1 of 2
Download to read offline

Recommended
┬ŚĮŌż╬Į╠ż©ĘĮĪó覿ėĘĮ



┬ŚĮŌż╬Į╠ż©ĘĮĪó覿ėĘĮYoshifumi Murakami
?
źšź©╝»ųą╚š▒ŠšZĮ╠ė²ź╗ź▀ź╩®`
Į╠▓─ĮBĮķĪó╩┬└²ĮBĮķĪóźĻźĮ®`ź╣ĮBĮķ
¢|Š®═Ō╣·šZ┤¾č¦
NHKźķźĖź¬ź╦źÕ®`ź╣
ź▒źĒźĒź░
Youtubeäė╗Łź╦źÕ®`ź╣
╚š▒Šš■Ė«ėQ╣ŌŠųäė╗Ł
Ü▌ż▐ż▐ż╦youtube
ź©źĻź¾ż¼╠¶æķŻĪ
źĄźżź▐źļźķźĖź¬Language Presentation 2013



Language Presentation 2013cindipatten
?
There were originally 7,000-8,000 languages spoken worldwide, but many are becoming extinct, especially in Australia and the Americas. Today there are around 165 languages spoken in the US and 1,000 languages each in Africa and New Guinea. Languages are grouped into families that share a common ancestral language, with the major families including Indo-European from 4,000 years ago and its branches like Germanic. English belongs to the Germanic branch of the Indo-European family and the West Germanic group within that branch. The document also provides information on the evolution of languages over time and definitions of related concepts like dialects, pidgins, lingua francas, and creoles.Cambodia



Cambodiacduong12
?
Cambodia is located in Southeast Asia, bordered by Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam. It has a population of over 15 million people, most of whom are ethnic Khmer and follow Buddhism. The country has a history of kingdoms and empires dating back to the 1st century CE. More recently, Cambodia endured heavy losses under the Khmer Rouge regime in the 1970s and is still recovering economically. The government is a multiparty democracy and constitutional monarchy, with the prime minister as head of government. The economy relies on agriculture, garment exports, and tourism, but poverty remains a significant challenge.Branches of linguistics



Branches of linguisticsAsarah Asarah
?
Linguistics is the study of language and examines many aspects including phonology, morphology, lexicology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. It recognizes that language exists through people and is still developing as a discipline. Sociolinguistics examines language variations and how language communicates ideas about others. Psycholinguistics studies how people use, misuse, and lose language over time. Applied linguistics applies insights from sociolinguistics and psycholinguistics to language teaching and learning. Stylistics analyzes linguistic variations and their appropriateness in literature.The Sound of Language



The Sound of Languagelilianamonserrat
?
The document discusses various aspects of pronunciation in language, including pitch, intonation, individual sounds, spelling differences from sounds, stress, and paralinguistic features. It notes that pitch and intonation convey mood and emotion and are used to signal questions versus statements. Individual sounds combine to form words but spelling does not correlate with sounds. Stress can change word meaning and function. Paralinguistic features include vocal tones and qualities as well as physical gestures that vary between cultures.Vietnam culture



Vietnam cultureYantsuthung Erui
?
Vietnam has a population of 83 million people, with Hanoi as the capital city and Ho Chi Minh City as the largest city. The main ethnic group is Kinh Vietnamese, and the primary religion is Buddhism. Pho, a beef or chicken noodle soup, is Vietnam's national food. Vietnamese weddings traditionally take place in autumn or winter and involve astrological consultations and gift-giving ceremonies. Funerals follow solemn traditions such as washing and dressing the body along with placing rice and coins in the mouth.Repetition Presentation



Repetition Presentationkarinvaknin1809
?
Repetition is defined as repeating something that has already been said or written, or the recurrence of an action or event. The document discusses how repetition can be used effectively in teaching by helping students remember new vocabulary, grammar rules, and dialogues, but it requires using varied methods to avoid becoming boring. Some effective ways to incorporate repetition into class include short reviews at the beginning and end of lessons, using flashcards, and having students repeat dialogues with fewer written prompts over time. While repetition can aid learning if done strategically, it depends on the teacher's implementation and ensuring students confirm their understanding rather than just repeating through rote learning.Multimedia Presentations



