CHD.pptx
- 2. ÔÇó Abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth ÔÇó Gestational weeks 3 through 8
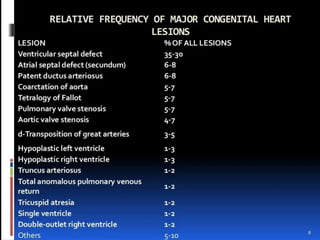
- 3. Incidence ÔÇó up to 0.5% ÔÇó among the most prevalent birth defects and are the most common type of pediatric heart disease.
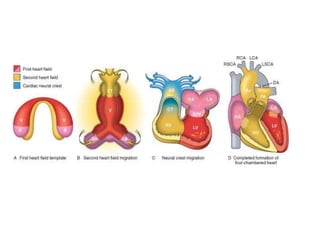
- 4. Cardiac Development. ÔÇó caused by errors during cardiac morphogenesis. ÔÇó precursors originate --- lateral mesoderm and move to midline in two migratory waves to create ----- first and second heart fields by about day 15. ÔÇó Both fields contain multipotent progenitor cells that can produce all of the major cell types of the heart: endocardium, myocardium, and smooth muscle cells. ÔÇó each heart field is differentially marked by the expression of distinct gene sets. ÔÇó first heart field expresses -- transcription factor H and 1 ÔÇó second heart field expresses --- transcription factor Hand2 and the secreted protein fibroblast growth factor-10.
- 5. ÔÇó each heart field --give rise to particular portions of the heart. ÔÇó left ventricle largely first heart field ÔÇó second heart field become the outflow tract, right ventricle, and most of the atria ÔÇó By day 20--- beating tube, which loops to the right andbegins to form the basic heart chambers ÔÇó two other critical events occur: ÔÇó (1) neural crestÔÇôderived cells migrate into the outflow tract -- formation of the aortic arches ÔÇó (2) interstitial connective tissue --- enlarges to produce swellings known as endocardial cushions. ÔÇó By day 50, further septation of the ventricles, atria, and atrioventricular valves produces a four-chambered heart.
- 6. ÔÇó depends on a network of transcription factors ---- regulated by --signaling pathways, ÔÇó the Wnt, hedgehog, (VEGF), bone morphogenetic factor, TGF╬▓, FGF, and Notch pathways ÔÇó In addition ÔÇô hemodynamic forces play an important role in cardiac development
- 9. ÔÇó inherited defects that involve genes that encode transcription factors; ÔÇó transient environmental stresses during the first trimester
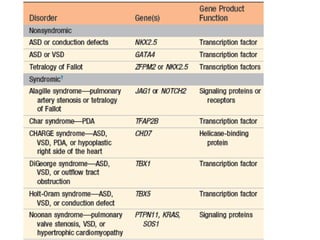
- 10. Etiology and Pathogenesis ÔÇó Sporadic genetic abnormalities are the major known causes of congenital heart disease. ÔÇó single gene mutations, small chromosomal losses, and additions or deletions of whole chromosomes (trisomies and monosomies). In the ÔÇó GATA4, TBX5, and NKX2-5---- atrial and ventricular septal defects
- 12. ÔÇó deletion 22q11.2----- DiGeorge syndrome ÔÇó syndrome, the fourth branchial arch , third and fourth pharyngeal pouches (thymus, parathyroids, and heart) develop abnormally. ÔÇó The syndrome --- multiple deficits ÔÇó CATCH-22: ÔÇó cardiac abnormality, abnormal facies, thymic aplasia, cleft palate, and hypocalcemia
- 13. ÔÇó Turner syndrome (monosomy X) and trisomies 13, 18, and 21. ÔÇó 40% of patients with Down syndrome have CHD ÔÇó environmental factors, ÔÇó congenital rubella infection, ÔÇó gestational diabetes ÔÇó teratogen exposure ÔÇó Nutritional factors --- folate supplementation during early pregnancy may reduce congenital heart disease risk. ÔÇó alcohol
- 14. Clinical Features. Three major categories: ÔÇó Malformations causing a left-to-right shunt ÔÇó Malformations causing a right-to-left shunt ÔÇó Malformations causing an obstruction ÔÇó Malpositions of heart
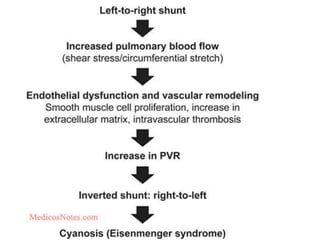
- 15. ÔÇó A shunt is an abnormal communication between chambers or blood vessels ÔÇó pressure gradients from the left (systemic) side to the right (pulmonary) side of the circulation or vice versa. ÔÇó right-to-left shunt--- hypoxemia and cyanosis ---- result because the pulmonary circulation is bypassed ÔÇó Right to- left shunts can allow emboli -- paradoxical embolism ÔÇó ÔÇ£clubbingÔÇØ of the tips of the fingers and toes as well as polycythemia.
