Cholinergic blocking agents (а№ҖаёһаёҲаёҲаёІаёҒа№ғаёҲаё«аёЎаёӯаёўаёІа№Ҷа№Ҷа№Ҷ)
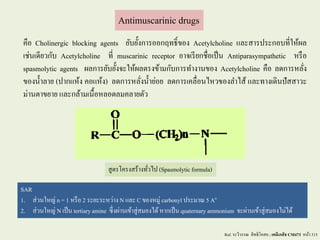
- 1. Antimuscarinic drugs аё„аё·аёӯ Cholinergic blocking agents аёўаёұаёҡаёўаёұа№үаёҮаёҒаёІаёЈаёӯаёӯаёҒаёӨаё—аёҳаёҙа№ҢаёӮаёӯаёҮ Acetylcholine а№ҒаёҘаё°аёӘаёІаёЈаёӣаёЈаё°аёҒаёӯаёҡаё—аёөа№Ҳа№ғаё«а№үаёңаёҘ а№ҖаёҠа№Ҳаёҷа№Җаё”аёөаёўаё§аёҒаёұаёҡ Acetylcholine аё—аёөа№Ҳ muscarinic receptor аёӯаёІаёҲа№ҖаёЈаёөаёўаёҒаёҠаё·а№Ҳаёӯа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷ Antiparasympathetic аё«аёЈаё·аёӯ spasmolytic agents аёңаёҘаёҒаёІаёЈаёўаёұаёҡаёўаёұа№үаёҮаёҲаё°а№ғаё«а№үаёңаёҘаё•аёЈаёҮаёӮа№үаёІаёЎаёҒаёұаёҡаёҒаёІаёЈаё—аёІаёҮаёІаёҷаёӮаёӯаёҮ Acetylcholine аё„аё·аёӯ аёҘаё”аёҒаёІаёЈаё«аёҘаёұа№ҲаёҮ аёӮаёӯаёҮаёҷа№үаёІаёҘаёІаёў (аёӣаёІаёҒа№Ғаё«а№үаёҮ аё„аёӯа№Ғаё«а№үаёҮ) аёҘаё”аёҒаёІаёЈаё«аёҘаёұа№ҲаёҮаёҷа№үаёІаёўа№Ҳаёӯаёў аёҘаё”аёҒаёІаёЈа№Җаё„аёҘаё·а№ҲаёӯаёҷไหวаёӮаёӯаёҮаёҘาไаёӘа№ү а№ҒаёҘаё°аё—аёІаёҮа№Җаё”аёҙаёҷаёӣаёұаёӘаёӘаёІаё§аё° аёЎа№ҲаёІаёҷаё•аёІаёӮаёўаёІаёў а№ҒаёҘаё°аёҒаёҘа№үаёІаёЎа№Җаёҷаё·а№үаёӯаё«аёҘаёӯаё”аёҘаёЎаё„аёҘаёІаёўаё•аёұаё§ SAR 1. аёӘа№Ҳаё§аёҷа№ғаё«аёҚа№Ҳ n = 1 аё«аёЈаё·аёӯ 2 аёЈаё°аёўаё°аёЈаё°аё«аё§а№ҲаёІаёҮ N а№ҒаёҘаё° C аёӮаёӯаёҮаё«аёЎаё№а№Ҳ carbonyl аёӣаёЈаё°аёЎаёІаё“ 5 Ao 2. аёӘа№Ҳаё§аёҷа№ғаё«аёҚа№Ҳ N а№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷ tertiaryamine аёӢаё¶а№ҲаёҮаёңа№ҲаёІаёҷа№ҖаёӮа№үаёІаёӘаё№а№ҲаёӘаёЎаёӯаёҮไดа№үаё«аёІаёҒа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷ quaternary ammonium аёҲаё°аёңа№ҲаёІаёҷа№ҖаёӮа№үаёІаёӘаё№а№ҲаёӘаёЎаёӯаёҮไมа№Ҳไดа№ү Ref. аёЈаё°аё§аёөаё§аёЈаёЈаё“ аёӘаёҙаё—аёҳаёҙа№ӮаёӯаёӘаё– ; а№Җаё„аёЎаёөа№Җаё аёӘаёұаёҠ CM473 аё«аёҷа№үаёІ 315 аёӘаё№аё•аёЈа№Ӯаё„аёЈаёҮаёӘаёЈа№үаёІаёҮаё—аёұа№Ҳวไаёӣ (Spasmolyticformula)
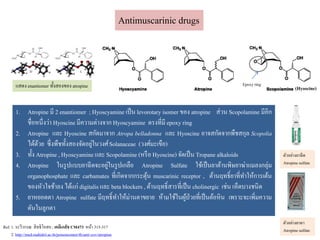