Multimedia PresentationsApple Tagum
?
GEC 5 - Purposive Communication Lesson on Multimedia Presentations covering the importance of Multimedia presentations and some authoring tools.The sounds of language



The sounds of languageClau Ar©”valo
?
This document discusses phonetics and the production of speech sounds. It describes how speech sounds are made (articulatory phonetics) and the two basic positions of the vocal cords that determine if a sound is voiced or voiceless. It then explains the place of articulation in the mouth where sounds are produced, such as bilabial, labiodental, alveolar, palatal, and velar. Finally, it discusses the manner of articulation, including stops, fricatives, nasals, liquids, glides, and other categories that describe how the articulators interact and affect airflow.Chinese Language and it's importance



Chinese Language and it's importancePARTNER, BADC, World Bank
?
The document provides an overview of the Chinese language, including its history, classification, and influence. It discusses how:
- Chinese is spoken by over 1 billion people in China and abroad and has influenced neighboring languages through trade and administration.
- The language has evolved over time from Old Chinese to Middle Chinese to Modern Standard Chinese and many regional dialects. Mandarin is now the most common dialect.
- Chinese dialects can be classified into 7 main groups based on phonological changes. Varieties within groups can be mutually unintelligible between regions.
- The Chinese writing system also evolved from early oracle bone script to seal script to clerical script used today.How to speak english fluently



How to speak english fluentlymegacq
?
The document provides tips for speaking English fluently, including encouraging students to speak by asking questions and having discussions, practicing speaking skills everywhere and anytime, not feeling shy, constantly learning new vocabulary, remembering what was learned, watching movies, having fun, and loving the English language. Credit is given to various sources that informed the tips.A History of the English Language



A History of the English LanguageCool
?
This detailed presentation gives a clear overview of the evolution of the English language throughout the ages.
Including the Old English, Middle English, Early Modern, Modern and Late Modern periods, the slideshow covers contextual elements, key features of language, key dates and examples of text for each.
Bullet points and images and a nice layout make the presentation concise and simple, while still containing a lot of information.
This presentation is suitable for English language A-level at A2 level (made for the WJEC A2 exam)
Correction: Old English example text states that the Anglo Saxon Chronicle was written in the 19th century. This is a typo - it was actually the 9th century!Vietnam History And Geography



Vietnam History And GeographyP N
?
Vietnam has a long history of resisting Chinese domination from 111 BC to 938 AD. It was then under French colonial rule from the late 19th century until its independence in 1954 after the First Indochina War. Vietnam has since experienced continued population growth and now has over 86 million people, making it the 14th most populous country globally. Its geography is characterized by tropical lowlands and a long coastline stretching from the Chinese border down through the Mekong Delta.Intonation



Intonationcarlsonadolfo
?
This document discusses intonation, which refers to variations in pitch when speaking. It notes intonation plays a key role in expressing meaning. There are different intonation patterns in English, such as statements with falling pitch and questions with rising pitch. These patterns add conventionalized meanings. The focus of a sentence is typically marked with an intonational accent on the last major word, but this can come earlier to emphasize other words. Questions, statements, commands and exclamations each have distinguishing intonation contours. Intonation patterns differ across languages and can lead to cross-cultural misunderstandings regarding emphasis, finality and other meanings.Linguistics



LinguisticsChristine Joanne Librero Desacado
?
There is evidence that certain linguistic properties are universal across all human languages. Early scholars like Alsted and Kilwardby were interested in discovering a general grammar that described rules common to all languages. More recently, Noam Chomsky and other linguists have proposed that humans possess an innate, biologically-determined "universal grammar" that allows children to easily acquire any language they are exposed to. Sign languages provide clear evidence for linguistic universals, as deaf children learning sign languages progress through the same stages of acquisition as hearing children learning spoken languages, demonstrating the human capacity for language is not dependent on vocalization. The study of language universals continues to be an important area of linguistic research.Phonetics and Phonology MCQS



Phonetics and Phonology MCQSSuhail jamali
?
There are 53 MCQs of Phonetics and Phonology to make learner clear about the topics like Place and manners of articulation, syllables et-ceteraLAOS - PPT



LAOS - PPTCharlene Grace Millano
?
Laos is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia surrounded by China, Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, and Myanmar. The Mekong River flows through the mountainous country. Theravada Buddhism is the dominant religion and strongly influences Lao culture. The Lao people live in extended family groups and value social harmony. Their architecture, arts, and way of life blend Theravada Buddhist traditions with French colonial influences.Clinical phonetics



Clinical phoneticsHazal Haya
?
The document discusses the topic of clinical phonetics. It defines clinical phonetics as the application of phonetics to describe speech differences and disorders. Clinical phonetics involves studying articulation errors, the five ways of scoring speech sounds, and developing therapy plans to address errors. Common articulation errors in children include substitutions, omissions, distortions, and additions of sounds. Speech-language pathologists evaluate clients' articulation and develop intervention plans that use techniques like modeling correct sounds. The document also discusses related topics like phonetics transcription, coarticulation, assimilation, dissimilation, and elision.What is Phonology?



What is Phonology?Mary Acevedo
?
This Power Point Presentation defines terminology and visual tools relevant to pronunciation. It also applies Second Language Acquisition Theory, providing possible explanations of why some ELLs learn English pronunciation better than others. Chinese language



Chinese languagePatricia B©órcena Barreiro
?
Una breve introducci©«n a esta lengua Oriental tan importante hoy en d©¬a para el mundo de los negocios.Chinese religious beliefs



Chinese religious beliefsPadme Amidala
?
In addition to the five main religions, Chinese people have some other traditional folk beliefs. More than 200 million people believe the existence of the ancestorsĪ» souls and worship them, while about 700 million have taken part in the activities to worship their ancestors or related activities. About 150 million people believe in Fengshui theory and 140 million people believe in God of Wealth. Chinese Astrology is very popular and many people think the sign can decide oneĪ»s characters and future. Thus, it is obvious that the traditional folk belief has a wide foundation among the local people. Now, more and more Chinese people are fond of constellation in western culture. In the beginning of a new year, some people will watch some fortune telling programs to see whether they can succeed in the next year and learn how to avoid back luck.
Presentation endangered languages and linguistic diversity



Presentation endangered languages and linguistic diversityZwidzai Chinyowa
?
Endangered languages are those spoken by relatively few people, often elderly, and in few communities, putting their future use in doubt. Many languages are endangered or extinct as their speakers stop passing them on. Linguistic diversity refers to the existence of multiple languages in communities. Zimbabwe has over 20 languages including English, Shona, Ndebele and minority languages like Kalanga and Sotho. Some languages like Tshwao are endangered with under 20 speakers remaining. Cameroon has high linguistic diversity with 248 languages though only French and English are official. The US has over 350 languages led by English and Spanish. Factors threatening linguistic diversity include small speaker populations, lack of government support, and languages shifting to more prestigious optionsEnglish as a germanic language



English as a germanic languagesyrahlilian
?
Although English has borrowed vocabulary from other languages like French and Latin, it remains a Germanic language in its sounds, structure, and other phonological innovations it shares with other Germanic languages. One example is Grimm's Law, which describes correspondences between consonants in different Germanic languages. Additionally, a shift in accent placement in Proto-Germanic caused final unstressed syllables to weaken and disappear over time, making English words relatively short. As a result, even in the Old English period, the language occupied a peripheral position within the West Germanic branch.Vietnam



VietnamFrank Calberg
?
The document summarizes key information about Vietnam. It discusses that 6 major cities account for 40% of Vietnam's sales and lists their populations. It also notes highlights about the cities, including tea tasting in Saigon and hiking near Saigon. The document then discusses Vietnam's ranking high in happiness and having a young population. It covers Vietnam's growth in internet usage and motorbike use. It also summarizes Vietnam's innovation in co-creation, rice and fish farming, and coffee. The document ends with notes on Vietnam's one-party 500-member national assembly and government control of media.Thailand



ThailandBSU-Salome Escalona
?
Thailand is a country located in Southeast Asia. It has a population of over 67 million people and its capital and largest city is Bangkok. Thailand has experienced rapid economic growth in recent decades and has a predominantly Buddhist population with a constitutional monarchy form of government. Tourism is an important part of the Thai economy, although sex tourism and prostitution are prevalent issues. Thai culture has been influenced by its neighbors and Theravada Buddhism plays a central role in society. ppt on phonology



ppt on phonologyGureysha Hassan
?
This document provides an introduction to phonology, which is the study of sound systems in languages. It discusses key concepts like phonemes, allophones, and phonetic elements. The document outlines categories of phonology like vowels and consonants. It describes features of speech like stress, intonation, and rhythm. The document also discusses the importance of phonology for language learning, noting how sounds are linked and how pronunciation impacts spelling. It provides examples of classroom activities to teach pronunciation. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of teachers having strong phonological knowledge to teach students.???? ??? ??????? - Stakeholder Register