- 16. ÔÇó left-to-right shunts increase pulmonary blood flow, but are not initially associated with cyanosis. ÔÇó elevate both volume and pressure in the normally low- pressure, low-resistance pulmonary circulation. ÔÇó Muscular pulmonary arteries ---- medial hypertrophy and vasoconstriction. ÔÇó prolonged pulmonary arterial vasoconstriction stimulates the development of irreversible obstructive intimal lesions --- frank atherosclerotic lesions. ÔÇó The right ventricle --- hypertrophy. ÔÇó Eventually, pulmonary vascular resistance = systemic levels--- right-to-left shunt --- poorly oxygenated blood into the systemic circulation (Eisenmenger syndrome).
- 18. ÔÇó Obstructive congenital heart disease occurs when there is abnormal narrowing of chambers, valves, or blood vessels. ÔÇó A complete obstruction --- atresia.
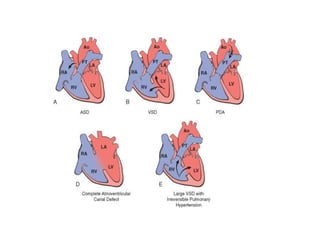
- 20. Left-to-Right Shunts ÔÇó Pink babies ÔÇó most common CHD ÔÇó ASD, VSD, and PDA. ÔÇó ASD increases volumes, VSD and PDA--- both flow and pressure.
- 22. Atrial Septal Defect ÔÇó abnormal, fixed openings in the atrial septum ÔÇó caused by incomplete tissue formation ÔÇó Communication of blood between the left and right atria ÔÇó ASDs -- usually asymptomatic until adulthood ÔÇó ASD should not be confused with patent foramen ovale , which represents the failure to close a foramen (hole) that is part of normal development.
- 23. ÔÇó The septum primum -- sits posteriorly between the right and left atria and partially separates them----- anterior opening, called the ostium primum---- fetal development. ÔÇó Before the growing septum primum completely obliterates the ostium primum, it develops a second posterior opening called the ostium secundum. ÔÇó The septum secundum is a subsequent membranous ingrowth located to the right and anterior of the septum primum. ÔÇó As the septum secundum grows-- opening called the foramen ovale --- continuous with the ostium secundum ÔÇó The septum secundum enlarge -- FLAP--- covers the foramen ovale on its left side
- 24. ÔÇó the valve opens only when the pressure is greater in the right atrium. ÔÇó In fetal life--- pulmonary circulation pressure is greater than that of the systemic circulation--- foramen ovale is normally open. ÔÇó At birth----pulmonary vascular pressures drop---- the valve of the foramen ovale closes
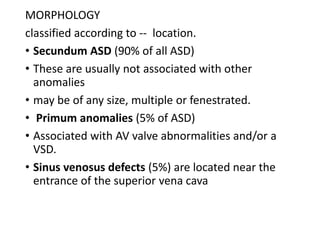
- 25. MORPHOLOGY classified according to -- location. ÔÇó Secundum ASD (90% of all ASD) ÔÇó These are usually not associated with other anomalies ÔÇó may be of any size, multiple or fenestrated. ÔÇó Primum anomalies (5% of ASD) ÔÇó Associated with AV valve abnormalities and/or a VSD. ÔÇó Sinus venosus defects (5%) are located near the entrance of the superior vena cava
- 27. Clinical Features ÔÇó Infant tires easily when feeding ÔÇó left-to-right shunt---- pulmonary vascular resistance is less and compliance of right ventricle is much greater ÔÇó Pulmonary blood -- two to four times normal ÔÇó A murmur --- excessive flow through the pulmonary valve. ÔÇó ASDs -- well tolerated till age 30 ÔÇó Surgical or catheter-based closure