- 2. Antimuscarinic drugs 1. Atropine аёЎаёө 2 enantiomer ; Hyoscyamine а№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷ levorotary isomer аёӮаёӯаёҮ atropine аёӘа№Ҳаё§аёҷ Scopolamine аёЎаёөаёӯаёөаёҒ аёҠаё·а№Ҳаёӯаё«аёҷаё¶а№ҲаёҮаё§а№ҲаёІ Hyoscine аёЎаёөаё„аё§аёІаёЎаё•а№ҲаёІаёҮаёҲаёІаёҒ Hyoscyamine аё•аёЈаёҮаё—аёөа№ҲаёЎаёө epoxy ring 2. Atropine а№ҒаёҘаё° Hyoscine аёӘаёҒаёұаё”аёЎаёІаёҲаёІаёҒ Atropa belladonna а№ҒаёҘаё° Hyoscine аёӯаёІаёҲаёӘаёҒаёұаё”аёҲаёІаёҒаёһаё·аёҠаёӘаёҒаёёаёҘ Scopolia ไดа№үаё”а№үаё§аёў аёӢаё¶а№ҲаёҮаёһаё·аёҠаё—аёұа№үаёҮаёӘаёӯаёҮаёҲаёұаё”аёӯаёўаё№а№Ҳа№ғаёҷаё§аёҮаёЁа№ҢSolanaceae (аё§аёҮаёЁа№ҢаёЎаё°а№ҖаёӮаё·аёӯ) 3. аё—аёұа№үаёҮ Atropine , Hyoscyamine а№ҒаёҘаё° Scopolamine (аё«аёЈаё·аёӯ Hyoscine) аёҲаёұаё”а№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷ Tropane alkaloids 4. Atropine а№ғаёҷаёЈаё№аёӣа№ҒаёҡаёҡаёўаёІаёүаёөаё”аёҲаё°аёӯаёўаё№а№Ҳа№ғаёҷаёЈаё№аёӣа№ҖаёҒаёҘаё·аёӯ Atropine Sulfate а№ғаёҠа№үа№Җаёӣа№ҮаёҷаёўаёІаё•а№үаёІаёҷаёһаёҙаё©аёўаёІаёҶа№ҲаёІа№ҒаёЎаёҘаёҮаёҒаёҘаёёа№ҲаёЎ organophosphate а№ҒаёҘаё° carbamates аё—аёөа№Ҳа№ҖаёҒаёҙаё”аёҲаёІаёҒаёҒаёЈаё°аё•аёёа№үаёҷ muscarinic receptor , аё•а№үаёІаёҷаёӨаё—аёҳаёҙа№ҢаёўаёІаё—аёөа№Ҳаё—аёІа№ғаё«а№үаёҒаёІаёЈа№Җаё•а№үаёҷ аёӮаёӯаёҮаё«аёұаё§а№ғаёҲаёҠа№үаёІаёҘаёҮ ไดа№үа№ҒаёҒа№Ҳ digitalisа№ҒаёҘаё° beta blockers , аё•а№үаёІаёҷаёӨаё—аёҳаёҙа№ҢаёӘаёІаёЈаё—аёөа№Ҳа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷ cholinergic а№ҖаёҠа№Ҳаёҷ а№Җаё«а№Үаё”аёҡаёІаёҮаёҠаёҷаёҙаё” 5. аёўаёІаё«аёўаёӯаё”аё•аёІ Atropine sulfate аёЎаёөаёӨаё—аёҳаёҙа№Ңаё—аёІа№ғаё«а№үаёЎа№ҲаёІаёҷаё•аёІаёӮаёўаёІаёў аё«а№үаёІаёЎа№ғаёҠа№үа№ғаёҷаёңаё№а№үаёӣа№Ҳаё§аёўаё—аёөа№Ҳа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷаё•а№үаёӯаё«аёҙаёҷ а№ҖаёһаёЈаёІаё°аёҲаё°а№Җаёһаёҙа№ҲаёЎаё„аё§аёІаёЎ аё”аёұаёҷа№ғаёҷаёҘаё№аёҒаё•аёІ а№ҒаёӘаё”аёҮ enantiomer аё—аёұа№үаёҮаёӘаёӯаёҮаёӮаёӯаёҮ atropine Epoxyring (Hyoscine) Ref. 1. аёЈаё°аё§аёөаё§аёЈаёЈаё“ аёӘаёҙаё—аёҳаёҙа№ӮаёӯаёӘаё–; а№Җаё„аёЎаёөа№Җаё аёӘаёұаёҠ CM473 аё«аёҷа№үаёІ 315-317 2. http://med.mahidol.ac.th/poisoncenter/th/anti-cov/atropine аё•аёұаё§аёӯаёўа№ҲаёІаёҮаёўаёІаёүаёөаё” Atropine sulfate аё•аёұаё§аёӯаёўа№ҲаёІаёҮаёўаёІаё•аёІ Atropine sulfate
