classification of Internal combustion engines
Download as PPTX, PDF2 likes1,159 views
This document discusses internal combustion engines. It describes the two main types as four-stroke and two-stroke engines, with two-stroke completing a cycle in one crankshaft revolution and four-stroke in two revolutions. The two types of internal combustion engines are also identified as petrol/gasoline engines which use a carburetor to mix fuel and air before ignition by a spark plug, and diesel engines which compress only air and inject fuel to ignite via compression heat. Key features of diesel engines are discussed as being eco-friendly with less carbon monoxide, more efficient fuel burning, durable requiring less maintenance, and compact with less noise. The basic working components and cycles of two-stroke engines are outlined.
1 of 14
Download to read offline













Recommended
SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Lubrication System.pptx



SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Lubrication System.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
╠²
The document summarizes the lubrication system of an internal combustion (IC) engine. It discusses the purposes of lubrication which are to reduce wear, reduce friction, provide cooling, create a seal, and clean the engine. It describes the splash and forced feed lubrication systems. The splash system uses splashing oil to lubricate while the forced feed system uses an oil pump to directly pump oil to parts. Key components of the forced feed system include the oil pump, oil filter, crankcase breather, and relief valve.SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Fuel System.pptx



SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Fuel System.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
╠²
The document discusses the fuel system of internal combustion (IC) engines. It describes the key components and functions of the fuel system in diesel engines, including the fuel filter, fuel injection pump, fuel injector, combustion chamber, turbocharger, and governor. It also briefly discusses the fuel supply system in spark ignition engines. The fuel system's purpose is to supply clean fuel to the engine cylinders so it can be combusted to produce energy to run the engine.2 stroke petrol engine



2 stroke petrol enginezakvan kadva
╠²
A two-stroke petrol engine completes the combustion cycle in two strokes of the piston rather than four as in a four-stroke engine. In a two-stroke engine, the intake and exhaust strokes are eliminated and ports instead of valves are used, with the exhaust gases driven out by the fresh fuel charge entering near the end of the power stroke. Everything a four-stroke engine does over two revolutions, a two-stroke engine accomplishes in one revolution, with the fuel-air mixture entering the crankcase and being compressed and ignited directly in the cylinder. While smaller, lighter and cheaper than a four-stroke engine, two-stroke engines wear parts faster, are less fuel efficient, and more polluting.Classification, working principals and construction of IC Engine.pdf



Classification, working principals and construction of IC Engine.pdfDrJayantaKumarMahato1
╠²
The document discusses engines and their classification. It begins by defining an engine as a device that converts chemical energy to mechanical energy. It then classifies heat engines based on whether combustion occurs externally or internally. Internal combustion engines are further classified based on the fuel used (diesel, petrol, gas), ignition type (spark ignition, compression ignition), and engine design (reciprocating, rotary). Reciprocating engines include inline, V-shaped, opposed piston, and radial configurations. The document also discusses two-stroke and four-stroke cycles and compares petrol and diesel engines. It concludes by describing the basic construction of an internal combustion engine.4 stroke diesel engine



4 stroke diesel engineHarisRiaz25
╠²
it is a perfect report if you are searching for 4 Stroke Diesel Engine. It includes History, Construction, Components, Working Principle, Strokes, PV Diagram, Advantages & Disadvantages and Applications.SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Cooling System.pptx



SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Cooling System.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
╠²
The document summarizes the cooling system of an internal combustion engine. It discusses that 30% of the heat produced during combustion is removed by the cooling system. There are two main types of cooling systems - air cooling and water cooling. Water cooling uses a water pump to circulate water through jackets around the engine and into a radiator for cooling, before returning to the engine. It maintains optimum engine temperature for efficient operation.lubrication system in ic engine



lubrication system in ic engineAnkit Jaiswal
╠²
The document discusses lubrication systems in internal combustion engines. It defines lubrication as applying a substance like oil or grease to minimize friction and allow smooth movement. There are three main types of lubrication systems - mist, wet sump, and dry sump. Wet sump systems use an oil sump at the engine base and either splash or pressure pumps to circulate oil. Dry sump systems store extra oil outside the engine and use scavenging pumps to circulate it through the engine and an external heat exchanger.SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE-Ignition system.pptx



SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE-Ignition system.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
╠²
This document summarizes the ignition system of internal combustion engines. It discusses the four main ignition systems used: spark ignition, compression ignition, hot tube ignition, and open flame ignition. It focuses on describing the components and working of spark ignition systems, which use a battery or magneto to generate sparks in the spark plugs. The key components discussed are the ignition coil, distributor, condenser, spark plugs, ignition switch, dynamo, and storage battery. It explains how these components work together to provide properly timed sparks to ignite the fuel-air mixture in each cylinder.I.C ENGINE PPT



I.C ENGINE PPTHOME
╠²
1) The document discusses the assembly, disassembly and maintenance of internal combustion (IC) engines. It covers the main components of IC engines like the cylinder block, cylinder head, piston, connecting rod, crankshaft and camshaft.
2) IC engines are classified based on their cycle of operation, thermodynamic cycle, type of fuel used, ignition method, cooling system and valve location. The working of four-stroke petrol engines, four-stroke diesel engines, and two-stroke petrol and diesel engines are explained.
3) The key components, working cycles and strokes of different engine types are described in detail.Valve timing diagram



Valve timing diagramMdNoorruddin
╠²
Valve timing diagram is one of the most important topic about engine. This gives u the idea about how engine's valves should open and close. Knowing this u can make your engine more efficient and effective.Ic engine



Ic engineNFC Institute of engineering and fertilizer research Faisalabad
╠²
The document discusses key parts of internal combustion engines including pistons, valves, spark plugs, cam shafts and describes cylinder arrangements like inline-4 and V6. It also covers topics like engine size measured in cubic centimeters, overhead camshafts, and the four stroke combustion cycle. The summary provides an overview of internal combustion engines, their classification based on fuel type, ignition method, cylinder arrangement and other factors. It outlines the basic idea of how combustion drives the piston to convert the motion to a rotating crankshaft.Firing diagram



Firing diagramMaheshHerath3
╠²
This document discusses firing diagrams and intervals for single, two, three, and four cylinder engines. It explains that for four-stroke engines, the firing interval is 720┬░ divided by the number of cylinders, and for two-stroke engines it is 360┬░ divided by the number of cylinders. Diagrams are provided showing the firing order and interval for sample single, two, three, and four cylinder inline engines. Contact information is given at the end for further information.Lubrication System - IC Engine - Unit-III



Lubrication System - IC Engine - Unit-IIIS.Vijaya Bhaskar
╠²
The document discusses the purpose and components of engine lubrication systems. It describes three main types of lubrication systems - wet sump, dry sump, and mist lubrication. Wet sump systems are most common and utilize an oil pan and pump to circulate oil through the engine. Dry sump systems separate the oil reservoir from the engine using external tanks and pumps. Mist lubrication mixes oil with fuel for two-stroke engines. The properties, types, additives, and viscosity ratings of engine lubricating oils are also outlined.SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Power transmission system.pptx



SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Power transmission system.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
╠²
This document discusses the power transmission system of an internal combustion engine. It describes the key components that transmit power from the engine to the wheels, including the clutch, transmission gears, differential, final drive, rear axle, and rear wheels. The clutch connects and disconnects the engine from the transmission and can be friction, dog, or fluid types. Gears provide various speed ratios to suit field conditions. The differential allows the rear wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.2 fuel-supply-systems



2 fuel-supply-systemsNarender Kumar
╠²
The fuel supply system prepares fuel-air mixtures of different ratios for optimal engine performance under varying conditions. In a spark ignition engine, the carburetor mixes air and fuel outside the combustion chamber. It maintains the proper air-fuel ratio for starting, normal running, and acceleration using devices like floats, jets, and valves. In a diesel engine, only air is admitted into the combustion chamber and fuel is directly injected in spray form by the fuel injection system. Various compensation methods like extra air valves and multiple jets help the carburetor maintain the correct air-fuel ratio across different engine speeds and loads.Lubrication system



Lubrication systemAriful Hasan
╠²
1. The document discusses the lubrication system of an internal combustion engine. It defines lubrication as applying oil or grease to minimize friction between moving parts.
2. The main types of lubrication systems discussed are the petrol, wet-sump, and dry-sump systems. The wet-sump system can be a splash, pressure-feed, or combination system.
3. The components of a lubrication system discussed include the oil sump, filter, pump, galleries, cooler, and strainer. The pump circulates oil through the engine while the filter and strainer clean the oil.Valve timing diagram 



Valve timing diagram Rupesh Kumar
╠²
Valve timing is the precise timing of the opening and closing of valves in an internal combustion engine. It is controlled by the camshaft and can be varied by modifying the camshaft or using variable valve timing. With traditional fixed valve timing, engines experience a period of valve overlap when both intake and exhaust valves are open simultaneously. Variable valve timing uses computer control and oil pressure to advance or retard cam timing while the engine is running, changing valve duration, overlap, and sometimes lift. It has been implemented in many Japanese and European engines since the 1980s-1990s and more recently in some American engines.FOUR STROKE ENGINE



