Class 10 Ch 1 SCIENCE FULL Notes FOR STUDY
- 1. 7 CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS GIST OF THE LESSON 1) Chemical reactionŌĆö Chemical changes or chemical reactions are the changes in which one or more new substances are formed. 2 )Chemical Equations ŌĆō Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3) Balanced Chemical equations ŌĆō The chemical equation in which the no. of atoms of different elements is same on both sides of the arrow is called balanced chemical equation. 4) The chemical reactions can be classified into different types such asŌĆö a) Combination reaction ŌĆō The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a new substance are called combination reaction. For example, 2Mg(s) + O2 (g) ’āĀ 2 MgO (s) b) Decomposition reaction - The reaction in which a single compound breaks up into two or more simpler substances are called decomposition reactions. For example, 2Pb (NO3)2 (s) ’āĀ 2PbO (s) + 4NO2 (g) +O2 (g) The decomposition of a substance by passing electric current through it is known as electrolysis. The decomposition of a substance on heating is known as thermal decomposition. The decomposition of a substance by absorbing light energy is called photochemical decomposition. c) Displacement reactions -The chemical reactions in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from a compound are known as displacement reactions. For example, i) Zn (s) + CuSO4 (aq) ’āĀ ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s). ii) Cu (s) + 2AgNO3 (aq) ’āĀ Cu (NO3)2 (aq) +2Ag (s). d) Double Displacement Reactions - The chemical reactions in which compounds react to form two different compounds by mutual exchange of ions are called double displacement reactions. These reactions take place in solution two common types of this reaction are precipitation reactions and neutralization reactions i) Precipitation reaction : In this reactions, aqueous solution of two salts are mixed whereby Some salts precipitate due to mutual exchange of ions between the two salts. For example AgNO3 (aq) + NaCI (aq) -----> AgCl(s) + NaNO3. ii) Neutralization reaction: In this type of reaction an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water by exchange of ions. NaOH (aq) + HCl (aq) ’āĀ NaCl (aq) + H2O.
- 2. 8 e) Redox reaction: Chemical reaction which shows both oxidation and reduction reaction. Oxidation: Reaction that involves the gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen. Reduction: Reaction that shows the loss of oxygen or gain of hydrogen. Both oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously and hence called redox reaction. ZnO + C ’āĀ Zn + CO ZnO reduce to Zn ---- reduction C oxidize to CO ------oxidation f) Exothermic reaction and endothermic reaction: On the basis of energy changes during chemical reaction, they can be classified as i) Exothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is produced. C + O2 ’āĀ CO2 (g) + heat ii) Endothermic reaction: A chemical reaction in which heat energy is absorbed. CaCO3 + Heat ’āĀ CaO + CO2 5 Corrosion ŌĆō The process of slow conversion of metals into their undesirable compounds due to their reaction with oxygen, water, acids, gases etc. present in the atmosphere is called corrosion. Rusting ŌĆō Iron when reacts with oxygen and moisture forms red substance called rust. 6 Rancidity ŌĆō The taste and odour of food materials containing fat and oil changes when they are left exposed to air for long time. This is called rancidity. It is caused due to oxidation of fat and oil present in food material. It can be prevented by using various methods such as by adding antioxidants to the food materials, Storing food in air tight container and by flushing out air with nitrogen.
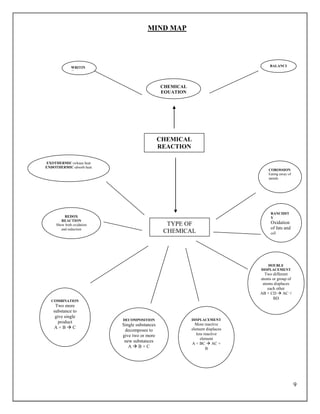
- 3. 9 MIND MAP TYPE OF CHEMICAL REACTION CHEMICAL REACTION EXOTHERMIC-release heat ENDOTHERMIC-absorb heat REDOX REACTION Show both oxidation and reduction COMBINATION Two more substance to give single product A + B ’āĀ C DECOMPOSITION Single substances decomposes to give two or more new substances A ’āĀ B + C DISPLACEMENT More reactive element displaces less reactive element A + BC ’āĀ AC + B DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT Two different atoms or group of atoms displaces each other AB + CD ’āĀ AC + BD RANCIDIT Y Oxidation of fats and oil COROSSION Eating away of metals CHEMICAL EQUATION WRITIN G BALANCI NG