- 3. http://www.phargarden.com/main.php?action=viewpage&pid=105 аёҠаё·а№ҲаёӯаёӘаёЎаёёаёҷไаёһаёЈ аёҘаёІа№ӮаёһаёҮ аёҠаё·а№Ҳаёӯаёӯаё·а№Ҳаёҷа№Ҷ аёҘаёІа№ӮаёһаёҮаёӮаёІаё§ аёЎаё°а№ҖаёӮаё·аёӯаёҡа№үаёІ аёҘаёІа№ӮаёһаёҮаёҒаёІаёӘаёҘаёұаёҒ аёҒаёІаёӘаёҘаёұаёҒ аёЎаё°а№ҖаёӮаё·аёӯаёҡа№үаёІаё”аёӯаёҒаё”аёІ аёҠаё·а№Ҳаёӯаё§аёҙаё—аёўаёІаёЁаёІаёӘаё•аёЈа№Ң Datura metel L. var. fastuosa (Bernh.) Danert. аёҠаё·а№Ҳаёӯаёһа№үаёӯаёҮ Datura fastuosa L. аёҠаё·а№Ҳаёӯаё§аёҮаёЁа№ҢSolanaceae аёӘаёЈаёЈаёһаё„аёёаё“: ตำรำยำไทย а№ғаёҠа№ү а№ғаёҡ аёЈаёӘаёӮаёЎа№ҖаёЎаёІа№Җаёҡаё·а№Ҳаёӯ аё•аёІаёһаёӯаёҒаёқаёө аё—аёІа№ғаё«а№үаёўаёёаёҡ а№ҒаёҒа№үаёӘаё°аёӯаё¶аёҒа№ғаёҷไаёӮа№үаёһаёҙษไаёӮа№үаёҒаёІаё¬ аёўаёІаёһаёӯаёҒа№ҒаёҒа№үа№ӮаёЈаё„аёңаёҙаё§аё«аёҷаёұаёҮаёҒаёҘаёІаёҒа№ҖаёҒаёҘаё·а№үаёӯаёҷ а№ҒаёҒа№үа№ҒаёңаёҘа№ҖаёЈаё·а№үаёӯаёЈаёұаёҮ а№ҒаёҒа№үаёһаёҙаё©аёӘаёұаё•аё§а№ҢаёҒаёұаё”аё•а№Ҳаёӯаёў а№ҒаёҒа№үаёһаёҙаё©аёқаёө а№ҒаёҒа№үаёӣаё§аё”а№ҒаёӘаёҡаёҡаё§аёЎаё—аёөа№Ҳа№ҒаёңаёҘ а№ҒаёҒа№үаёӣаё§аё”аёҡаё§аёЎ аёӯаёұаёҒа№ҖаёӘаёҡ а№ғаёҠа№үаё—аёІа№ҒаёҒа№үаёӯаёұаёҒа№ҖаёӘаёҡа№Җаё•а№үаёІаёҷаёЎ аёЎаёөаёӨаё—аёҳаёҙа№Ңаё„аёҘаёІаёўаёҒаёҘа№үаёІаёЎа№Җаёҷаё·а№үаёӯа№ҖаёЈаёөаёўаёҡ а№ҒаёҒа№үаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёӣаё§аё”а№ҖаёҒаёЈа№ҮаёҮаё—а№үаёӯаёҮ а№ҒаёҘаё°аёӮаёўаёІаёўаё«аёҘаёӯаё”аёҘаёЎ а№ҒаёҒа№үаё«аёӯаёҡ аё«аё·аё” аёЎаёөаёӨаё—аёҳаёҙа№ҢаёҒаё”аёӘаёЎаёӯаёҮ а№ҒаёҒа№үаёӯаёІа№ҖаёҲаёөаёўаёҷаёҲаёІаёҒа№ҖаёЎаёІаёЈаё–а№ҖаёЎаёІа№ҖаёЈаё·аёӯ а№Ғаё•а№ҲаёЎаёөаёӯаёіаёҒаёіаёЈаёӮа№үаёіаёҮа№Җаё„аёөаёўаёҮаё„аё·аёӯ аёӣаёІаёҒаё„аёӯа№Ғаё«а№үаёҮ а№ғаёҡа№ҒаёҘаё°аёўаёӯаё” аёЎаёөаёӯаёұаёҘаё„аёІаёҘаёӯаёўаё”а№Ң аё—аёөа№ҲаёЎаёөаёӨаё—аёҳаёҙа№Ңаё„аёҘаёІаёўаёҒаёҘа№үаёІаёЎа№Җаёҷаё·а№үаёӯа№ҖаёЈаёөаёўаёҡ а№ҒаёҒа№үаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёӣаё§аё” аё—а№үаёӯаёҮа№ҖаёҒаёЈа№ҮаёҮ а№ҒаёҘаё°аёӮаёўаёІаёўаё«аёҘаёӯаё”аёҘаёЎ аё”аёӯаёҒ аёЈаёӘа№ҖаёЎаёІа№Җаёҡаё·а№Ҳаёӯ аё•аёІаёҒа№Ғаё«а№үаёҮаёңаёӘаёЎаёўаёІа№ҖаёӘа№үаёҷаёӘаё№аёҡ а№ҒаёҒа№үаё«аёӯаёҡаё«аё·аё” а№ӮаёһаёЈаёҮаёҲаёЎаё№аёҒаёӯаёұаёҒа№ҖаёӘаёҡ а№ҒаёҒа№үаёЈаёҙаё”аёӘаёөаё”аё§аёҮаёҲаёЎаё№аёҒ аёЎаёөаёӘаёІаёЈа№ҒаёҒа№үаёҒаёІаёЈаё•аёөаёҡаё•аёұаё§аёӮаёӯаёҮаё«аёҘаёӯаё”аёҘаёЎ а№ҖаёЎаёҘа№Үаё” аёЈаёӘа№ҖаёЎаёІа№Җаёҡаё·а№Ҳаёӯ аё„аёұа№Ҳаё§а№ғаё«а№үаё«аёЎаё”аёҷа№үаёІаёЎаёұаёҷ аёӣаёЈаёёаёҮаёўаёІа№ҒаёҒа№үไаёӮа№үаёһаёҙаё© ไаёӮа№үаёҒаёЈаё°аёӘаёұаёҡаёҒаёЈаё°аёӘа№ҲаёІаёў аёҷа№үаёіаёЎаёұаёҷаёҲаёіаёҒа№ҖаёЎаёҘа№Үаё” аёЈаёӘа№ҖаёЎаёІа№Җаёҡаё·а№Ҳаёӯ аёӣаёЈаёёаёҮаёўаёІа№ғаёӘа№Ҳа№ҒаёңаёҘ а№ҒаёҒа№үаёҒаёҘаёІаёҒа№ҖаёҒаёҘаё·а№үаёӯаёҷ аёңаё·а№Ҳаёҷаё„аёұаёҷ аё«аёҙаё”а№Җаё«аёІ а№ҖаёЎаёҘа№Үаё”аё—аёІаёҡаёЈаёЈа№Җаё—аёІ аёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёӣаё§аё”а№ҖаёЎаё·а№Ҳаёӯаёў аёӮаёұаё”аёўаёӯаёҒ а№Ӯаё”аёўаёҷаёІа№ҖаёЎаёҘа№Үаё” 30 аёҒаёЈаёұаёЎ аё—аёёаёҡаёһаёӯа№Ғаё«аёҘаёҒ а№ҒаёҘа№үаё§а№ҒаёҠа№ҲаёҒаёұаёҡаёҷа№үаёІаёЎаёұаёҷаёһаё·аёҠ аё—аёІаё•аёЈаёҮаёҡаёЈаёҙа№Җаё§аё“аё—аёөа№Ҳаёӣаё§аё”а№ҖаёЎаё·а№Ҳаёӯаёў аё«аёЈаё·аёӯаёӮаёұаё”аёўаёӯаёҒ аёҲаё°аёҠа№Ҳаё§аёўаёҡаёЈаёЈа№Җаё—аёІаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёӣаё§аё” а№Ғаё•а№Ҳаё•а№үаёӯаёҮ а№ҒаёҠа№Ҳа№Җаёӯาไวа№үаёӣаёЈаё°аёЎаёІаё“ 7 аё§аёұаёҷ аёҲаё¶аёҮаёҲаё°аёҷаёІаёЎаёІа№ғаёҠа№үไดа№ү а№ҒаёҘаё°а№ғаёҠа№үа№ғаёӘа№Ҳаёҹаёұаёҷаё—аёөа№Ҳа№Җаёӣа№ҮаёҷаёЈаё№ аёҠа№Ҳаё§аёўаёҡаёЈаёЈа№Җаё—аёІаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёӣวดไดа№ү аёЈаёіаёҒ аёЈаёӘа№ҖаёЎаёІа№Җаёҡаё·а№Ҳаёӯаё«аё§аёІаёҷ аёқаёҷаё—аёІаёһаёҙаё©аёЈа№үаёӯаёҷ аё”аёұаёҡаёһаёҙаё©аёқаёө а№ҒаёҒа№үаёӣаё§аё”аёҡаё§аёЎа№ҒаёҒа№ү аёӯаёұаёҒа№ҖаёӘаёҡ аёӘаёёаёЎа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷаё–а№ҲаёІаёҷаёӣаёЈаёёаёҮаёўаёІаёЈаёұаёҡаёӣаёЈаё°аё—аёІаёҷ а№ҒаёҒа№үไаёӮа№үаёһаёҙаё© ไаёӮа№үаёҒаёІаё¬ ไаёӮа№үа№ҖаёӢаё·а№ҲаёӯаёҮаёӢаё¶аёЎ а№ҖаёӣаёҘаё·аёӯаёҒаёңаёҘ аёЈаёӘа№ҖаёЎаёІа№Җаёҡаё·а№Ҳаёӯ а№ҒаёҒа№үаёЎаё°а№ҖаёЈа№ҮаёҮ аё„аёёаё”аё—аё°аёЈаёІаё” а№ҒаёҒа№үаёҒаёЈаё°аё©аёұаёў а№ҒаёҒа№үаёЈаёҙаё”аёӘаёөаё”аё§аёҮ аё—аёёаёҒаёӘа№Ҳаё§аёҷ аёЎаёөаёӨаё—аёҳаёҙа№Ңа№Җаёӣа№ҮаёҷаёўаёІ а№ҖаёӘаёһаё•аёҙаё”аёЈаё°аёҮаёұаёҡаёӣаё§аё” а№ҒаёҒа№үаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈа№ҖаёҒаёЈа№ҮаёҮ аё—аёұа№үаёҮаё•а№үаёҷ а№Җаёӣа№ҮаёҷаёўаёІаёЈаё°аёҮаёұаёҡаёӣаё§аё” а№ҒаёҒа№үаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈа№ҖаёҒаёЈа№ҮаёҮ аёҷа№үаёІаё„аёұа№үаёҷаёҲаёІаёҒаё•а№үаёҷа№ҖаёЎаё·а№Ҳаёӯаё«аёўаёӯаё”аё•аёІаёҲаё°аё—аёІа№ғаё«а№үаёЎа№ҲаёІаёҷаё•аёІаёӮаёўаёІаёў аёӮа№үаёӯаё„аё§аёЈаёЈаё°аё§аёұаёҮ аёңаёҘа№ҒаёҘаё°а№ҖаёЎаёҘа№Үаё”а№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷаёһаёҙаё© аёЎаёөаёӘаёІаёЈаёӯаёұаёҘаё„аёІаёҘаёӯаёўаё”а№Ң hyoscine, hyoscyamine аё–а№үаёІаёҒаёҙаёҷа№ҖаёӮа№үาไаёӣаё—аёІа№ғаё«а№үа№ҖаёҒаёҙаё”аёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈа№ҖаёЈаёҙа№ҲаёЎаё•а№үаёҷаё„аё·аёӯаёӘаёІаёўаё•аёІаёһаёЈа№ҲаёІаёЎаёұаё§ аёӣаёІаёҒа№Ғаё«а№үаёҮ аёҒаёЈаё°аё«аёІаёўаёҷа№үаёІаёЎаёІаёҒ аёЎа№ҲаёІаёҷаё•аёІаёӮаёўаёІаёўа№ҒаёҘаё°аёӣаёЈаёұаёҡаёӘายตาไมа№Ҳไดа№үаё—аёІа№ғаё«а№үตาไมа№ҲаёӘаё№а№үа№ҒаёӘаёҮ аёңаёҙаё§аё«аёҷаёұаёҮаёЈа№үаёӯаёҷа№Ғаё”аёҮа№ҒаёҘаё°аёЎаёөаёңаё·а№Ҳаёҷа№Ғаё”аёҮаё•аёІаёЎа№ғаёҡаё«аёҷа№үаёІ аё„аёӯа№ҒаёҘаё°аё«аёҷа№үаёІаёӯаёҒ ไаёӮа№үаёӮаё¶а№үаёҷаёӘаё№аёҮ аёӣаё§аё”аёЁаёөаёЈаё©аё° аё„аё§аёІаёЎаёЈаё№а№үаёӘаё¶аёҒаёӘаёұаёҡаёӘаёҷ аёҒаёІаёЈ аё—аёІаёҮаёІаёҷаёӮаёӯаёҮаёҒаёҘа№үаёІаёЎа№Җаёҷаё·а№үаёӯаёңаёҙаё”аёӣаёҒаё•аёҙ аё–а№үาไดа№үаёЈаёұаёҡаёЎаёІаёҒ аё§аёҙаёҒаёҘаёҲаёЈаёҙаё• а№Җаёһа№үаёӯаё„аёҘаёұа№ҲаёҮ а№Җаё„аёҘаёҙа№үаёЎаёқаёұаёҷ аёЎаёөаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаё—аёІаёҮаёҲаёҙаё•а№ҒаёҘаё°аёӣаёЈаё°аёӘаёІаё— аё•аё·а№Ҳаёҷа№Җаё•а№үаёҷ аё•аёІа№ҒаёӮа№ҮаёҮ аё«аёІаёўа№ғаёҲไมа№ҲаёӘаё°аё”аё§аёҒ аёһูดไมа№ҲаёӯаёӯаёҒ аё«аёІаёўа№ғаёҲаёҠа№үаёІаёҘаёҮ аё•аёұаё§а№ҖаёӮаёөаёўаё§ а№ҖаёЎаё·а№Ҳаёӯа№ҒаёҒа№үаёһаёҙаё©аё«аёІаёўа№ҒаёҘа№үаё§ аёҲаё°аёЎаёөаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаё§аёҙаёҒаёҘаёҲаёЈаёҙаё•аё•аёҙаё”аёӯаёўаё№а№Ҳаё•аёҘаёӯดไаёӣ аёЈаёұаёҒษาไมа№Ҳаё„а№Ҳаёӯаёўаё«аёІаёў Herbal antimuscarinic drugs
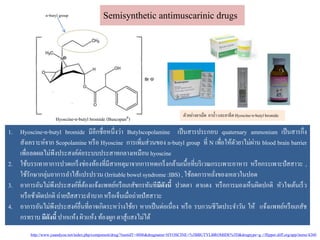