???? ??? ??????? - Stakeholder RegisterMohammad Birjandy,PMP
?
????? ???? "??? ???????" ?? ???? ????????? ?????? ????? PMBOKTheories Of The Origins Of Language By Rabia



Theories Of The Origins Of Language By RabiaDr. Cupid Lucid
?
There are several theories about the origins of human language:
1) Onomatopoeic theories propose that early sounds imitated environmental noises like animal calls.
2) Instinctive sound theories suggest language emerged from instinctive noises people made.
3) Symbolism theories postulate language developed from reacting to one's surroundings.
4) Physical need theories claim communal grunts from tasks evolved into chants.
5) Romantic theories argue language originated from the romantic aspects of human life.
Scientific approaches study language formation through glossogenetics and paleontological evidence. Comparisons of ancient human fossils show physiological capacity for speech in early humans.║║ūų╝õ╝▄Įß╣╣▒Ē CHINESE CHARACTER STRUCTURE CHART



║║ūų╝õ╝▄Įß╣╣▒Ē CHINESE CHARACTER STRUCTURE CHARTLEGOO MANDARIN
?
This document is a Chinese character structure table. It provides information on character structures and is managed by KM NETWORK SDN BHD in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. The copyright is reserved.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
The sounds of language



The sounds of languageClau Ar©”valo
?
This document discusses phonetics and the production of speech sounds. It describes how speech sounds are made (articulatory phonetics) and the two basic positions of the vocal cords that determine if a sound is voiced or voiceless. It then explains the place of articulation in the mouth where sounds are produced, such as bilabial, labiodental, alveolar, palatal, and velar. Finally, it discusses the manner of articulation, including stops, fricatives, nasals, liquids, glides, and other categories that describe how the articulators interact and affect airflow.Chinese Language and it's importance



Chinese Language and it's importancePARTNER, BADC, World Bank
?
The document provides an overview of the Chinese language, including its history, classification, and influence. It discusses how:
- Chinese is spoken by over 1 billion people in China and abroad and has influenced neighboring languages through trade and administration.
- The language has evolved over time from Old Chinese to Middle Chinese to Modern Standard Chinese and many regional dialects. Mandarin is now the most common dialect.
- Chinese dialects can be classified into 7 main groups based on phonological changes. Varieties within groups can be mutually unintelligible between regions.
- The Chinese writing system also evolved from early oracle bone script to seal script to clerical script used today.How to speak english fluently



How to speak english fluentlymegacq
?
The document provides tips for speaking English fluently, including encouraging students to speak by asking questions and having discussions, practicing speaking skills everywhere and anytime, not feeling shy, constantly learning new vocabulary, remembering what was learned, watching movies, having fun, and loving the English language. Credit is given to various sources that informed the tips.A History of the English Language



A History of the English LanguageCool
?
This detailed presentation gives a clear overview of the evolution of the English language throughout the ages.
Including the Old English, Middle English, Early Modern, Modern and Late Modern periods, the slideshow covers contextual elements, key features of language, key dates and examples of text for each.
Bullet points and images and a nice layout make the presentation concise and simple, while still containing a lot of information.
This presentation is suitable for English language A-level at A2 level (made for the WJEC A2 exam)
Correction: Old English example text states that the Anglo Saxon Chronicle was written in the 19th century. This is a typo - it was actually the 9th century!Vietnam History And Geography



Vietnam History And GeographyP N
?
Vietnam has a long history of resisting Chinese domination from 111 BC to 938 AD. It was then under French colonial rule from the late 19th century until its independence in 1954 after the First Indochina War. Vietnam has since experienced continued population growth and now has over 86 million people, making it the 14th most populous country globally. Its geography is characterized by tropical lowlands and a long coastline stretching from the Chinese border down through the Mekong Delta.Intonation