- 28. Patent Foramen Ovale ÔÇó small hole created by an open flap of tissue in the atrial septum at the oval fossa. ÔÇó at birth -- flap closes -- 80% of people. ÔÇó 20% of people-- flap can open when there is more pressure on the right side of the heart ÔÇó sustained pulmonary hypertension or even transient increases in right-sided pressures-- during a bowel movement, coughing, or sneezing- brief periods of right-to-left shunting
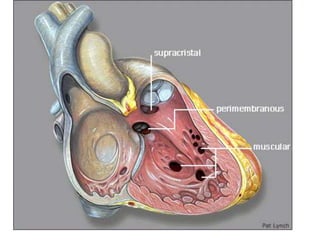
- 29. Ventricular Septal Defect ÔÇó incomplete closures -- ventricular septum, ÔÇó free communication -- left to right ventricles
- 30. ÔÇó classified --- size and location ÔÇó Most are size of the aortic valve orifice ÔÇó 90%occur in the region of the membranous septum (membranous VSD) ÔÇó The remainder occur below the pulmonary valve (infundibular VSD) or within the muscular septum. ÔÇó Single ÔÇó Muscular septum may be multiple so-called ÔÇ£Swiss- cheeseÔÇØ septum
- 33. ÔÇó Clinical Features. ÔÇó depend on the size and associated with right-sided malformations. ÔÇó Large --- difficulties from birth ÔÇó smaller -- well tolerated for years ÔÇó 50% of small muscular VSDs close spontaneously ÔÇó Large defects are usually membranous or infundibular, ÔÇó left-to-right shunting--- right ventricular hypertrophy and pulmonary hypertension ---- ultimately resulting in shunt reversal, cyanosis, and death. ÔÇó Surgical or catheter-based closure
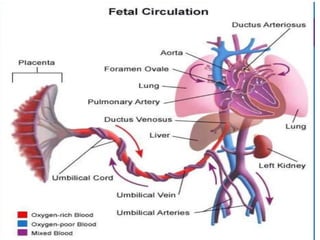
- 34. Patent Ductus Arteriosus ÔÇó The ductus arteriosus arises from the pulmonary artery and joins the aorta ÔÇó Intrauterine´âá blood flow from the pulmonary artery to the aorta--- bypassing the lungs. ÔÇó functionally closed after 1 to 2 days ÔÇó increased arterial oxygenation---- decreased pulmonary vascular resistance--- declining prostaglandin E2. ÔÇó ligamentum arteriosum. ÔÇó Ductal closure is often delayed (or even absent) in infants with hypoxia (due to respiratory distress or heart disease), ÔÇó PDAs account for about 7% of cases of congenital heart disease
- 36. ÔÇó continuous harsh ÔÇ£machinery-likeÔÇØ murmur. ÔÇó PDA is usually asymptomatic at birth ÔÇó Upto -- 2cm long, 1 cm dia ÔÇó large shunts, the additional volume and pressure overloads eventually produce obstructive changes in small pulmonary arteries, leading to reversal of flow and its associated consequences.
- 37. Right-to-Left Shunts ÔÇó Blue babies ÔÇó cyanosis (cyanotic congenital heart disease) ÔÇó Tetralogy of Fallot the most common in this group ÔÇó transposition of the great arteries ÔÇó The others include persistent truncus arteriosus, tricuspid atresia, and total anomalous pulmonary venous connection.
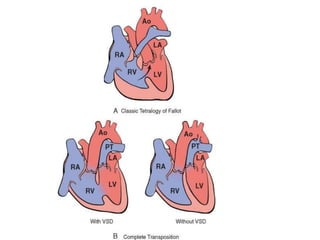
- 38. Tetralogy of Fallot ÔÇó (1) VSD ÔÇó (2) obstruction of the right ventricular outflow tract (subpulmonary stenosis) ÔÇó (3) an aorta that overrides the VSD ÔÇó (4) right ventricular hypertrophy ÔÇó anterosuperior displacement of the infundibular septum.
- 41. Morphology. ÔÇó heart -- enlarged -- ÔÇ£boot-shapedÔÇØ ÔÇó The aortic valve forms the superior border of the VSD, thereby overriding the defect and both ventricular chambers. ÔÇó The obstruction to right ventricular outflow --- due to narrowing of the infundibulum (subpulmonic stenosis) can be accompanied by pulmonary valvular stenosis. ÔÇó Aortic valve insufficiency or an ASD may also be present; a right aortic arch is present in about 25% of cases.
