristics of services. Finally, it discusses concepts like product mix decisions, product line appraisal, and the product-service continuum.Products, services, and brands
Products, services, and brandsMayanka Singh
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts related to products, services, and brands. It defines a product as anything that can satisfy a want or need, including both tangible goods and intangible services. Products have tangible attributes like packaging as well as intangible attributes like perceptions. The document also discusses classifying products based on durability and tangibility, the significance of product planning, differentiating products, and the importance of building strong brands to create customer value and competitive advantages.Product(a tool of marketing mix)
Product(a tool of marketing mix)Mithilesh Trivedi
Ěý
This document discusses different aspects of products and marketing mix. It defines what a product is, different types of products including goods and services. It describes the levels of a product from core benefit to actual and augmented product. It discusses types of consumer products based on consumer buying behavior and marketing considerations. It also defines industrial products and explains the three levels of product and service decisions - individual, product line, and product mix decisions.Product planning and product life cycle
Product planning and product life cycleOchom
Ěý
The document discusses new product planning and the product life cycle. It begins by defining what a product is, including both tangible goods and intangible services. It then outlines the stages of the product life cycle: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. The document also discusses the different levels of a product from the core benefits to the actual product to augmented services. Finally, it outlines the process of new product development from idea generation through test marketing to improve the odds of success.Product planning and product life cycle
Product planning and product life cycleOchom
Ěý
The document discusses new product planning and the product life cycle. It begins by defining what a product is, including both tangible goods and intangible services. It then outlines the stages of the product life cycle: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. The document also discusses the different levels of a product from the core benefit to the actual product to augmented services. Finally, it outlines the process of new product development from idea generation through test marketing to improve the odds of success.Chapter 3 Defining and Delivering the Product(Tourism and Hospitality Marketing)
Chapter 3 Defining and Delivering the Product(Tourism and Hospitality Marketing)Md Shaifullar Rabbi
Ěý
This document discusses defining and delivering products. It begins by defining what a product is in marketing terms, noting that products can be physical goods, services, or ideas. It then discusses different ways products can be classified, such as whether they are tangible or intangible, the type of customer they target (consumer vs. business), purchasing behaviors, and industry served. The document also discusses branding strategies and building strong brands. Finally, it provides an overview of the new product development process, outlining key steps such as idea generation, concept development and testing, and commercialization.Maanagement of Marketing UNIT-3 &4 product.ppt
Maanagement of Marketing UNIT-3 &4 product.pptetebarkhmichale
Ěý
The document outlines the concept of 'product' in marketing, detailing its various forms, levels, and classifications, including core benefits, expected products, augmented products, and potential products. It discusses product differentiation strategies, consumer goods classifications, and product mix pricing, emphasizing how product attributes and branding can influence consumer perception. Additionally, it delves into packaging's role in marketing, highlighting its significance in brand recognition and consumer convenience.What is the product _ Things to know about product life cycle.pdf
What is the product _ Things to know about product life cycle.pdfraufkhalid104
Ěý
The document provides an overview of products in marketing, outlining their broader definition beyond just physical items to include intangible offerings. It breaks down the levels of products, includes classification methods based on usage time, purchasing habits, and means of production, and details the product life cycle stages. Ultimately, it aims to enhance understanding of product concepts essential for effective marketing strategies.Bus169 Kotler Chapter 08
Bus169 Kotler Chapter 08Alwyn Lau
Ěý
This document discusses product marketing concepts including the nature of products, classifications of consumer and business products, and services. It defines the three levels of a product - core, actual, and augmented. Consumer products are classified as convenience, shopping, specialty, or unsought. Business products include materials/parts, capital items, and supplies/services. Key characteristics that differentiate services are discussed. The document also covers extending product classifications and the firm's product decisions around attributes, branding, and brand strategies.Chapter 8 Products, Services, and Brands -Building Customer Value.pptx
Chapter 8 Products, Services, and Brands -Building Customer Value.pptxBishoyRomani
Ěý
This document discusses different types of products and services. It defines a product as anything offered for attention, acquisition, use or consumption that might satisfy a want or need, and a service as an intangible activity or benefit offered for sale. Products and services exist at three levels - the core benefit, the actual product, and augmented services. Consumer products are classified as convenience products, shopping products, specialty products, and unsought products based on how and when consumers purchase them. Industrial products include materials and parts, capital items, and supplies and services.PRODUCT AND BRAND MANAGEMENT - MB - 305 A.pptx