Intonationcarlsonadolfo
?
This document discusses intonation, which refers to variations in pitch when speaking. It notes intonation plays a key role in expressing meaning. There are different intonation patterns in English, such as statements with falling pitch and questions with rising pitch. These patterns add conventionalized meanings. The focus of a sentence is typically marked with an intonational accent on the last major word, but this can come earlier to emphasize other words. Questions, statements, commands and exclamations each have distinguishing intonation contours. Intonation patterns differ across languages and can lead to cross-cultural misunderstandings regarding emphasis, finality and other meanings.Linguistics



LinguisticsChristine Joanne Librero Desacado
?
There is evidence that certain linguistic properties are universal across all human languages. Early scholars like Alsted and Kilwardby were interested in discovering a general grammar that described rules common to all languages. More recently, Noam Chomsky and other linguists have proposed that humans possess an innate, biologically-determined "universal grammar" that allows children to easily acquire any language they are exposed to. Sign languages provide clear evidence for linguistic universals, as deaf children learning sign languages progress through the same stages of acquisition as hearing children learning spoken languages, demonstrating the human capacity for language is not dependent on vocalization. The study of language universals continues to be an important area of linguistic research.Phonetics and Phonology MCQS



Phonetics and Phonology MCQSSuhail jamali
?
There are 53 MCQs of Phonetics and Phonology to make learner clear about the topics like Place and manners of articulation, syllables et-ceteraLAOS - PPT



LAOS - PPTCharlene Grace Millano
?
Laos is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia surrounded by China, Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, and Myanmar. The Mekong River flows through the mountainous country. Theravada Buddhism is the dominant religion and strongly influences Lao culture. The Lao people live in extended family groups and value social harmony. Their architecture, arts, and way of life blend Theravada Buddhist traditions with French colonial influences.Clinical phonetics



Clinical phoneticsHazal Haya
?
The document discusses the topic of clinical phonetics. It defines clinical phonetics as the application of phonetics to describe speech differences and disorders. Clinical phonetics involves studying articulation errors, the five ways of scoring speech sounds, and developing therapy plans to address errors. Common articulation errors in children include substitutions, omissions, distortions, and additions of sounds. Speech-language pathologists evaluate clients' articulation and develop intervention plans that use techniques like modeling correct sounds. The document also discusses related topics like phonetics transcription, coarticulation, assimilation, dissimilation, and elision.What is Phonology?



What is Phonology?Mary Acevedo
?
This Power Point Presentation defines terminology and visual tools relevant to pronunciation. It also applies Second Language Acquisition Theory, providing possible explanations of why some ELLs learn English pronunciation better than others. Chinese language



Chinese languagePatricia B©órcena Barreiro
?
Una breve introducci©«n a esta lengua Oriental tan importante hoy en d©¬a para el mundo de los negocios.Chinese religious beliefs



Chinese religious beliefsPadme Amidala
?
In addition to the five main religions, Chinese people have some other traditional folk beliefs. More than 200 million people believe the existence of the ancestorsĪ» souls and worship them, while about 700 million have taken part in the activities to worship their ancestors or related activities. About 150 million people believe in Fengshui theory and 140 million people believe in God of Wealth. Chinese Astrology is very popular and many people think the sign can decide oneĪ»s characters and future. Thus, it is obvious that the traditional folk belief has a wide foundation among the local people. Now, more and more Chinese people are fond of constellation in western culture. In the beginning of a new year, some people will watch some fortune telling programs to see whether they can succeed in the next year and learn how to avoid back luck.
Presentation endangered languages and linguistic diversity



Presentation endangered languages and linguistic diversityZwidzai Chinyowa
?
Endangered languages are those spoken by relatively few people, often elderly, and in few communities, putting their future use in doubt. Many languages are endangered or extinct as their speakers stop passing them on. Linguistic diversity refers to the existence of multiple languages in communities. Zimbabwe has over 20 languages including English, Shona, Ndebele and minority languages like Kalanga and Sotho. Some languages like Tshwao are endangered with under 20 speakers remaining. Cameroon has high linguistic diversity with 248 languages though only French and English are official. The US has over 350 languages led by English and Spanish. Factors threatening linguistic diversity include small speaker populations, lack of government support, and languages shifting to more prestigious optionsEnglish as a germanic language



English as a germanic languagesyrahlilian
?
Although English has borrowed vocabulary from other languages like French and Latin, it remains a Germanic language in its sounds, structure, and other phonological innovations it shares with other Germanic languages. One example is Grimm's Law, which describes correspondences between consonants in different Germanic languages. Additionally, a shift in accent placement in Proto-Germanic caused final unstressed syllables to weaken and disappear over time, making English words relatively short. As a result, even in the Old English period, the language occupied a peripheral position within the West Germanic branch.Vietnam



VietnamFrank Calberg
?
The document summarizes key information about Vietnam. It discusses that 6 major cities account for 40% of Vietnam's sales and lists their populations. It also notes highlights about the cities, including tea tasting in Saigon and hiking near Saigon. The document then discusses Vietnam's ranking high in happiness and having a young population. It covers Vietnam's growth in internet usage and motorbike use. It also summarizes Vietnam's innovation in co-creation, rice and fish farming, and coffee. The document ends with notes on Vietnam's one-party 500-member national assembly and government control of media.Thailand



ThailandBSU-Salome Escalona
?
Thailand is a country located in Southeast Asia. It has a population of over 67 million people and its capital and largest city is Bangkok. Thailand has experienced rapid economic growth in recent decades and has a predominantly Buddhist population with a constitutional monarchy form of government. Tourism is an important part of the Thai economy, although sex tourism and prostitution are prevalent issues. Thai culture has been influenced by its neighbors and Theravada Buddhism plays a central role in society. ppt on phonology



ppt on phonologyGureysha Hassan
?
This document provides an introduction to phonology, which is the study of sound systems in languages. It discusses key concepts like phonemes, allophones, and phonetic elements. The document outlines categories of phonology like vowels and consonants. It describes features of speech like stress, intonation, and rhythm. The document also discusses the importance of phonology for language learning, noting how sounds are linked and how pronunciation impacts spelling. It provides examples of classroom activities to teach pronunciation. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of teachers having strong phonological knowledge to teach students.???? ??? ??????? - Stakeholder Register



???? ??? ??????? - Stakeholder RegisterMohammad Birjandy,PMP
?
????? ???? "??? ???????" ?? ???? ????????? ?????? ????? PMBOKTheories Of The Origins Of Language By Rabia



Theories Of The Origins Of Language By RabiaDr. Cupid Lucid
?
There are several theories about the origins of human language:
1) Onomatopoeic theories propose that early sounds imitated environmental noises like animal calls.
2) Instinctive sound theories suggest language emerged from instinctive noises people made.
3) Symbolism theories postulate language developed from reacting to one's surroundings.
4) Physical need theories claim communal grunts from tasks evolved into chants.
5) Romantic theories argue language originated from the romantic aspects of human life.
Scientific approaches study language formation through glossogenetics and paleontological evidence. Comparisons of ancient human fossils show physiological capacity for speech in early humans.Viewers also liked (20)
║║ūų╝õ╝▄Įß╣╣▒Ē CHINESE CHARACTER STRUCTURE CHART



║║ūų╝õ╝▄Įß╣╣▒Ē CHINESE CHARACTER STRUCTURE CHARTLEGOO MANDARIN
?
This document is a Chinese character structure table. It provides information on character structures and is managed by KM NETWORK SDN BHD in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. The copyright is reserved.[Assignment/Research] handwriting![[Assignment/Research] handwriting](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chinesehandwriting-160724212329-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Assignment/Research] handwriting](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chinesehandwriting-160724212329-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Assignment/Research] handwriting](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chinesehandwriting-160724212329-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
![[Assignment/Research] handwriting](https://cdn.slidesharecdn.com/ss_thumbnails/chinesehandwriting-160724212329-thumbnail.jpg?width=560&fit=bounds)
[Assignment/Research] handwritingMimi Mokhtar
?
This document provides an overview of the history and evolution of Chinese handwriting and characters. It discusses how Chinese writing began with oracle bones around 1500 BC and evolved through different scripts over thousands of years, including bronze inscriptions, small seal characters, official script, regular script, cursive writing, and freehand cursive. It also describes how Chinese characters are formed and structured, as well as the standardization and simplification of characters that occurred in the 1950s-60s in mainland China.╚²╩«┴∙╝Ų 03 ĮĶĄČ╔▒╚╦ kill with a borrowed sword Č■╠ę╔▒╚²╩┐