- 42. Clinical Features. ÔÇó survive into adult life; ÔÇó depend primarily on the severity of the subpulmonary stenosis, since this determines the direction of blood flow. ÔÇó If mild--- resembles an isolated VSD, and the shunt may be left-to-right, without cyanosis (so-called ÔÇ£pink tetralogyÔÇØ). ÔÇó severe obstruction, right-sided pressures approach or exceed left-sided pressures-- right-to-left shunting --- cyanosis (classic TOF). ÔÇó The more severe the subpulmonic stenosis, the more hypoplastic are the pulmonary arteries (i.e., smaller and thinner-walled), and the larger is the overriding aorta.
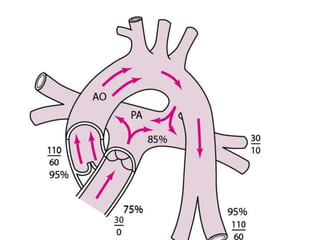
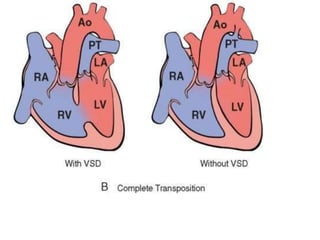
- 43. Transposition of the Great Arteries ÔÇó TGA produces ventriculoarterial discordance. ÔÇó aorta -- arises from right ventricle ÔÇó pulmonary artery --- from the left ventricle. ÔÇó atrium-to-ventricle connections are normal (concordant), ÔÇó Embryologic defect ----abnormal formation of the truncal and aortopulmonary septa. ÔÇó Separation of the systemic and pulmonary circulations ÔÇó incompatible with life unless a shunt
- 46. ÔÇó . Patients with TGA and a VSD (approximately 35%) often have a stable shunt. ÔÇó patent foramen ovale or ductus arteriosus for blood mixing (approximately 65%) is problematic.
- 47. Tricuspid Atresia ÔÇó complete occlusion of the tricuspid valve orifice. ÔÇó the mitral valve is larger than normal ÔÇó right ventricular hypoplasia ÔÇó circulation can be maintained by right-to-left shunting through an interatrial communication (ASD or patent foramen ovale), in addition to a VSD
- 48. Obstructive Lesions ÔÇó Congenital obstruction can occur at the level of the heart valves or within a great vessel. ÔÇó Common examples include aortic or pulmonary valve stenosis or atresia, and coarctation of the aorta.
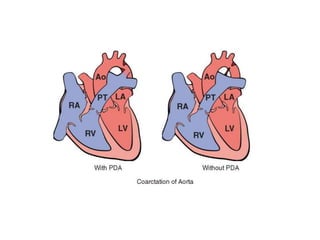
- 49. Coarctation of the Aorta ÔÇó common structural anomalies. ÔÇó twice as common in M ÔÇó There are two classic forms: ÔÇó (1) an ÔÇ£infantileÔÇØ formÔÇöoften symptomatic in early childhoodÔÇötubular hypoplasia ÔÇó (2) an ÔÇ£adultÔÇØ form --- ridgelike infolding of the aorta just opposite the closed ductus arteriosus (ligamentum arteriosum) ÔÇó solitary defect or is accompanied by a bicuspid aortic valve
- 51. ÔÇó Clinical manifestations ---severity of the narrowing and the patency of the ductus arteriosus. ´âÿCoarctation of the aorta with a PDA usually manifests early in life; ÔÇó the delivery of unsaturated blood through the PDA produces cyanosis localized to the lower half of the body. ´âÿcoarctation of the aorta without a PDA--- . Most children are asymptomatic ÔÇó Hypertension in the upper extremities with weak pulses and hypotension in the lower extremities--- claudication and coldness ÔÇó Development of collateral circulation -- through enlarged intercostal and internal mammary arteries------- visible erosions (ÔÇ£notchingÔÇØ) of the undersurfaces of the ribs. ÔÇó murmurs -- throughout systole; sometimes ÔÇ£thrillÔÇØ ÔÇó long-standing pressure -- left ventricular hypertrophy.
- 52. Pulmonary Stenosis and Atresia ÔÇó obstruction at the level of the pulmonary valve. ÔÇó This can be mild to severe ÔÇó isolated or part of a more complex anomalyÔÇö either TOF or TGA ÔÇó Right ventricular hypertrophy typically develops,
- 53. Aortic Stenosis and Atresia ÔÇó obstruction of the aortic valve ÔÇó can occur at three locations: valvular, subvalvular, and supravalvular. ÔÇó hypoplasia of the left ventricle and ascending aorta ÔÇó The ductus must be open to allow blood flow to the aorta and coronary arteries