FOUR STROKE ENGINEshaffu786
╠²
The document discusses the history and workings of different types of engines. It describes how Nicolaus Otto invented the four-stroke engine in 1876. A four-stroke engine completes one cycle over four strokes and two revolutions of the crankshaft. It also describes how a two-stroke engine, invented in 1878 by Clerk, completes a cycle in one revolution due to the use of ports instead of valves.Spark and Compression Ignition Engines.pptx



Spark and Compression Ignition Engines.pptxnaseeruddinshah2
╠²
There are two main types of internal combustion engines: spark ignition engines (gasoline/petrol engines) and compression ignition engines (diesel engines). Spark ignition engines use a carburetor to mix air and fuel, which is then ignited by a spark plug. Compression ignition engines only draw in air, and fuel is injected at the end of the compression stroke and ignites due to the high temperature from compression. Both types of engines require a cooling system to remove excess heat from combustion and maintain optimal engine temperatures for efficient operation and protection of components like the cylinder and piston.Components of IC engines



Components of IC enginesSyed Yaseen
╠²
The main components of an internal combustion (IC) engine include the cylinder block, cylinder head, piston, cylinder, piston rings, connecting rod, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, fuel injector or spark plug, crankcase, and flywheel. The cylinder block forms the main structure and houses the cylinders, while the cylinder head covers the top of the cylinders and includes components like the valves and fuel injector. The piston is fitted inside the cylinder and transfers the force from combustion to the connecting rod. The connecting rod then converts the reciprocating motion of the piston to rotational motion through the crankshaft.TWO STROKE AND FOUR STROKE ENGINE PPT



TWO STROKE AND FOUR STROKE ENGINE PPTHanuwantSingh Dewal
╠²
This document provides information about 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. It defines a 2-stroke engine as completing its cycle in one crankshaft revolution, while a 4-stroke engine takes two revolutions. The basic parts of each engine are described, along with their working principles. Advantages of 2-stroke engines include higher power density, while disadvantages include lower fuel efficiency. A comparison notes that 4-stroke engines have higher volumetric efficiency but lower power density than 2-stroke engines.Basics of Gas Turbine Power Plant



Basics of Gas Turbine Power PlantS.Vijaya Bhaskar
╠²
Gas turbine plants use compressed air and combustion to drive a turbine and generate power. They have high efficiency, quick start-up times, and can use different fuels. The key components are an air compressor, combustor, and turbine connected by a common shaft. Air is compressed then mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustor. The hot gases drive the turbine which powers the compressor and generator. Axial compressors are commonly used due to their ability to deliver large air volumes at moderate pressures.Introduction of fuel system kvg



Introduction of fuel system kvgkaushal gadariya
╠²
This document provides an introduction to fuel systems for tractors and farm machinery. It defines fuel as a substance that produces energy when consumed by an engine. The key components and workings of fuel systems for spark ignition (SI) and compression ignition (diesel) engines are described. For SI engines, the fuel system includes a fuel tank, filter, carburetor and intake manifold. The carburetor mixes air and fuel. For diesel engines, the high-pressure system includes a fuel tank, filter, injection pump and injectors, which supply precisely metered fuel into the combustion chamber. Fuel quality and proper maintenance of filters are discussed as important for optimal system operation.Engine Components.pptx



Engine Components.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
╠²
The document describes the main components of an engine. It discusses 16 components including the cylinder, cylinder block, cylinder head, piston, connecting rod, crankshaft, camshaft, flywheel, crankcase, intake manifold, and exhaust manifold. The cylinder provides the combustion space where the piston operates. The connecting rod transmits power from the piston to the crankshaft. The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion. The camshaft opens and closes the intake and exhaust valves.Battery Ignition System



Battery Ignition SystemNikhil Londhe
╠²
The document discusses a battery ignition system for internal combustion engines. It consists of a battery, ignition switch, ballast resistor, ignition coil, contact breaker, capacitor, distributor, and spark plug. The ignition coil steps up the low voltage from the battery to a high voltage spark. When the contact points open, the current flows through the capacitor to induce a collapsing magnetic field in the coil, creating a high voltage spark in the spark plug. Battery ignition systems have advantages like fewer moving parts requiring less maintenance and improved fuel efficiency. Disadvantages include issues from contact point arcing over time. It is commonly used in modern vehicle and industrial engines.Petrol engine



