Cis(11122223333)
This document discusses the structural and functional features of computer information systems. It describes how information systems have evolved from early human practices of writing, reading, and memorizing information to today's computer-based infrastructures. The key components of an information system are identified as hardware, software, infrastructure, personnel, and procedures. Different information architectures like centralized, decentralized, client-server, and enterprise-wide architectures are explained. The evolution of computer information systems from early scientific and military applications to today's internet-based systems is outlined. The document concludes that information systems now rely on computers to perform their functions and that continued development is needed in both information science and computer technology to make systems more efficient and functional.













Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Viewers also liked (7)
Similar to Cis(11122223333) (20)
Cis(11122223333)
- 1. STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL FEATURES OF CIS By zaid daŌĆÖood Supervisor prof. ─░lky salihoglu
- 2. WHAT IS INFORMATION SYSTEM ? A combination of hardware, software, infrastructure and trained personnel organized to facilitate planning, control, coordination, and decision making in an organization.
- 3. FIRST INFORMATION SYSTEM IN HUMANŌĆÖS HISTORY ŌĆó We are all having this system already and human starting go forward to technology. ŌĆó writing ,reading, computing, and memorizing all information result of these processes. ŌĆó then human reaching to computer and use it to do most of the processes that information system need.
- 4. COMPUTER INFORMATION SYSTEM ’āÆ Information systems are computer-based infrastructures , organizations, personnel, and components that collect, process, store, transmit, display, disseminate, and act on information. Information systems generally provide computer-based assistance to people engaging their environment.
- 5. INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE Everything that supports information processing except information itself: computer hardware general-purpose software ’é¦ networks and communication facilities.
- 6. INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE database information management personnel and, procedures
- 7. INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE ’āÆ isa general scheme of the Information requirements in the organization (including information flows)
- 8. CENTRALIZED INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE ’āÆ Input transactions do not need to be processed in real time. ’āÆ On-line-data-entry personal can be centrally located. ’āÆ Large number of periodic outputs are produced by the system.
- 9. CENTRALIZED INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE ’éå Single-computer architecture ’ā« Mainframe environment; ’ā« PC environment ’éå Multi-computer architecture ’ā« Group of similar computers ’ā« Group of different computers implementing different tasks.
- 10. DECENTRALIZED (DISTRIBUTED) INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE ’éå PC in a LAN or WAN ’éå Client/Server ’ā« Client/Server in a LAN ’ā« Enterprise wide computing ’éå Client/Server evolution into Internet-based architecture
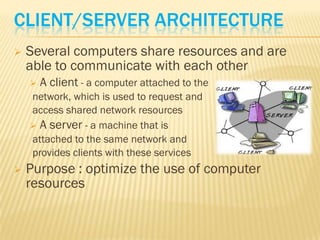
- 11. CLIENT/SERVER ARCHITECTURE ’āś Several computers share resources and are able to communicate with each other ’āś A client - a computer attached to the network, which is used to request and access shared network resources ’āś A server - a machine that is attached to the same network and provides clients with these services ’āś Purpose : optimize the use of computer resources
- 12. ENTERPRISE WIDE ARCHITECTURES ’āÆ It is broadly used to describe business initiatives and technology; for example, an "enterprise-wide focus upon customer satisfaction ," or an "enterprise-wide security application. " These are more often company-wide ,restricted to a company's employees and internal workings.
- 13. ENTERPRISE WIDE ARCHITECTURES ’āÆAccess to data, applications, services, and real- time flows of data in Different LANs or databases ’āÆUse client/server architecture to create a cohesive, flexible, and powerful computing environment
- 14. ENTERPRISE WIDE ARCHITECTURES ’āÆ Provide total integration of departmental and corporate IS resources ’āÆ Increase the availability of information and thereby maximize the value of information.
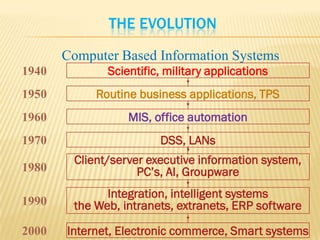
- 15. THE EVOLUTION Computer Based Information Systems 1940 Scientific, military applications 1950 Routine business applications, TPS 1960 MIS, office automation 1970 DSS, LANs Client/server executive information system, 1980 PCŌĆÖs, AI, Groupware Integration, intelligent systems 1990 the Web, intranets, extranets, ERP software 2000 Internet, Electronic commerce, Smart systems
- 16. CONCLUSIONS: ’āÆ All information systems nowadays can not work without computers in each of its functions therefore is necessary developing information science and deal with it and managing it and develop the structural, efficiency and functionality of a computer for using in information systems in addition to the development of how to deal with the information and data input, output and efficiency to deal with them through user and dealing with it through the development of the computer internally ,and reduce errors to make computer systems more efficient in the constructional and functional features.
- 17. References: 1-Computer-Aided Analysis and Design of Information Systems J.F. Nunamaker Jr. and Benn R. Konsynski Jr.University of Arizona Thomas Ho and Carl Singer Purdue University. 2-Computer and Information Systems Policy of The Baptist College of Florida. 3-The Protection of Information in Computer Systems JEROME H. SALTZER, SENIOR MEMBER, IEEE, AND MICHAEL D. SCHROEDER, MEMBER, IEEE. 4-UNDERSTANDING COMPUTERS: AN OVERVIEW FOR RECORDS AND ARCHIVES STAFF MANAGING PUBLIC SECTOR RECORDS A STUDY PROGRAMME General Editor, Michael Roper; Managing Editor, Laura Millar . 5- A Functional Taxonomy of Computer Based Information Systems Gregory Mentzas Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Technical University of Athens Published in: "International Journal of Information Management" (Volume 14, No. 6, December, pp. 397-410.) .
- 18. THANK YOU FOR LISTENING
