CIT presentation.pptx
- 1. Technology of natural fibre composite B.Senthil kumar,M.Tech,Ph.D Assistant professor The Gandhigram Rural Institute-DU Dindigul
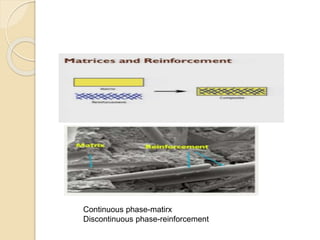
- 2. Concept of composite ï The term composite material refers to all the solid material composed of more than one component, where in those components are in separate phase ï The constituents retain their identity and a interface between each other ï Martix and Reinforcement ?
- 4. Why composites ïComposite can be very strong and stiff, yet very light in weight so the ratio of Strength to weight and stiffness to weight is several times higher than steel/aluminum ïGood fatigue properties ïToughness is often good ïNon corrode ïPossibilities of getting combination of properties
- 9. Interface
- 10. Difference between metal to composite
- 12. Metals Fibre reinforced composites Most of the time the finishing task is essential Nearnet shaped parts can be produced with fibre reinforced composite It is difficult to execute the online monitoring of service life of the composites Inservice monitoring can be possible with the support of embedded sensors
- 18. Flakes
- 19. Matrices
- 21. Matrix properties Polyester resin Vinyl ester Epoxy Phenolics Polyuretha ne ïCheap ïHigh versatile ïCross links are enabled with C=C between the neighboring chain ïSuperior chemical resistance ïFatigue characteristi c ïExcellent mechanical strength ïLow shrinkage ïFatigue characteristi c ïGood heat resistance ïSuitable for fire proof application ïMinimal smoke ïHigh temp. resistance ïNon toxic ïSuperior strength at high temp High energy absorption High strength
- 22. Simple slab model of composite
- 27. Manufacturing techniques for natural fibre processing ï Pultrusion is a combination of two words: pull and extrusion ï Continuous moulding Technique ï Continuous fi bre rovings or tapes are pulled by means of a puller through a resin bath of thermosetting polymer ï Pultrusion process of kenaf fibre composite(Courtesy of A.M.Fairuz)
- 28. ï Fairuz et al. ( 2014 ) reported the work on pultruded kenaf fibre reinforced vinyl ester composites using pultrusion process. Kenaf composite rods were produced.
- 29. Hand Lay-Up ï Hand lay-up is an open moulding process to produce polymer composite product. This is a labour-intensive process where a high skill operator is required to perform the fabrication task. ï A roller is used to consolidate the composites and the composites are made layer by layer ï cured at room temperature or in an oven. ï Misri et al. ( 2014a ) have used hand lay-up process to develop a small boat from hybrid glass- sugar palm fi bre reinforced unsaturated polyester composites
- 30. Filament Winding ï Filament winding is a composite manufacturing process to produce components that are normally circular in shape. It can be considered an open mould process and the mould is actually ï continuous fibre rovings are being drawn by a puller through a resin batha rotating mandrel ï Misri et al. ( 2015 ) developed kenaf fi bre reinforced unsaturated polyester composite hollow shafts
- 31. Resin Transfer Moulding ï RTM is an established composite manufacturing process that is normally used to fabricate automotive and aircraft components. ï In this process, fibre reinforcement, either long or woven fibres are initially cut out using a template and a knife or scissors. These reinforcements called performs are bound by means of thermoplastic binder and then placed inside the mould cavity. ï Resin is being transferred into the mould cavity by means of a variety of equipments such as by pressure or vacuum. Resins that are normally used in this process include polyester, epoxy, vinyl ester, and phenolic. ï Salim et al. ( 2011 ) used RTM to develop composite specimens for nonwoven kenaf fi bre mat reinforced epoxy composites.
- 32. Vacuum bagging ï Vacuum bagging is a composite manufacturing process that utilizes a vacuum bag to provide compaction pressure and consolidation of plies within the laminate ï It is an extended version of hand lay-up process ï Mariatti and Abdul Khalil ( 2009 ) used vacuum bagging process to prepare samples of bagasse fi bre
- 33. Compression Moulding ï Compression moulding is a composite manufacturing process normally used to produce composite components in high production volume such as automotive components. ï Wirawan et al. ( 2011 ) and El-Shekeil et al. ( 2012 ) used laboratory scale compression moulding (Fig. 1.3 ) to prepare composite specimens from sugar cane bagasse and poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC)
- 34. Injection Moulding ï Injection moulding is one of the most widely used manufacturing processes to produce plastic components. Injection moulding can also be used to produce polymer composite products, but the fi bres used in the composites are short fi bres in the form of particles or powder. ï Azaman et al. ( 2013 , 2014 ) carried out mould flow analysis of wood fibre reinforced polypropylene composites using Autodesk MoldFlow
- 35. Growing interest of NFC Manufacturing of Natural Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites, DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-07944-8_2
- 36. Types and Sources of Natural Fibres ï Plant ï Animal ï Mineral
- 37. ï Plant-based fibres can be classified as seed fibre, bast fibres, and leaf fibres ï Some examples are cotton (seed hairs); hemp, ramie, jute, kenaf, and fl ax (bast fi bres); and sisal, banana, coir, and abaca (leaf fi bres).