Petrol engineyajurvendra tomar
╠²
A petrol engine, also known as a gasoline engine, works by burning fuel within cylinders to create motion. It uses the four-stroke cycle of intake, compression, power, and exhaust or the two-stroke cycle. In a four-stroke engine, the piston completes the cycle over two revolutions of the crankshaft, while a two-stroke engine completes the cycle in one revolution. Petrol engines are commonly used in automobiles but have lower efficiency than diesel engines due to their lower compression ratios.power transmission of tractor



power transmission of tractormahiii12345
╠²
This document summarizes the key components and functions of a tractor power transmission system. It discusses the basic components which include the clutch, gearbox, differential, final drive, and drive wheels. It then explains the purpose and operation of each component, including how the clutch connects and disconnects power, how the gearbox selects speeds and directions, how the differential equalizes power for turning, and how the final drive reduces speed and increases torque. The document also covers power take-off systems and the various types of tractor wheels and tires.Gas turbine



Gas turbinenaphis ahamad
╠²
A gas turbine uses a gaseous working fluid to generate mechanical power that can power industrial devices. It has three main parts - an air compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine. The air is compressed in the compressor, mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustion chamber, and the hot gases spin the turbine to generate power. Some applications of gas turbines include aviation, power generation, and the oil and gas industry. The efficiency of gas turbines is typically 20-30% compared to 38-48% for steam power plants.I.c. engines



I.c. enginesPartheshwarMishra
╠²
The document outlines the contents of a presentation on internal combustion engines. It includes sections on the introduction and classification of I.C. engines, components of I.C. engines, terminology used, and descriptions of the four stroke cycles of petrol and diesel engines. The key components of I.C. engines such as the cylinder, piston, crankshaft, valves and manifolds are defined. Advantages and disadvantages are provided for four stroke petrol and diesel engines.Mechanical technology lab report



Mechanical technology lab reportMuhammad Bilal
╠²
this lab report include details and demonstrations about internal combustion ( IC) engine. its types like CI and SI engines, different parts of engine, 2 stroke and 4 stroke engine. The ignition system of engine, cooling system of Engine and lubricating system of Engine in detail.More Related Content
What's hot (20)
I.C ENGINE PPT



I.C ENGINE PPTHOME
╠²
1) The document discusses the assembly, disassembly and maintenance of internal combustion (IC) engines. It covers the main components of IC engines like the cylinder block, cylinder head, piston, connecting rod, crankshaft and camshaft.
2) IC engines are classified based on their cycle of operation, thermodynamic cycle, type of fuel used, ignition method, cooling system and valve location. The working of four-stroke petrol engines, four-stroke diesel engines, and two-stroke petrol and diesel engines are explained.
3) The key components, working cycles and strokes of different engine types are described in detail.Valve timing diagram



Valve timing diagramMdNoorruddin
╠²
Valve timing diagram is one of the most important topic about engine. This gives u the idea about how engine's valves should open and close. Knowing this u can make your engine more efficient and effective.Ic engine



Ic engineNFC Institute of engineering and fertilizer research Faisalabad
╠²
The document discusses key parts of internal combustion engines including pistons, valves, spark plugs, cam shafts and describes cylinder arrangements like inline-4 and V6. It also covers topics like engine size measured in cubic centimeters, overhead camshafts, and the four stroke combustion cycle. The summary provides an overview of internal combustion engines, their classification based on fuel type, ignition method, cylinder arrangement and other factors. It outlines the basic idea of how combustion drives the piston to convert the motion to a rotating crankshaft.Firing diagram



Firing diagramMaheshHerath3
╠²
This document discusses firing diagrams and intervals for single, two, three, and four cylinder engines. It explains that for four-stroke engines, the firing interval is 720┬░ divided by the number of cylinders, and for two-stroke engines it is 360┬░ divided by the number of cylinders. Diagrams are provided showing the firing order and interval for sample single, two, three, and four cylinder inline engines. Contact information is given at the end for further information.Lubrication System - IC Engine - Unit-III



Lubrication System - IC Engine - Unit-IIIS.Vijaya Bhaskar
╠²
The document discusses the purpose and components of engine lubrication systems. It describes three main types of lubrication systems - wet sump, dry sump, and mist lubrication. Wet sump systems are most common and utilize an oil pan and pump to circulate oil through the engine. Dry sump systems separate the oil reservoir from the engine using external tanks and pumps. Mist lubrication mixes oil with fuel for two-stroke engines. The properties, types, additives, and viscosity ratings of engine lubricating oils are also outlined.SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Power transmission system.pptx