- 5. Hyoscine-n-butyl bromide (BuscopanR) n-butyl group Semisynthetic antimuscarinic drugs 1. Hyoscine-n-butyl bromide аёЎаёөаёӯаёөаёҒаёҠаё·а№Ҳаёӯаё«аёҷаё¶а№ҲаёҮаё§а№ҲаёІ Butylscopolamine а№Җаёӣа№ҮаёҷаёӘаёІаёЈаёӣаёЈаё°аёҒаёӯаёҡ quaternary ammonium а№Җаёӣа№ҮаёҷаёӘаёІаёЈаёҒаё¶а№ҲаёҮ аёӘаёұаёҮа№Җаё„аёЈаёІаё°аё«а№ҢаёҲаёІаёҒ Scopolamine аё«аёЈаё·аёӯ Hyoscine аёҒаёІаёЈа№Җаёһаёҙа№ҲаёЎаёӘа№Ҳаё§аёҷаёӮаёӯаёҮ n-butyl group аё—аёөа№Ҳ N а№Җаёһаё·а№Ҳаёӯа№ғаё«а№үаё•аёұวยาไมа№Ҳаёңа№ҲаёІаёҷ blood brain barrier а№Җаёһаё·а№ҲаёӯаёҘаё”аёңаёҘไมа№Ҳаёһаё¶аёҮаёӣаёЈаё°аёӘаёҮаё„а№Ңаё•а№ҲаёӯаёЈаё°аёҡаёҡаёӣаёЈаё°аёӘаёІаё—аёҒаёҘаёІаёҮа№Җаё«аёЎаё·аёӯаёҷ hyoscine 2. а№ғаёҠа№үаёҡаёЈаёЈа№Җаё—аёІаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёӣаё§аё”а№ҖаёҒаёЈа№ҮаёҮаёҠа№ҲаёӯаёҮаё—а№үаёӯаёҮаё—аёөа№ҲаёЎаёөаёӘаёІа№Җаё«аё•аёёаёЎаёІаёҲаёІаёҒаёҒаёІаёЈаё«аё”а№ҖаёҒаёЈа№ҮаёҮаёҒаёҘа№үаёІаёЎа№Җаёҷаё·а№үаёӯаё—аёөа№ҲаёҡаёЈаёҙа№Җаё§аё“аёҒаёЈаё°а№ҖаёһаёІаё°аёӯаёІаё«аёІаёЈ аё«аёЈаё·аёӯаёҒаёЈаё°а№ҖаёһаёІаё°аёӣаёұаёӘаёӘаёІаё§аё° , а№ғаёҠа№үаёЈаёұаёҒаё©аёІаёҒаёҘаёёа№ҲаёЎаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёҘาไаёӘа№үа№ҒаёӣаёЈаёӣаёЈаё§аёҷ (Irritablebowel syndrome :IBS) , а№ғаёҠа№үаёҘаё”аёҒаёІаёЈаё«аёҘаёұа№ҲаёҮаёӮаёӯаёҮа№Җаё«аёҘаё§а№ғаёҷаёӣаёӯаё” 3. аёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёӯаёұаёҷไมа№Ҳаёһаё¶аёҮаёӣаёЈаё°аёӘаёҮаё„а№Ңаё—аёөа№Ҳаё•а№үаёӯаёҮа№ҒаёҲа№үаёҮа№Ғаёһаё—аёўа№Ңаё«аёЈаё·аёӯа№Җаё аёӘаёұаёҠаёҒаёЈаё—аёұаёҷаё—аёөаёЎаёөаё”аёұаёҮаёҷаёөа№ү аёӣаё§аё”аё•аёІ аё•аёІа№Ғаё”аёҮ аё«аёЈаё·аёӯаёҒаёІаёЈаёЎаёӯаёҮа№Җаё«а№Үаёҷаёңаёҙаё”аёӣаёҒаё•аёҙ аё«аёұаё§а№ғаёҲа№Җаё•а№үаёҷа№ҖаёЈа№Үаё§ аё«аёЈаё·аёӯаёҠа№үаёІаёңаёҙаё”аёӣаёҒаё•аёҙ аё–а№ҲаёІаёўаёӣаёұаёӘаёӘаёІаё§аё°аёҘаёІаёҡаёІаёҒаё«аёЈаё·аёӯа№ҖаёҲа№Үаёҡа№ҖаёЎаё·а№Ҳаёӯаё–а№ҲаёІаёўаёӣаёұаёӘаёӘаёІаё§аё° 4. аёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёӯаёұаёҷไมа№Ҳаёһаё¶аёҮаёӣаёЈаё°аёӘаёҮаё„а№Ңаёӯаё·а№Ҳаёҷаё—аёөа№ҲаёӯаёІаёҲа№ҖаёҒаёҙаё”аёЈаё°аё«аё§а№ҲаёІаёҮа№ғаёҠа№үаёўаёІ аё«аёІаёҒа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷаё•а№Ҳаёӯа№Җаёҷаё·а№ҲаёӯаёҮ аё«аёЈаё·аёӯ аёЈаёҡаёҒаё§аёҷаёҠаёөаё§аёҙаё•аёӣаёЈаё°аёҲаёІаё§аёұаёҷ а№ғаё«а№ү а№ҒаёҲа№үаёҮа№Ғаёһаё—аёўа№Ңаё«аёЈаё·аёӯа№Җаё