╚²╩«┴∙╝Ų 03 ĮĶĄČ╔▒╚╦ kill with a borrowed sword Č■╠ę╔▒╚²╩┐LEGOO MANDARIN
?
Yan Ying advises the king of Qi to remove three generals after they disrespect him in court. Yan Ying tells the king he has a plan to use two peaches to kill the three generals without direct confrontation. His plan involves awarding the peaches based on military achievements, causing the generals to argue and kill each other. With this "borrowed sword" approach, Yan Ying is able to eliminate the threat posed by the generals through manipulation rather than force.▒╩╦│╣µį“Š┘└²ĮŌ╦Ą Rules of Chinese Characters Stroke order 



▒╩╦│╣µį“Š┘└²ĮŌ╦Ą Rules of Chinese Characters Stroke order LEGOO MANDARIN
?
This document outlines 8 basic rules for Chinese stroke order and provides examples. It discusses writing characters from left to right, top to bottom, with horizontal strokes preceding vertical ones. It also covers writing certain structures like dots, enclosing shapes, and multi-sided characters. The document aims to teach proper stroke ordering in writing Chinese characters.╩ū20Ė÷▓┐╩ū ║║ūų▒╩╗Ł├¹│Ų▒Ē CHINESE CHARACTER RADICALS-FIRST TWENTY, MOST USED OUT OF 104



╩ū20Ė÷▓┐╩ū ║║ūų▒╩╗Ł├¹│Ų▒Ē CHINESE CHARACTER RADICALS-FIRST TWENTY, MOST USED OUT OF 104LEGOO MANDARIN
?
This document lists the top 20 most frequently used Chinese characters in texts based on their frequency of appearance. The characters are listed along with their pinyin and English translation. It shows that the top 3 most frequent characters that appear in the first 10% of texts are "water", "hand", and "mouth". The top 5 characters that appear in the first 20% of texts are those 3 plus "wood, forest" and "grass".Xiao yu 2 A Ąńūė┐╬▒Š CHINA Primary Year 2A ųą╣·ąĪč¦Č■─Ļ╝Č╔Ž 



Xiao yu 2 A Ąńūė┐╬▒Š CHINA Primary Year 2A ųą╣·ąĪč¦Č■─Ļ╝Č╔Ž LEGOO MANDARIN
?
Xiao yu 2 A Ąńūė┐╬▒Š CHINA Primary Year 2A ųą╣·ąĪč¦Č■─Ļ╝Č╔ŽChinese writing 



Chinese writing LAUSD
?
The document provides an overview of Chinese writing and language. It discusses oracle bones as an early form of Chinese writing dating back thousands of years. It also summarizes that Chinese uses characters rather than an alphabet, with over 60,000 characters in the writing system. Finally, it notes that simplified Chinese uses simpler versions of traditional characters, as seen on some early oracle bones.Introduction about Chinese calligraphy 



Introduction about Chinese calligraphy Darpan Agarwal (░▓┤’╚)
?
Chinese calligraphy originated over 4,600 years ago and is considered an art form that reflects personality and thinking styles. There are various calligraphy styles that emerged over dynasties including seal script, clerical script, running script, regular script, and cursive script. The four treasures of calligraphy include the brush, inkstick, paper, and inkstone. Calligraphy is highly respected in Chinese culture and is one of the basic skills of Chinese literati along with painting, music, and board games. It can take over 20 years to become a master calligrapher requiring extensive practice and study of classical texts.Chinese Calligraphy



Chinese CalligraphyRandi Burford
?
Chinese calligraphy uses four traditional tools: brushes, ink sticks, ink stones, and paper. Brushes are made from animal hair and come in hard, soft, or mixed tips. Ink sticks are made from pine, oil, and lacquer and are used to make ink by grinding on an ink stone. Paper was invented in China and various papermaking techniques were developed. Proper technique involves correct posture, knowledge of tools, control of the brush, rhythmic flow of strokes, and balanced lines. Stroke sequence follows rules such as starting at the top and moving downward, starting on the left and moving right, and completing inner parts before outer.Chinese Calligraphy By Caroline



Chinese Calligraphy By Carolinecaroline01pd2014
?
1) Calligraphy originated in China over 4,600 years ago, starting as paintings before evolving into characters. It uses specialized tools like ink, paper, brushes, and ink sticks.
2) Wang Xian Zhi was a famous calligrapher born in 303 AD who is known for his piece "Lan Ting Xu". There are different styles of calligraphy like seal script and official script.
3) Painting and calligraphy are closely related, using similar techniques. Famous painter Qi Bai Shi taught himself despite coming from a poor family and focused on paintings of animals and scenery. Ancient Chinese painters took a more serious approach than some modern ones.Modern Chinese Calligraphy



Modern Chinese CalligraphyKim A Munson
?
This presentation accompanied an art history lecture about the evolution of calligraphy in China, from ancient tradition to post-modern applications.Applied writing example for ib sat ii gcse etc with cover



Applied writing example for ib sat ii gcse etc with coverLEGOO MANDARIN
?
The document provides information about applied writing formats for examinations such as GCSE, IB, SAT II, and A levels. It discusses 14 examples of different writing styles. It also provides contact information for Lego Mandarin, an online education provider that offers live courses for exams like HSK, GCSE, IB, and SAT.╩ū20Ė÷▓┐╩ū ║║ūų▒╩╗Ł├¹│Ų▒Ē CHINESE CHARACTER RADICALS-FIRST TWENTY, MOST USED OUT OF 104



╩ū20Ė÷▓┐╩ū ║║ūų▒╩╗Ł├¹│Ų▒Ē CHINESE CHARACTER RADICALS-FIRST TWENTY, MOST USED OUT OF 104LEGOO MANDARIN
?
Recently uploaded (8)
Faizane Namaz Urdu Book.....contact No +91- 9322666509 / 8451030343



Faizane Namaz Urdu Book.....contact No +91- 9322666509 / 8451030343DUFM Educational & Charitable Trust
?
Faizane Namaz Urdu Book.....contact No +91- 9322666509 / 84510303432025 ISIZULU HL INTERMEDIATE PHASE MULTIGRADING CLASSROOMS SUPPORT DOCUMENT[1...



2025 ISIZULU HL INTERMEDIATE PHASE MULTIGRADING CLASSROOMS SUPPORT DOCUMENT[1...PhindileNgubane
?
Isizulu HLBRENDA (1).pdf tranajo de tecnooilogisa



BRENDA (1).pdf tranajo de tecnooilogisaisabelisaza5
?
trabajo de excel de brenda marian ceballos suarez Emotional Intelligence in Yoga philosophy



Emotional Intelligence in Yoga philosophyRashmiTiwari72
?
Yoga philosophy emphasizes self-awareness, self-regulation, motivation and empathy, which are key components of emotional intelligence. Yoga practices like chitta-prasadana, kriyayoga and astangayoga help you develop these skills. Faizane Namaz Urdu Book.....contact No +91- 9322666509 / 8451030343



Faizane Namaz Urdu Book.....contact No +91- 9322666509 / 8451030343DUFM Educational & Charitable Trust
?
Chinese alphabet
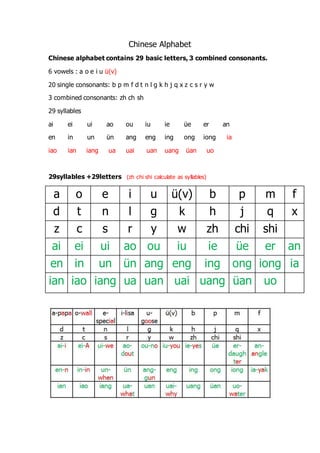
- 1. Chinese Alphabet Chinese alphabet contains 29 basic letters, 3 combined consonants. 6 vowels : a o e i u ©╣(v) 20 single consonants: b p m f d t n l g k h j q x z c s r y w 3 combined consonants: zh ch sh 29 syllables ai ei ui ao ou iu ie ©╣e er an en in un ©╣n ang eng ing ong iong ia iao ian iang ua uai uan uang ©╣an uo 29syllables +29letters (zh chi shi calculate as syllables) a o e i u ©╣(v) b p m f d t n l g k h j q x z c s r y w zh chi shi ai ei ui ao ou iu ie ©╣e er an en in un ©╣n ang eng ing ong iong ia ian iao iang ua uan uai uang ©╣an uo