SYSTEMS OF IC ENGINE- Power transmission system.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
╠²
This document discusses the power transmission system of an internal combustion engine. It describes the key components that transmit power from the engine to the wheels, including the clutch, transmission gears, differential, final drive, rear axle, and rear wheels. The clutch connects and disconnects the engine from the transmission and can be friction, dog, or fluid types. Gears provide various speed ratios to suit field conditions. The differential allows the rear wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns.2 fuel-supply-systems



2 fuel-supply-systemsNarender Kumar
╠²
The fuel supply system prepares fuel-air mixtures of different ratios for optimal engine performance under varying conditions. In a spark ignition engine, the carburetor mixes air and fuel outside the combustion chamber. It maintains the proper air-fuel ratio for starting, normal running, and acceleration using devices like floats, jets, and valves. In a diesel engine, only air is admitted into the combustion chamber and fuel is directly injected in spray form by the fuel injection system. Various compensation methods like extra air valves and multiple jets help the carburetor maintain the correct air-fuel ratio across different engine speeds and loads.Lubrication system



Lubrication systemAriful Hasan
╠²
1. The document discusses the lubrication system of an internal combustion engine. It defines lubrication as applying oil or grease to minimize friction between moving parts.
2. The main types of lubrication systems discussed are the petrol, wet-sump, and dry-sump systems. The wet-sump system can be a splash, pressure-feed, or combination system.
3. The components of a lubrication system discussed include the oil sump, filter, pump, galleries, cooler, and strainer. The pump circulates oil through the engine while the filter and strainer clean the oil.Valve timing diagram 



Valve timing diagram Rupesh Kumar
╠²
Valve timing is the precise timing of the opening and closing of valves in an internal combustion engine. It is controlled by the camshaft and can be varied by modifying the camshaft or using variable valve timing. With traditional fixed valve timing, engines experience a period of valve overlap when both intake and exhaust valves are open simultaneously. Variable valve timing uses computer control and oil pressure to advance or retard cam timing while the engine is running, changing valve duration, overlap, and sometimes lift. It has been implemented in many Japanese and European engines since the 1980s-1990s and more recently in some American engines.FOUR STROKE ENGINE



FOUR STROKE ENGINEshaffu786
╠²
The document discusses the history and workings of different types of engines. It describes how Nicolaus Otto invented the four-stroke engine in 1876. A four-stroke engine completes one cycle over four strokes and two revolutions of the crankshaft. It also describes how a two-stroke engine, invented in 1878 by Clerk, completes a cycle in one revolution due to the use of ports instead of valves.Spark and Compression Ignition Engines.pptx



Spark and Compression Ignition Engines.pptxnaseeruddinshah2
╠²
There are two main types of internal combustion engines: spark ignition engines (gasoline/petrol engines) and compression ignition engines (diesel engines). Spark ignition engines use a carburetor to mix air and fuel, which is then ignited by a spark plug. Compression ignition engines only draw in air, and fuel is injected at the end of the compression stroke and ignites due to the high temperature from compression. Both types of engines require a cooling system to remove excess heat from combustion and maintain optimal engine temperatures for efficient operation and protection of components like the cylinder and piston.Components of IC engines



Components of IC enginesSyed Yaseen
╠²
The main components of an internal combustion (IC) engine include the cylinder block, cylinder head, piston, cylinder, piston rings, connecting rod, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, fuel injector or spark plug, crankcase, and flywheel. The cylinder block forms the main structure and houses the cylinders, while the cylinder head covers the top of the cylinders and includes components like the valves and fuel injector. The piston is fitted inside the cylinder and transfers the force from combustion to the connecting rod. The connecting rod then converts the reciprocating motion of the piston to rotational motion through the crankshaft.TWO STROKE AND FOUR STROKE ENGINE PPT



TWO STROKE AND FOUR STROKE ENGINE PPTHanuwantSingh Dewal
╠²
This document provides information about 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines. It defines a 2-stroke engine as completing its cycle in one crankshaft revolution, while a 4-stroke engine takes two revolutions. The basic parts of each engine are described, along with their working principles. Advantages of 2-stroke engines include higher power density, while disadvantages include lower fuel efficiency. A comparison notes that 4-stroke engines have higher volumetric efficiency but lower power density than 2-stroke engines.Basics of Gas Turbine Power Plant



Basics of Gas Turbine Power PlantS.Vijaya Bhaskar
╠²
Gas turbine plants use compressed air and combustion to drive a turbine and generate power. They have high efficiency, quick start-up times, and can use different fuels. The key components are an air compressor, combustor, and turbine connected by a common shaft. Air is compressed then mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustor. The hot gases drive the turbine which powers the compressor and generator. Axial compressors are commonly used due to their ability to deliver large air volumes at moderate pressures.Introduction of fuel system kvg



Introduction of fuel system kvgkaushal gadariya
╠²
This document provides an introduction to fuel systems for tractors and farm machinery. It defines fuel as a substance that produces energy when consumed by an engine. The key components and workings of fuel systems for spark ignition (SI) and compression ignition (diesel) engines are described. For SI engines, the fuel system includes a fuel tank, filter, carburetor and intake manifold. The carburetor mixes air and fuel. For diesel engines, the high-pressure system includes a fuel tank, filter, injection pump and injectors, which supply precisely metered fuel into the combustion chamber. Fuel quality and proper maintenance of filters are discussed as important for optimal system operation.Engine Components.pptx



Engine Components.pptxAjay Singh Lodhi
╠²
The document describes the main components of an engine. It discusses 16 components including the cylinder, cylinder block, cylinder head, piston, connecting rod, crankshaft, camshaft, flywheel, crankcase, intake manifold, and exhaust manifold. The cylinder provides the combustion space where the piston operates. The connecting rod transmits power from the piston to the crankshaft. The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion. The camshaft opens and closes the intake and exhaust valves.Battery Ignition System



Battery Ignition SystemNikhil Londhe
╠²
The document discusses a battery ignition system for internal combustion engines. It consists of a battery, ignition switch, ballast resistor, ignition coil, contact breaker, capacitor, distributor, and spark plug. The ignition coil steps up the low voltage from the battery to a high voltage spark. When the contact points open, the current flows through the capacitor to induce a collapsing magnetic field in the coil, creating a high voltage spark in the spark plug. Battery ignition systems have advantages like fewer moving parts requiring less maintenance and improved fuel efficiency. Disadvantages include issues from contact point arcing over time. It is commonly used in modern vehicle and industrial engines.Petrol engine



Petrol engineyajurvendra tomar
╠²
A petrol engine, also known as a gasoline engine, works by burning fuel within cylinders to create motion. It uses the four-stroke cycle of intake, compression, power, and exhaust or the two-stroke cycle. In a four-stroke engine, the piston completes the cycle over two revolutions of the crankshaft, while a two-stroke engine completes the cycle in one revolution. Petrol engines are commonly used in automobiles but have lower efficiency than diesel engines due to their lower compression ratios.power transmission of tractor



power transmission of tractormahiii12345
╠²
This document summarizes the key components and functions of a tractor power transmission system. It discusses the basic components which include the clutch, gearbox, differential, final drive, and drive wheels. It then explains the purpose and operation of each component, including how the clutch connects and disconnects power, how the gearbox selects speeds and directions, how the differential equalizes power for turning, and how the final drive reduces speed and increases torque. The document also covers power take-off systems and the various types of tractor wheels and tires.Gas turbine



Gas turbinenaphis ahamad
╠²
A gas turbine uses a gaseous working fluid to generate mechanical power that can power industrial devices. It has three main parts - an air compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine. The air is compressed in the compressor, mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustion chamber, and the hot gases spin the turbine to generate power. Some applications of gas turbines include aviation, power generation, and the oil and gas industry. The efficiency of gas turbines is typically 20-30% compared to 38-48% for steam power plants.Similar to classification of Internal combustion engines (20)
I.c. engines



I.c. enginesPartheshwarMishra
╠²
The document outlines the contents of a presentation on internal combustion engines. It includes sections on the introduction and classification of I.C. engines, components of I.C. engines, terminology used, and descriptions of the four stroke cycles of petrol and diesel engines. The key components of I.C. engines such as the cylinder, piston, crankshaft, valves and manifolds are defined. Advantages and disadvantages are provided for four stroke petrol and diesel engines.Mechanical technology lab report



Mechanical technology lab reportMuhammad Bilal
╠²
this lab report include details and demonstrations about internal combustion ( IC) engine. its types like CI and SI engines, different parts of engine, 2 stroke and 4 stroke engine. The ignition system of engine, cooling system of Engine and lubricating system of Engine in detail.Basics of ic engine 



