Cinnamon oil Chemistry
- 2. Cinnamon Synonyms; Cinnamon Bark Kalmi Dal chini Celon Cinnamon Biological source; Genus Cinnamomum Family Lauraceae Species 250-350 Biologically important species; Cinnamomum verum / Cinnamomum zeylanicum
- 3. Cinnamon (Chemical Composition) The term cinnamon commonly refers to the dried bark of C. zeylanicum and C. aromaticum. Cinnamon consist of a variety of resinous compounds , including – cinnamaldehyde , – trans-cinnamaldehyde, – cinnamyl acetate , – caryophyllene, – cinnamate , – cinnamic acid , – ethyl cinnamate – eugenol and – The flavour of Cinnamon is due – to aromatic essential oil that
- 4. Major constituents of Cinnamon Oil Cinnamon oil contains 15 chemical constituents that contribute to its distinct aroma, remedial values, consistency and superiority of this splendid oil. Bark Oil Leaf Oil (E)-Cinnamaldehyde Eugenyl Acetate Eugenol Eugenol (E)-Cinnamyl acetate (E)-Cinnamyl acetate Linalool Linalool B-Caryophyllene Benzyl Benzoate p-Cymene as major compounds
- 5. Active Ingredients of Cinnamomum barks Constituents Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Cinnamomum Cassia Volatile Oils % Upto 4% Upto 2% Cinnamic Aldhyde (Irritant) 65% 80% Eugenol 10% Absent Mucilage 2% 10% Mono and Sesqueterpens Present Absent Tennins Present Present Coumarins Absent Present
- 6. Cinnamon Oil (Active component) – Composition of the Cinnamon oil depends on the source, cultivation, vegetative stage and the growing season of the plant of Cinnamon. – The bark oil is generally preferred over Cinnamon Leaf Essential Oil. – "Ground Cinnamon" that we purchase in grocery stores, and even most of the "Cinnamon Sticks" that are sold are not true cinnamon, but are really its more affordable cousin, Cassia, (Cinnamomum cassia). – Cinnamaldehyde is responsible for spicy taste and odor and occur due to the absorption of oxygen . As cinnamon ages, it darkness in color, improving the resinous compound – (E)-Cinnamaldehyde has the highest area with a proportion of about 76.8% of Cinnamon oil components.
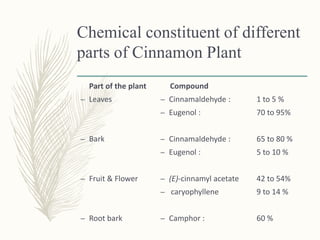
- 7. Chemical constituent of different parts of Cinnamon Plant Part of the plant – Leaves – Bark – Fruit & Flower – Root bark Compound – Cinnamaldehyde : 1 to 5 % – Eugenol : 70 to 95% – Cinnamaldehyde : 65 to 80 % – Eugenol : 5 to 10 % – (E)-cinnamyl acetate 42 to 54% – caryophyllene 9 to 14 % – Camphor : 60 %