Chapter1
- 1. CHAPTER 1 : FUNDAMENTAL OF CONTROL THEORY INTRODUCTION GP 619 â ADVANCED CONTROL SYSTEM CONTROL PROCESSES Prepared by OPEN & CLOSED LOOP SYSTEM Mr. Mohd Taufik Rezza B Mohd Foudzi BASIC ELEMENT CASE STUDY
- 2. INTRODUCTION
- 3. CONTROL SYSTEM A control system can be thought of as a system which for some particular input or inputs is used to control its output to some particular value , give a particular sequence of events or give an event if certain conditions are met . âĒ Control a variable to obtain the required value âĒControl the sequence of events âĒControl whether an event occurs or not
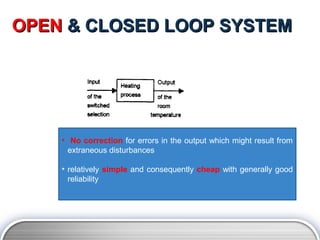
- 4. OPEN & CLOSED LOOP SYSTEM âĒ No correction for errors in the output which might result from extraneous disturbances âĒ relatively simple and consequently cheap with generally good reliability
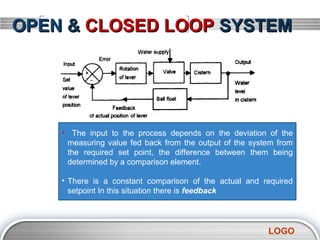
- 5. OPEN & CLOSED LOOP SYSTEM âĒ The input to the process depends on the deviation of the measuring value fed back from the output of the system from the required set point, the difference between them being determined by a comparison element. âĒ There is a constant comparison of the actual and required setpoint In this situation there is feedback LOGO
- 6. OPEN & CLOSED LOOP SYSTEM + set value - feedback value = error âĒ the comparison element in the closed-loop control system is represented by a circular symbol with a + opposite the set value input and a - opposite the feedback signal. âĒ This difference between the set value and feedback value, the so-called error LOGO
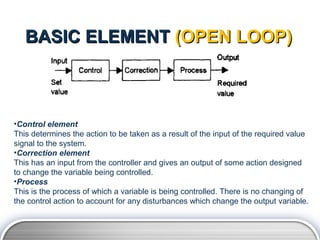
- 7. BASIC ELEMENT (OPEN LOOP) âĒControl element This determines the action to be taken as a result of the input of the required value signal to the system. âĒCorrection element This has an input from the controller and gives an output of some action designed to change the variable being controlled. âĒProcess This is the process of which a variable is being controlled. There is no changing of the control action to account for any disturbances which change the output variable.
- 8. BASIC ELEMENT (CLOSED LOOP) LOGO
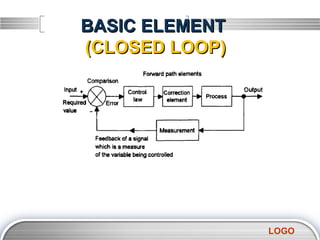
- 9. BASIC ELEMENT (CLOSED LOOP) 1. Comparison element This element compares the required value of the variable being controlled with the measured value of what is being achieved and produces an error signal: error = required value signal - measured actual value signal 2. Control law implementation element The control law element determines what action to take when an error signal is received. The control law used by the element may be just to supply a signal which switches on or off when there is an error, as in a room thermostat, or perhaps a signal which is proportional to the size of the error so that if the error is small a small control signal is produced and if the error is large a large proportional control signal is produced. Other control laws include integral mode where the control signal continues to increase as long as there is an error and derivative mode where the control signal is proportional to the rate at which the error is changing. LOGO
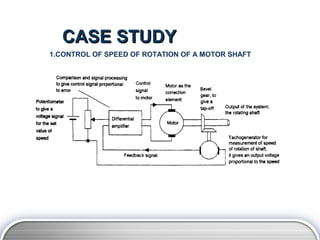
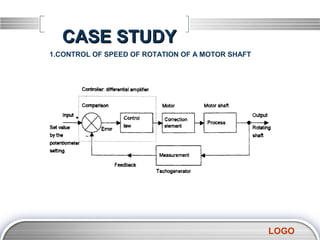
- 10. BASIC ELEMENT (CLOSED LOOP) The term control unit or controller is often used for the combination of the comparison element 3. Correction element The correction element or, as it is often called, the final control element, produces a change in the process which aims to correct or change the controlled condition. The term actuator is used for the element of a correction unit that provides the power to carry out the control action. Examples of correction elements are directional control valves which are used to switch the direction of flow of a fluid and so control the movement of an actuator such as the movement of a piston in a cylinder. Another example is an electric motor where a signal is used to control the speed of rotation of the motor shaft LOGO
- 11. BASIC ELEMENT (CLOSED LOOP) 4 . Process The process is the system in which there is a variable that is being controlled, e.g. it might be a room in a house with the variable of its temperature being controlled. 5. Measurement element The measurement element produces a signal related to the variable condition of the process that is being controlled. For example, it might be a temperature sensor with suitable signal processing. 1. Feedback path Feedback is a means whereby a signal related to the actual condition being achieved is fed back to modify the input signal to a process. The feedback is said to be negative when the signal which is fed back subtracts from the input value. It is negative feedback that is required to control a system. Positive feedback occurs when the signal fed back adds to the input signal. 2. Forward path The term forward path is used for the path from the error signal to the output. In before these forward path elements are the control law element, the correction element and the process element. LOGO
- 12. CASE STUDY 1.CONTROL OF SPEED OF ROTATION OF A MOTOR SHAFT
- 13. CASE STUDY 1.CONTROL OF SPEED OF ROTATION OF A MOTOR SHAFT LOGO