аёӘаёұаёҠ аёҒаёЈаё—аёЈаёІаёҡ аёЎаёөаё”аёұаёҮаёҷаёөа№ү аёӣаёІаёҒа№Ғаё«а№үаёҮ аёңаёҙаё§а№Ғаё«а№үаёҮ аё—а№үаёӯаёҮаёңаё№аёҒ аё•аёІаёӘаё№а№үа№ҒаёӘаёҮไมа№Ҳไดа№ү аё•аёұаё§аёӯаёўа№ҲаёІаёҮаёўаёІа№ҖаёЎа№Үаё” аёўаёІаёҷа№үаёІ а№ҒаёҘаё°аёўаёІаёүаёөаё” Hyoscine-n-butylbromide http://www.yaandyou.net/index.php/component/drug/?nsetidT=4806&drugname=HYOSCINE+%5BBUTYLBROMIDE%5D&drugtype=g://flipper.diff.org/app/items/4260
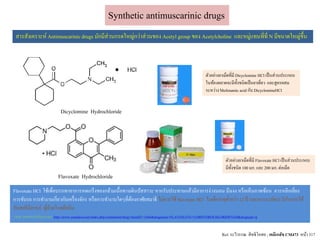
- 6. Dicyclomine Hydrochloride Synthetic antimuscarinic drugs Flavoxate Hydrochloride аёӘаёІаёЈаёӘаёұаёҮа№Җаё„аёЈаёІаё°аё«а№Ң Antimuscarinicdrugs аёЎаёұаёҒаёЎаёөаёӘа№Ҳаё§аёҷаёҒаёЈаё”а№ғаё«аёҚа№ҲаёҒаё§а№ҲаёІаёӘа№Ҳаё§аёҷаёӮаёӯаёҮ Acetyl group аёӮаёӯаёҮ Acetylcholine а№ҒаёҘаё°аё«аёЎаё№а№Ҳа№Ғаё—аёҷаё—аёөа№Ҳаё—аёөа№Ҳ N аёЎаёөаёӮаёҷаёІаё”а№ғаё«аёҚа№ҲаёӮаё¶а№үаёҷ аё•аёұаё§аёӯаёўа№ҲаёІаёҮаёўаёІа№ҖаёЎа№Үаё”аё—аёөа№ҲаёЎаёө Dicyclomine HCl а№Җаёӣа№ҮаёҷаёӘа№Ҳаё§аёҷаёӣаёЈаё°аёҒаёӯаёҡ а№ғаёҷаё—а№үаёӯаёҮаё•аёҘаёІаё”аёҲаё°аёЎаёөаё—аёұа№үаёҮаёҠаёҷаёҙаё”а№Җаёӣа№ҮаёҷаёўаёІа№Җаё”аёөа№Ҳаёўаё§ а№ҒаёҘаё°аёӘаё№аё•аёЈаёңаёӘаёЎ аёЈаё°аё«аё§а№ҲаёІаёҮ Mefenamic acid аёҒаёұаёҡ DicyclomineHCl аё•аёұаё§аёӯаёўа№ҲаёІаёҮаёўаёІа№ҖаёЎа№Үаё”аё—аёөа№ҲаёЎаёө Flavoxate HCl а№Җаёӣа№ҮаёҷаёӘа№Ҳаё§аёҷаёӣаёЈаё°аёҒаёӯаёҡ аёЎаёөаё—аёұа№үаёҮаёҠаёҷаёҙаё”100 аёЎаёҒ. а№ҒаёҘаё° 200аёЎаёҒ. аё•а№Ҳаёӯа№ҖаёЎа№Үаё” Ref. аёЈаё°аё§аёөаё§аёЈаёЈаё“ аёӘаёҙаё—аёҳаёҙа№ӮаёӯаёӘаё– ; а№Җаё„аёЎаёөа№Җаё аёӘаёұаёҠ CM473 аё«аёҷа№үаёІ 317 Flavoxate HCl а№ғаёҠа№үа№Җаёһаё·а№ҲаёӯаёҡаёЈаёЈа№Җаё—аёІаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаё«аё”а№ҖаёҒаёЈа№ҮаёҮаёӮаёӯаёҮаёҒаёҘа№үаёІаёЎа№Җаёҷаё·а№үаёӯаё—аёІаёҮа№Җаё”аёҙаёҷаёӣаёұаёӘаёӘаёІаё§аё° аё«аёІаёҒаёЈаёұаёҡаёӣаёЈаё°аё—аёІаёҷа№ҒаёҘа№үаё§аёЎаёөаёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈаёҮа№Ҳаё§аёҮаёҷаёӯаёҷ аёЎаё¶аёҷаёҮаёҮ аё«аёЈаё·аёӯа№Җаё«а№Үаёҷаё аёІаёһаёӢа№үаёӯаёҷ аё„аё§аёЈаё«аёҘаёөаёҒа№ҖаёҘаёөа№ҲаёўаёҮ аёҒаёІаёЈаёӮаёұаёҡаёЈаё– аёҒаёІаёЈаё—аёІаёҮаёІаёҷа№ҖаёҒаёөа№Ҳаёўаё§аёҒаёұаёҡа№Җаё„аёЈаё·а№ҲаёӯаёҮаёҲаёұаёҒаёЈ аё«аёЈаё·аёӯаёҒаёІаёЈаё—аёІаёҮаёІаёҷа№ғаё”а№Ҷаё—аёөа№Ҳаё•а№үаёӯаёҮаёӯаёІаёЁаёұаёўаёӘаёЎаёІаёҳаёҙ ไมа№Ҳаё„аё§аёЈа№ғаёҠа№ү flavoxate HCl а№ғаёҷа№Җаё”а№ҮаёҒаёӯаёІаёўаёёаё•а№ҲаёІаёҒаё§а№ҲаёІ 12 аёӣаёө а№ҒаёҘаё°аё„аё§аёЈаёЈаё°аёЎаёұаё”аёЈаё°аё§аёұаёҮа№ғаёҷаёҒаёІаёЈа№ғаёҠа№ү аёҒаёұаёҡаёӘаё•аёЈаёөаёЎаёөаё„аёЈаёЈаё а№Ң аёңаё№а№үаёӣа№Ҳаё§аёўа№ӮаёЈаё„аё•а№үаёӯаё«аёҙаёҷ (аёҲаёІаёҒ а№ҖаёӯаёҒаёӘаёІаёЈаёҒаёІаёҒаёұаёҡаёўаёІ а№ҒаёҘаё° http://www.yaandyou.net/index.php/component/drug/?nsetidT=1604&drugname=FLAVOXATE+%5BHYDROCHLORIDE%5D&drugtype=g
- 7. Antispasmodic drug But Not Anticholinergic drug Drotaverine аёўаёұаёҡаёўаёұа№үаёҮаёҒаёІаёЈаё—аёІаёҮаёІаёҷаёӮаёӯаёҮ enzyme Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) аёӢаё¶а№ҲаёҮа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷа№ҖаёӯаёҷไаёӢаёЎа№Ңаё—аёөа№Ҳа№ҖаёӣаёҘаёөа№Ҳаёўаёҷ cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) а№ғаё«а№үа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷ AMP аёӘа№ҲаёҮаёңаёҘа№ғаё«а№үаёӘаёІаёЈ cAMP а№ғаёҷа№ҖаёӢаёҘаёҘа№Ңа№Җаёһаёҙа№ҲаёЎаёӮаё¶а№үаёҷаёӢаё¶а№ҲаёҮ ไаёӣаёўаёұаёҡаёўаёұа№үаёҮ myosin light chain kinase аё—аёІа№ғаё«а№ү аёҒаёҘа№үаёІаёЎа№Җаёҷаё·а№үаёӯа№ҖаёЈаёөаёўаёҡไมа№Ҳаё«аё”аё•аёұаё§ аёўаёІаё•аёұаё§аёҷаёөа№үаёҲаё¶аёҮไมа№ҲаёЎаёө antichloinergic effects аёӘаё№аё•аёЈа№Ӯаё„аёЈаёҮаёӘаёЈа№үаёІаёҮ related to papaverine аёЎаёөаёӮа№үаёӯаё«а№үаёІаёЎа№ғаёҠа№үа№ғаёҷаёңаё№а№үаё—аёөа№Ҳ а№Ғаёһа№үаёўаёІ drotaverine , аёңаё№а№үаё—аёөа№Ҳа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷа№ӮаёЈаё„ porphyria аёӢаё¶а№ҲаёҮа№Җаёӣа№Үаёҷа№ӮаёЈаё„а№ҖаёҘаё·аёӯаё”аёҠаёҷаёҙаё”аё«аёҷаё¶а№ҲаёҮ, аё•аёұаёҡ ไตа№ҒаёҘаё° аё«аёұаё§а№ғаёҲаё—аёІаёҮаёІаёҷаёҡаёҒаёһаёЈа№ҲаёӯаёҮаёӯаёўа№ҲаёІаёҮаёЈаёёаёҷа№ҒаёЈаёҮ аёӯаёІаёҒаёІаёЈ ไมа№Ҳаёһаё¶аёҮаёӣаёЈаё°аёӘаёҮаё„а№ҢаёӯаёІаёҲаёһаёҡаё„аё§аёІаёЎаё”аёұаёҷаё•а№ҲаёІ аёӣаё§аё” аёЁаёөаёЈаё©аё° а№Җаё§аёөаёўаёҷаёЁаёөаёЈаё©аё°а№Ғаёҡаёҡаё«аёЎаёёаёҷ http://drug.pharmacy.psu.ac.th/Question.asp?ID=13339&gid=7