Basics of ic engine Nandeshwor Chaudhary
╠²
The document provides information on the basics of internal combustion (IC) engines. It discusses the differences between two-stroke and four-stroke engines, the sequence of operations in an IC engine cycle, valve timing diagrams for petrol and diesel engines, and comparisons of petrol and diesel engines. It also covers topics like scavenging, ignition systems, supercharging, lubrication, governing, carburetors, spark plugs, detonation, and octane ratings of fuels for spark ignition engines.IC Engine.pptx



IC Engine.pptxHrBhupendra
╠²
This document provides an overview of farm machinery engine systems. It discusses the classification and components of internal combustion engines, including differences between two-stroke and four-stroke engines. The fuel, lubrication, ignition, cooling and governor systems are also mentioned. Tractor systems such as power transmission, steering, brakes and hydraulics are briefly covered. The summary discusses the key components and cycles of petrol and diesel engines in 2-3 sentences.Automobile 2 and 11 marks unit i and ii



Automobile 2 and 11 marks unit i and iiDasarathan Thandapani
╠²
This document provides a summary of a mechanical engineering document on automobile engineering. It includes 2 mark and 11 mark questions and answers on topics related to internal combustion engines. Some key details include:
- Components of engines like the cylinder block, cylinder head, crankcase, pistons and more are listed.
- The major types of automobiles based on fuel used are defined.
- Drive types like front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive are classified.
- Differences between SI and CI engines are outlined regarding fuel, compression ratio, operating cycle and efficiency.
- Four-stroke and two-stroke engines are explained with diagrams showing engine components and cycles.Basic Diesel Engine SANY_KOEL.PDF



Basic Diesel Engine SANY_KOEL.PDFAvinashSilimkar2
╠²
The document provides information about diesel engines, including:
1. It describes the basics of how diesel engines work by compressing hot air to ignite fuel without a spark plug.
2. It compares diesel engines to petrol engines, noting that diesels are heavier, have no carburetor, run on cheaper fuel, and are more efficient.
3. It explains the four stroke cycle of intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes and defines key engine components and systems like the air, lubrication, cooling, and fuel systems.Four stroke engine pro



Four stroke engine proCH.PURUSHOTHAM (Aeronautical Engineering)
╠²
The document discusses the four-stroke engine cycle and its key components. It describes the four strokes of intake, compression, power, and exhaust. It then lists and describes the main engine parts, including the cylinder block, pistons and piston rings, spark plug, valves, connecting rod and crankshaft, injector, camshaft, and sump. The core function of these parts is to intake air and fuel, compress it, ignite it to create power, and exhaust spent gases in the four-stroke cycle.ENGINE POWER PETROL REPORT-AE 215-SOURCES OF FARM POWER



ENGINE POWER PETROL REPORT-AE 215-SOURCES OF FARM POWERmusadoto
╠²
What is an Engine?
Before knowing about how the Petrol Engine works, let's first understand what an engine is. This is common for both petrol and diesel engines alike. An engine is a power generating machine which converts potential energy of the fuel into heat energy and then into motion. It produces power and also runs on its own power.
The engine generates its power by burning the fuel in a self-regulated and controlled ŌĆ×CombustionŌƤ process. The combustion process involves many sub-processes which burn the fuel efficiently and results in the smooth running of the engine.
These processes include:
The suction of air (also known as breathing or aspiration).
Mixing of the fuel with air after breaking the liquid fuel into highly atomized / mist form.
Igniting the air-fuel mixture with a spark (petrol engine).
Burning of highly atomized fuel particles which results in releasing / ejection of heat energy.
How does an Engine work?
The engine converts Heat Energy into Kinetic Energy in the form of ŌĆ×Reciprocating MotionŌƤ. The expansion of heated gases and their forces act on the engine pistons. The gases push the pistons downwards which results in reciprocating motion of pistons.
This motion of the piston enables the crank-shaft to rotate. Thus, it finally converts the reciprocating motion into the 'Rotary motion' and passes on to wheels.
A petrol engine (known as a gasoline engine in American English) is an internal combustion engine with spark-ignition, designed to run on petrol (gasoline) and similar volatile fuels.
In most petrol engines, the fuel and air are usually mixed after compression (although some modern petrol engines now use cylinder-direct petrol injection). The pre-mixing was formerly done in a carburetor, but now it is done by electronically controlled fuel injection, except in small engines where the cost/complication of electronics does not justify the added engine efficiency. The process differs from a diesel engine in the method of mixing the fuel and air, and in using spark plugs to initiate the combustion process. In a diesel engine, only air is compressedIcengine ppt



