Clacite & Dolomite
- 2. Calcite ŌĆō Introduction ŌĆó Most common and widespread mineral on or near the EarthŌĆÖs surface. ŌĆó Only stable form is CaCO3 ŌĆó Principal constituent of Sedimentary limestones ŌĆó Occurs in carbonate shells as fine precipitates and as clastic materials.
- 3. ŌĆó Color : Colorless or white, sometimes grey, yellow, blue, red, brown
- 4. ŌĆó Luster : Vitreous ŌĆó Diaphaneity : Transparent to opaque ŌĆó Streak : White Streak
- 5. ŌĆó Crystal Shape : Triagonal ŌĆó Cleavage : Rhombohedral ŌĆó Fracture : Conchoidal but rarely visible due to perfect cleavage ŌĆó Hardness : 3.0
- 6. ŌĆó Specific Gravity : 2.715(if pure) to 2.94 ŌĆó Reaction with HCl powdered + dil. HCl Brisk effervescence proving presence of carbonate group
- 7. Optical Properties ŌĆó no = 1.658 ŌĆó ne = 1.486 ŌĆó no ŌĆō ne = 0.172 = ╬┤ ŌĆó Maximum Birefringence with fourth order or higher colors.
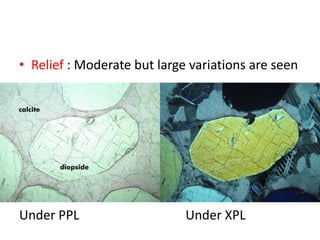
- 8. ŌĆó Relief : Moderate but large variations are seen Under PPL Under XPL
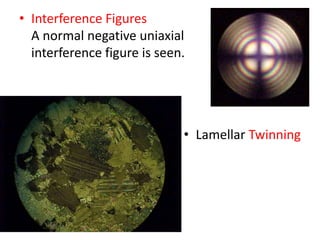
- 9. ŌĆó Interference Figures A normal negative uniaxial interference figure is seen. ŌĆó Lamellar Twinning
- 10. Uses of Calcite ŌĆó Many different uses according to its purity and character. ŌĆó Marbles and crystalline limestones ŌĆō ornamental stones. ŌĆó Calcium Carbonate is used as a flux in smelting ŌĆó Certain variety of calcium carbonate is used in printing ŌĆó Lime neutralize the natural acids in the soil.
- 11. Dolomite ŌĆō Introduction ŌĆó Occurs in extensive beds at many geological horizons ŌĆó Dolomite may be deposited directly from sea water, but most dolomite beds have been formed by the alteration of limestones, the calcite of which is replaced by dolomite. ŌĆó Chemical Composition : (CaMg)(CO3)2
- 12. ŌĆó Color : White, yellowish, brown, and sometimes red, green, or black
- 13. ŌĆó Luster : Vitreous to pearly of crystals; dull of massive varieties. ŌĆó Diaphaneity : Translucent to opaque ŌĆó Streak : White ŌĆó Crystal Shape : Triagonal Presence of Mg reduces the symmetry
- 14. ŌĆó Cleavage : Rhombohedral ŌĆó Fracture : Conchoidal or Uneven ŌĆó Hardness : 3.5 to 4.0 ŌĆó Specific Gravity : 2.86 ŌĆó Reaction with HCl powdered + dil. HCl Does not rapidly dissolve or effervesce.
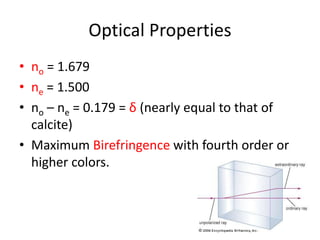
- 15. Optical Properties ŌĆó no = 1.679 ŌĆó ne = 1.500 ŌĆó no ŌĆō ne = 0.179 = ╬┤ (nearly equal to that of calcite) ŌĆó Maximum Birefringence with fourth order or higher colors.
- 16. ŌĆó Relief : Low to moderate or high ŌĆó Interference Figures : A normal negative uniaxial interference figure is seen. ŌĆó Glide Twin lamellae seen on many sections
- 17. Uses of Dolomite ŌĆó Important Building material. ŌĆó Making of Refractory furnace lining and source of carbon dioxide,
- 18. How do we differentiate Calcite & Dolomite ŌĆó Dolomite differs from calcite because of the presence of MAGNESIUM. ŌĆó Calcite reacts quickly with acids and produce carbon dioxide bubbles. But dolomite, weakly reacts with acids producing bubbles very slowly. ŌĆó Dolomite is slightly harder and denser than calcite. ŌĆó Calcites form scalenohedrons but dolomites never form scalenohedrons.
- 19. Thank You