Chapter 6 selecting methods,media, and materials.
- 1. Chapter 6 SELECTING METHODS, MEDIA, AND MATERIALS
- 2. Members in our group ’éŚ 1. Miss Thawanrach Souyarom ID 523050529-4 ’éŚ 2. Miss Wasita Neerapan ID 543050470-3 ’éŚ 3. Miss Jutamas Ninlawan ID 543050 - ’éŚ 4. Miss Patsachon Srisoipraw ID 543050464-8
- 3. Introduction This chapter focuses on how to select methods and media and acquire the specific instructional materials you will use to achieve your plan. Selecting existing materials You may acquire instructional materials by: Modifying available materials Creating a new materials
- 4. Methods, Media, and Materials ’éŚ There are several methods to help them learning in the class such as.. 1.Motivation 5.Evaluation 2.Application 4.Information 3.Orientation
- 5. ’éŚ Which Methods Should I choose? ’éŚ THE METHODS SELECTION CHECKLIST
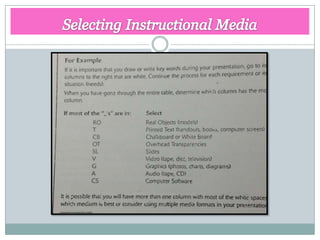
- 6. Selecting Instructional Media A second decision you much make is which instructional medium or media to use. There are six types of Instructional methods that we learn in chapter 5. There are multimedia, video, graphics, audio, text, and real objects and models. As with Checklist instructional methods, we have Picture compiled the advantages of the various media into a checklist, that
- 8. Media Selectio n Checklis t
- 9. The third decision you must make is which specific instructional materials to use. Locating and selecting instructional materials involve the 1. Determine following steps: needs. 2. Check a variety of sources such as a computer database. Instructional materials publish catalogs listing materials you can buy and, in some cases, rent. To talk with vendors and other teachers to find out what is available.
- 10. 3. Obtain and 4. Try the 5. Compare preview the materials out any competing materials. with students. materials. 7. Keep 6. Make your accurate selection. records. If the content of the instructional materials you fine doesnŌĆÖt match ’éŚ the objectives of your instructional plan, you have two alternatives: 1 modify the materials so they do meet your objectives, or 2 create new instructional
- 11. Modifying Available Instructional Materials ŌĆóIt is more efficient to modify available materials than to create new materials. It is also an opportunity for you to be creative. You can modify almost any type of instructional material. You can adapt the material to
- 12. ’éŚ Classroom are usually filled with a variety of teaching materials, from concrete objects to posters, bulletin boards, and printed material of every kind. Photocopying machine are now standard equipment in the school. Computer-based tools make it much easier to produce high-quality, professional-looking materials.
- 13. How do I create effective materials? - Creative materials allows you opportunity to reflect on what is needed, use experience from the past, synthesize new materials, and creatively bring together an effective learning experience.
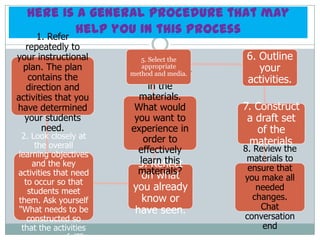
- 14. Here is a general procedure that may 1. Refer help you in this process repeatedly to your instructional 5. Select the 6. Outline plan. The plan appropriate your contains the 4. Putand media. method yourself activities. direction and in the activities that you materials. have determined What would 7. Construct your students you want to a draft set need. experience in of the 2. Look closely at order to the overall materials . effectively 8. Review the learning objectives materials to and the key learn this 3. Reflect materials? ensure that activities that need on what to occur so that you make all students meet you already needed them. Ask yourself know or changes. "What needs to be have seen. Chat constructed so conversation that the activities end are successful?"
- 15. ’éŚ Formative Evaluation is evaluation done during the planning or production of instructional materials to determine what, if any, revisions should be made to make them more useful. - Modifying existing materials or creating materials.
- 16. Copyright Issues ’éŚ Copyright refer to the legal right to an original work.
- 17. ’éŚ What are copyrighted materials? - Copyrighted materials are original works of authorship that are fixed in any tangible medium of expression.
- 18. ŌĆó - for the life of author + 70 How long years. does ŌĆó - Works for hire are protected copyright for 95 years from the date of publication or 120 years from last? the date of creation, which ever come first.
- 19. ŌĆó - They have right to reproduce work, What create derivative rights does works, sell or the law distribute work, and perform or give display the work in copyright public. owner?
- 20. ’éŚ Are there any limitations or exceptions to copyright ownersŌĆÖ rights? - The law spell out several specific exceptions to the exclusive rights of copyright owners. That means students or teacher can use things without special permission. There are exceptions related to software backup, face to face teaching,
- 21. Software Backup. ŌĆó - School must purchase network licenses or multiple copies of the software to run multiple copies on network, and the network must monitor use to prevent violation if the license is restricted to a specific number of copies.
- 22. Face to Face Teaching ’éŚ Face to Face Teaching -Teacher can use copyrighted materials in case of face to face teaching mean that using copyrightrd material to teach only in class at a nonprofit educational institution. In distance education is permitted, but only when transmission is into classrooms or similar education
- 23. Fare use ’éĪ Fare use - Fair use can apply to education. For example, students or teachers can make single copy of articles from the library journals as part 1.The purpose and of a published review of the of character work. the use 4.The effect of the use on Fair use the potential 2.The nature market for in of copyrighted work education work 3.The amount of the work used in relation to the whole
- 24. Fare use ’āĘFair use guideline 2.It is 1.The excerpt spontaneous is used less use than 1000 ( the decision words or less in the class it than 10% occur at that moment) 4.Other rules 3.There is no you can cumulative consult with effect ( it isnŌĆÖt specialist foe repeat) specific guidelines.
- 25. Fare use ’éĪEstablished fair use guideline (copyrighted material in digital format: text, graphics, audio, or video). Teacher can use it to teach in classroom however, use beyond the classroom is problem. ’éĪTEACHER AND STUDENTS CAN AVOID the problem with copyrighted material. One solution is to request permission to use them. Another is to
- 26. Applications in the learner centered classroom ’éŚ TeacherŌĆÖs point of view. ŌĆ£ What can the teacher do to effectively select materials, methods, and media?ŌĆØ Perhaps the question that should be asked is, ŌĆ£what can the teacher do to help students learn to develop and use selection criteria of their own?ŌĆØ
- 27. Applications in the learner centered classroom ’éŚ Learning higher-order thinking skills is an important element of the learner-centered classroom. How to think about oneŌĆÖs own thinking and learning? Identify what they need to be able to effectively learn.
- 28. Applications in the learner centered classroom ’éŚ What can you do within your classroom to help learners gain experience with selecting methods, media, and material? ’éĪ First, help students understand and to make all sorts of selections. ’éĪ Second, model the process to make the final selection. Students need to know that obstacles. Finally, students need to know that they should reflect on their selection process. Did it work? What was successful? What could have been improved?. Students should ask themselves about their selected criteria.
- 29. ’éŚ The goal of developing higher-order thinking skills is to help learners understand their own learning process.
- 30. ’éŚ Selecting instructional methods, media, and materials that will match your students, objectives, learning environment, and instructional activities.
- 31. ŌĆ£Thank you AllŌĆØ ..’üŖ