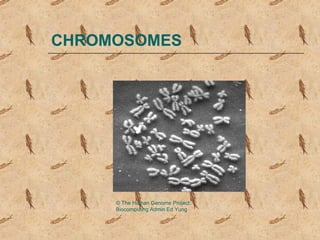
Chromosomes
- 1. CHROMOSOMES ÂĐ The Human Genome Project: Biocomputing Admin Ed Yung
- 2. Chromosomes in eukaryotes and prokaryotes are different PROKARYOTES EUKARYOTES single chromosome plus plasmids many chromosomes circular chromosome linear chromosomes made only of DNA made of chromatin, a nucleoprotein (DNA coiled around histone proteins) found in cytoplasm found in a nucleus copies its chromosome and divides copies chromosomes, then the immediately afterwards cell grows, then goes through mitosis to organise chromosomes in two equal groups ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 3. Chromosomes in eukaryotes ïĄ Found in the nucleus ïĄ Condensed and visible during cell division ïĄ At the beginning of mitosis they can be seen to consist of two threads (sister chromatids) joined by a centromere ïĄ The sister chromatids are identical copies ïĄ During mitosis the sister chromatids separate and are placed into two nuclei Image believed to be in the Public Domain ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 4. Numbers of chromosomes ïĄ Constant for each cell in the body (except sex cells which only have half sets). ïĄ Constant throughout the life of an individual (you donât lose or gain chromosomes) ïĄ Constant for all members of a species ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 5. Mouse Maize Image believed to be in the Public Domain ÂĐ A. Lane Rayburn
- 6. Organism Chromosome numbers Human 46 Chimpanzee 48 House Mouse 40 Maize 20 ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 7. Human chromosomes Image believed to be in the Public Domain
- 8. The chromosomes of a human female ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS Image believed to be in the Public Domain
- 9. Identifying chromosomes Chromosomes can be identified by: ïĄ Their size ïĄ Their shape (the position of the centromere) NB Chromosomes are flexible ïĄ Banding patterns produced by specific stains (Giemsa) ÂĐ Biologyreference.com Chromosomes are analysed by organising them into a KARYOTYPE ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 10. Female Male Images believed to be in the Public Domain
- 11. Downâs syndrome Image believed to be in the Public Domain
- 12. Development and chromosomes ïĄ Differences in chromosomes are associated with difference in the way we grow. ïĄ The karyotypes of males and females are not the same Females have two large X chromosomes Males have a large X and a small Y chromosome The X and the Y chromosomes are called sex chromosomes The sex chromosomes are placed at the end of the karyotype ïĄ Unusual growth can be associated with chromosome abnormalities e.g. People who develop Downâs syndrome have trisomy 21 ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 13. Chromosomal abnormalities Trysomy-21 â Downâs syndrome Trysomy-18 â Edwardâs syndrome Images believed to be in the Public Domain
- 14. Therefore genetic information is found on our chromosomes ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 15. Chromosomes and cell division ïĄ Multicellular organisms copy their chromosomes before cell division. Interphase ïĄ They must grow to a mature size. ïĄ The nucleus divides, distributing the chromosomes into two equal groups (mitosis). ïĄ The cytoplasm then divides (cytokinesis) each part taking a nucleus. ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS Image believed to be in the Public Domain
- 16. The cell cycle Cytokinesis Some cells may Division of the cytoplasm stay in this stage G0 for over a year M G1 First growth phase. Varies in length G2 Second growth phase S Copying of chromosomes G1 + S + G2 = INTERPHASE ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 17. The cell cycles in different cells Cell type Cell cycle / hours Bean root tip 19.3 Mouse fibroblast 22 Chinese hamster 11 fibroblast Mouse small intestine 17 epithelium Mouse oesophagus 181 epithelium ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 18. Chromosomes and reproduction ïĄ Chromosomes come in pairs One of the pair is maternal the other is paternal ïĄ When parents make sex cells the number of chromosomes must be halved One of each type of chromosome is taken ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 19. Meiosis and fertilisation Mother Father 23 pairs of 23 pairs of chromosomes chromosomes Meiosis Sex cells 23 unpaired 23 unpaired 23 unpaired 23 unpaired chromosomes chromosomes chromosomes chromosomes Fertilisation 23 pairs of chromosomes Child ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS Images believed to be in the Public Domain
- 20. Meiosis ïĄ A special type of cell division ïĄ Used to make sex cells ïĄ Meiosis halves the numbers of chromosomes ïĄ Meiosis picks one chromosome from each pair at random and places them in a sex cell. This results in enormous variation amongst the sex cells. ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 21. The inheritance of gender Is it going to be a boy or a girl? ÂĐ University of New Mexico
- 22. The inheritance of gender Mother Father XX XY Meiosis Sex cells X X X Y X Y Fertilisation X XX XY Possible children X XX XY Chance of a girl 50% Chance of a boy 50% ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 23. Sex chromosomes ïĄ The sex of many animals is determined by genes but on chromosomes called sex chromosomes ïĄ The other chromosomes are called autosomes ïĄ One sex is homogametic ïĄ The other sex is heterogametic ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
- 24. Sex determination in different animals HOMOGAMETIC HETEROGAMETIC SEX DETERMINATION SEX SEX Female XX Male XY Presence of Y- chromosome = maleness (mammals and fish) Presence of second X- chromosome = femaleness (Drosophila, the fruit fly) Male ZZ Female ZW Birds, amphibians, reptiles, butterflies, moths. Female XX Male Xo Grasshoppers ÂĐ 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS