Chronic and subacute osteomyelitis
- 2. Content ŌŚÅ Subacute osteomyelitis ŌŚÅ Chronic osteomyelitis ŌŚÅ Clinical and radiological features of various forms of chronic osteomyelitis (sequester,rarefying,hyperplastic, primary-chronic) ŌŚÅ Differential diagnosis of Acute periodontitis,periostitis and odontogenic osteomyelitis. ŌŚÅ Treatment
- 3. ŌŚÅ Acute osteomyelitis phase last upto 3 weeks and only then subacute phase occur after which last for 2 weeks ŌŚÅ Usually on the 3rd to 5th week the disease transform to chronic stage.
- 4. Sub-acute osteomyelitis stage ŌŚÅ The clinical signs and Symptoms are less severe compared to the acute condition, it is the stage of stabilization of inflammatory process. ŌŚÅ Clinical signs : Dull pain Temperature decreases but doesnŌĆÖt fall to normal Edema of face decreases Teeth in the inflammation area are more mobile
- 5. Chronic osteomyelitis ŌŚÅ Chronic osteomyelitis is characterized by a clinical course lasting over a month. It may occur after the acute phase or it may be a complication of tooth-related infection without a preceding acute phase. The clinical presentation is milder, with painful exacerbations and discharge of pus or sinus tracts.
- 6. Clinical Picture ŌĆó Acute odontogenic osteomyelitis. ŌĆó Acute intensive pain in 1 tooth area, several teeth area, jaw area. - intoxication - Body temperature of 39,5-40 degrees Celsius - Edema after 2-3 days - Abscess and phlegmona. - Lymphadenitis. - Hard mouth opening (inflammatory contracture of the m.masseter), painful swallowing - edema of the mucous membrane, hyperemia of the gum, halitosis - Tooth mobility, painful percussion, pus - Positive Vincent syndrome
- 8. Hyperplastic form of chronic osteomyelitis ŌŚÅ Also called primary chronic process of osteomyelitis ŌŚÅ Common in young people ŌŚÅ On X-ray it shows the thickness of the bone mass.
- 10. Sequestering form ŌŚÅ Caused by decreased vascularity ŌŚÅ Decrease in blood flow cause bone necrosis
- 11. Rarefying form ŌŚÅ It is a diffuse process with small sequesters ŌŚÅ Thickening of the bone scars on the past fistula ŌŚÅ X-ray shows bone destruction with inner sequesters
- 13. Treatment of chronic osteomyelitis ŌŚÅ Extraction of causative tooth ŌŚÅ Antibacterial Therapy : metronidazole, 500 mg IV, 48-72 hrs,switch to penicillin 500mg PO for 4 weeks. Patients allergic to penicillin : clindamycin 450 mg PO ŌŚÅ Antifungal therapy to avoid dysbacteriosis (levorine and nystatin) ŌŚÅ Stimulating Therapy : Vitamins to boost immune system ŌŚÅ Surgical treatment (sequesterectomy) perfomed under Local anesthesia
- 14. sequesterectomy ŌŚÅ Local or General anesthesia ŌŚÅ Incision and mobilization of mucoperiosteal flap ŌŚÅ Bone is trepanated at the sequester area ŌŚÅ Big sequesters are removed using forceps and small sequesters are removed with curettage ŌŚÅ Sequester cavity is washed with Hydrogen peroxide ŌŚÅ Bone is filled with Bone graft materials ŌŚÅ The wound is stitched and drained
- 15. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF APICAL PERIODONTITIS, PERIOSTITIS AND OSTEOMYELITIS
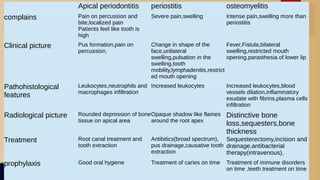
- 16. Apical periodontitis periostitis osteomyelitis complains Pain on percussion and bite,localized pain Patients feel like tooth is high Severe pain,swelling Intense pain,swelling more than periostitis Clinical picture Pus formation,pain on percussion, Change in shape of the face,unilateral swelling,pulsation in the swelling,tooth mobility,lymphadenitis,restrict ed mouth opening Fever,Fistula,bilateral swelling,restricted mouth opening,parasthesia of lower lip Pathohistological features Leukocytes,neutrophils and macrophages infiltration Increased leukocytes Increased leukocytes,blood vessels dilation,inflammatory exudate with fibrins,plasma cells infiltration Radiological picture Rounded depression of bone tissue on apical area Opaque shadow like flames around the root apex Distinctive bone loss,sequesters,bone thickness Treatment Root canal treatment and tooth extraction Antibitics(broad spectrum), pus drainage,causative tooth extraction Sequesterectomy,incision and drainage,antibacterial therapy(intravenous), prophylaxis Good oral hygiene Treatment of caries on time Treatment of immune disorders on time ,teeth treatment on time
- 18. THANK YOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION