Chlorine -minerals and trace elements
- 1. Clinical Biochemistry SIMS-305 Dr. Ali Raza Senior Lecturer Centre for Human Genetics and Molecular Medicine (CHGMM), Sindh Institute of Medical Sciences (SIMS), SIUT. 1
- 2. CHLORINE 2
- 3. CHLORINE ? Sodium Chloride (NaCl) in diet Absorption: a) Small intestines. ? The mechanism of chloride depend on an exchange process with the HCO©C3 , accompanying sodium exchange for a hydrogen ion. b) Renal: (99 % )Cl©Cis reabsorbed by renal tubules mainly in ? Proximal tubule (60-70%), ? loop of Henle (20-25%) ? Collecting duct (10-15%) 3
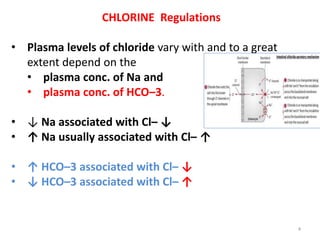
- 4. CHLORINE Regulations ? Plasma levels of chloride vary with and to a great extent depend on the ? plasma conc. of Na and ? plasma conc. of HCO©C3. ? Ī² Na associated with Cl©C Ī² ? Ī³ Na usually associated with Cl©C Ī³ ? Ī³ HCO©C3 associated with Cl©C Ī² ? Ī² HCO©C3 associated with Cl©C Ī³ 4