PRODUCT AND BRAND MANAGEMENT - MB - 305 A.pptxPrashantMishra919139
Ěý
The document discusses the fundamentals of product and brand management, highlighting the importance of product as a central marketing tool that meets consumer needs through tangible and intangible features. It elaborates on the different levels of products, from core to potential, and categorizes products into consumer and industrial goods, further detailing subcategories like convenience, shopping, specialty, and unsought products. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of understanding market dynamics and consumer behavior in developing effective marketing strategies.Product levels classification product mix & pricing stratagies
Product levels classification product mix & pricing stratagiesVenkat. P
Ěý
The document discusses the various concepts of product levels, classifications, and mixes in marketing management as presented by Philip Kotler. It details five levels of products: core, expected, augmented, potential, and their importance in meeting consumer expectations. Additionally, it categorizes products into consumer and industrial products, along with types based on durability and tangibility, emphasizing how these classifications impact marketing strategies.Products-services-and-brands.pptx
Products-services-and-brands.pptxLAISALabiba
Ěý
This document discusses key concepts related to products, services, and brands. It defines a product as anything offered for sale that might satisfy a want or need, while a service is an intangible activity or benefit offered for sale. It discusses different levels of products from the core benefit to the actual product to augmented services. It also covers classifications of consumer and industrial products, as well as product line and mix decisions companies must make. Finally, it discusses packaging, branding, and brand equity.price.pdf
price.pdfFahadChowdhury25
Ěý
This document provides an overview of Chapter 12 which covers product and pricing strategies. It begins by defining key terms like product, price, and the total product concept. It then discusses how goods and services are classified, including convenience goods, shopping goods, specialty goods, and industrial goods categories. The document outlines the product life cycle model and its four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. It provides examples to illustrate each stage and how marketing strategies must adapt.Kotler_pom_15e_inppt_08_GEmarketing.pptx
Kotler_pom_15e_inppt_08_GEmarketing.pptxAmanySayedMostafa
Ěý
The document covers product, services, and branding strategies aimed at building customer value through effective marketing practices. It outlines the definitions, classifications, and levels of products and services, and discusses key marketing considerations such as customer behavior, service characteristics, and brand management strategies. Additionally, it highlights the product life cycle stages and the strategic decisions involved in developing and managing products and brands.Quarter-2-Week-1-4-Ms-of-Production-final.pptx
Quarter-2-Week-1-4-Ms-of-Production-final.pptxJasminMateo1
Ěý
The document discusses the key elements of production systems and business models. It describes the four M's of production as manpower, materials, machine, and method. Manpower refers to the human labor involved, materials include both direct and indirect raw materials, machine means the manufacturing equipment, and method is the production process. An effective business model incorporates consideration of these four M's, identifies customers, outlines business processes and resources, develops value propositions, and determines partnerships and marketing strategies. Developing a prototype, engaging suppliers and optimizing supply chain management are also important facets of a strong production system and business model.Setting product strategy
Setting product strategyeyad-gh
Ěý
The document outlines the components and levels of product strategy, including core, generic, expected, augmented, and potential products, essential for meeting customer needs. It classifies consumer products based on durability, tangibility, and shopping habits, while also covering industrial goods and differentiation strategies through features, quality, and service. Additionally, it discusses branding, packaging, labeling, and product design as critical factors in marketing and product management.Chapter 3 Defining and Delivering the Product(Tourism and Hospitality Marketing)
Chapter 3 Defining and Delivering the Product(Tourism and Hospitality Marketing)Md Shaifullar Rabbi
Ěý
Ad
Chapter 4 product
- 1. Chapter 3 Product Planning and Development
- 2. Chapter Four Products, Services, and Branding Strategies By Rafique Ahmed
- 3. Definitions Product ď‚— Anything offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a need or want. ď‚— Products; includes goods, services, places, persons, and ideas ď‚— Some products are sold only to consumers, while others are sold to organizations ď‚— Whether a product is a consumer product or a business 8 - 2
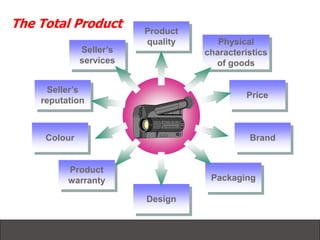
- 4. Seller’s services Product quality Physical characteristics of goods Price Brand Design Packaging Product warranty Seller’s reputation Colour The Total Product
- 5. Classification of product ď‚— Consumer product Product that are bought by the consumers for personal use. Consumer products include Convenience, Shopping, Specialty and Unsought Products ď‚— Business or Industrial Product Product bought by individuals and organizations for further processing or for use in conducting a business.
- 8. Classification of Consumer Goods ď‚— Consumer goods are further classified as ď‚— Convenience Goods ď‚— Shopping Goods ď‚— Specialty Goods ď‚— Unsought Goods
- 9. Convenience Goods ď‚— Convenience goods are close goods the customer usually purchased frequently, immediately and with minimum effort ď‚— For Example. ď‚— Soap, candy, newspaper and fast food, cosmetics jeans etc 8 - 8
- 10. Types of consumer products ď‚— Convenience products
- 11. Shopping Goods ď‚— Consumer product that the consumer, in the process of selection and purchases, characteristically compares on such basis as suitability, quality, price and style. ď‚— Less frequent purchases ď‚— More shopping effort for comparisons. ď‚— Higher than convenience good pricing ď‚— Selective distribution in fewer outlets ď‚— Advertising and personal selling ď‚— For example. Furniture, clothing, cars, major appliances, hotel 8 - 10
- 12. Types of consumer products ď‚— Shopping products
- 13. Specialty Goods ď‚— Consumer product with unique characteristics or brand identification for which a significant group of buyers are willing to make a special purchasing effort. ď‚— High price ď‚— Exclusive distribution ď‚— Carefully targeted promotions ď‚— For example, specific brand types of cars, BMW, Armani. ď‚— Designer clothes 8 - 12
- 14. Types of consumer products
- 15. Unsought Goods ď‚— Unsought Products are products you haven't actively been looking for. ď‚— Unsought goods are those now unknown to the consumer or, if known, undesired. ď‚— For example: life insurance. Gravestone etc ď‚— Smoke detectors 8 - 14
- 16. Classifying Business Products 1.Raw materials: unprocessed, become part of other manufactured products 2.Manufactured parts and materials: processed products that become part of other products 3.Installations: plant & machinery, major buildings and equipment etc 4.Accessory equipment: used in operations, include computers, desks, tools 5.Operating supplies: low value goods, like pencils, stationery, convenience products for businesses 9 - 15
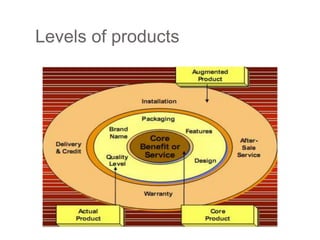
- 18. 1) The Core Products ď‚— The basic product which you wants to purchase for satisfaction of your needs and wants. ď‚— Actual Product The actual product may have as many as five characteristics that combine to deliver the core product benefits. ď‚— The characteristics are: ď‚— Quality ď‚— Feature , Design ď‚— Brand name , Packaging
- 19. 3) Augmented product ď‚— Any additional consumer services and benefits built around the core and actual products. ď‚— For example: ď‚— Warranty/ guarantee ď‚— After sales services ď‚— Installation ď‚— delivery
- 20. Service A service is defined as any activity or benefit that one party can offer to another which is basically intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything.
- 21. Examples of Service Industries ď‚— Health Care ď‚— hospital, medical practice, dentistry, eye care ď‚— Professional Services ď‚— Accounting, legal, architectural ď‚— Financial Services ď‚— Banking , insurance ď‚— Hospitality ď‚— restaurant, hotel ď‚— Travel ď‚— airline, travel agency, theme park ď‚— Others ď‚— hair styling, plumbing, lawn maintenance, counseling services, health club, interior design
- 22. Service characteristics ď‚· Intangibility ď‚· Inseperarability ď‚· Variability ď‚· Perishability ď‚· Lack of ownership
- 23. Intangibility ď‚— Cannot be seen, ď‚— Tasted, ď‚— Felt, ď‚— Heard ď‚— Services cannot be readily displayed ď‚— or Smell before they are bought.
- 24. Inseparability ď‚— Services produced and consumed at the same time. ď‚— Cannot be separated from providers, whether people or machines. ď‚— Customers are always involved
- 25. Variability ď‚— Quality may vary greatly depending on who provides the service, when and how. ď‚— Staff need to know how to do something well. ď‚— Staff must be well motivated to maintain high standards of service.
- 26. Perishability ď‚— Services cannot be stored for later sale or use.
- 27. Lack of ownership No physical product is exchanged and therefore nothing owned.
- 28. 7 P’S of Service Marketing Mix… Product Price Promotion Place People Physical evidence Process
- 29. PEOPLE  All human actors who play a part in service delivery and thus influence the buyer’s perceptions: namely, the firm’s personnel, the customer, and other customers in the service environment.
- 30. PEOPLE People are important because: ď‚— Providing a service, rather than selling a product. ď‚— Quality of personal relationships between company and clients becomes vital. Technicians Dealers Other Employees
- 31. Process  The actual procedures, mechanisms, and flow of activities by which the service is delivered—the service delivery and operating systems.
- 32. Process of Taking a Mobile connection Go to Etisalat Shop Choose a product (Say Pre-paid connection) Pay the appropriate fees Take the Respective product (Like SIM Card in this case) Avail the facilities Give the feedback
- 33. Physical Evidence ď‚— The environment in which the service is delivered and where the firm and customer interact, and any tangible components that facilitate performance or communication of the service.
- 34. Physical Evidence…. Sim cards Bills Before and After sale documents PHYSICAL EVIDENCE
- 35. Brand represents the consumer’s perceptions and feelings about a product and its performance. It is the company’s promise to deliver a specific set of features, benefits, services, and experiences consistently to the buyers OR Brand is the name, term, sign, or design—or a combination of these—that identifies the maker or seller of a product or service Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands
- 36. Brand Name Selection Desirable qualities 1. Suggest benefits and qualities 2. Easy to pronounce, recognize, and remember 3. Distinctive 4. Extendable 5. Translatable for the global economy 6. Capable of registration and legal protection 8 - 35