Icengine pptmohan narayanan
╠²
This document provides an overview of internal combustion engines. It discusses the classification of IC engines based on fuel used, thermodynamic cycle, number of strokes, ignition method, cooling method, speed, number of cylinders, and cylinder position. It describes the four-stroke cycles of Otto petrol and diesel engines. The key differences between petrol and diesel engines are outlined. The document also compares two-stroke and four-stroke engines, discussing their cycles, revolutions, power strokes, flywheels, ports/valves, lubrication, efficiencies, and applications. Indicated power, mechanical efficiency, thermal efficiency, and specific fuel consumption are defined.Aeng 251 farm machinery and power precise



Aeng 251 farm machinery and power preciseANFAS KT
╠²
The document provides information on various systems of a tractor, including:
- The power transmission system which reduces engine speed and transmits power to the rear wheels. It includes a clutch to connect and disconnect the engine from transmission gears.
- The cooling system which uses forced circulation of water through an engine water jacket and radiator to cool the engine.
- The lubrication system which supplies oil under pressure to engine parts like the crankshaft and cylinder walls for cooling, sealing, and cleaning effects.VCR ENGINE PROJECT PART 2



VCR ENGINE PROJECT PART 2MILAN HAZRA
╠²
1. INTRODUCTION TO IC ENGINE
2. FUNDAMENTALS OF IC ENGINE
3. CONSTRUCTIONAL FEATURES & FUNCTIONS OF IC ENGINE
4. MATERIALS USED
5.IC ENGINE ŌĆō TERMINOLOGY
6.SEQUENCE OF OPERATION(A. Four Stroke Engine/B. Two Stroke Engine)
7. COMPARISON BETWEEN TWO STROKE AND FOUR STROKE ENGINES
8.Otto Cycle,Diesel Cycle,Dual Cycle & their Comparison
9.VALVE TIMING DIAGRAM
10.ENGINE PERFORMANCE PARAMETERS RELATED TO IC ENGINE
11. CHARACTERISTICS CURVES OF VARIOUS PERFORMANCE PARAMETERS
12. FUEL-AIR CYCLE & THEIR ANALYSIS ( 1.Brake Specific Fuel Consumption vs Size 2. Brake Specific Fuel Consumption vs Speed 3. Performance Maps )
13. ACTUAL INDICATOR DIAGRAM
14. V.C.R ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS & ITS DESCRIPTION
15. FUTURE WORKS & DISCUSSION
16. CONCLUSION
Advancement of IC engine



Advancement of IC enginePrakash Giri
╠²
The document discusses the advancement of internal combustion engines. It covers topics like the classification of IC engines based on combustion and strokes. Major areas of advancement discussed include engine design, material selection, timing controls, fuels and fuel injection systems, and pollution control. Some specific technologies covered are variable valve timing, direct injection, superchargers, turbochargers, six-stroke engines, and methods to reduce air pollution from engines like catalytic converters. The goals of engine advancement are listed as higher power, better fuel efficiency, lower emissions and weight.Lab report 



Lab report Taimur Muhammad
╠²
This document contains a thermodynamics lab report submitted by a mechanical engineering student. The report summarizes 11 experiments conducted in the thermodynamics lab, including demonstrations of internal combustion engine components and systems, different engine types, and measurements. It also includes detailed descriptions of 3 specific experiments on introducing the lab and layout, demonstrating main engine components, and demonstrating 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines.diesel power station



diesel power stationAbdul Chhipa
╠²
1) The document describes the components and working of a diesel power station, which uses a diesel engine as the prime mover to power an alternator and generate electrical energy.
2) It explains the key systems involved - the fuel supply system, air intake system, exhaust system, cooling system, lubricating system and starting system.
3) Diesel power stations can be used as central stations for small/medium power supplies or as stand-by plants for emergency power during outages of main power sources.Two stroke & Four stroke Diesel Engine



Two stroke & Four stroke Diesel EngineDhrumil Maniar
╠²
The document discusses internal combustion engines. It defines them as engines where combustion occurs inside the engine cylinder. It then describes the basic parts of an I.C. engine like the cylinder, piston, crankshaft. It explains the differences between a 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine and how their cycles work. A 2-stroke engine completes one cycle per revolution while a 4-stroke takes two revolutions. It provides details on the workings and compares the advantages and disadvantages of 2-stroke and 4-stroke diesel engines.IC Engines



IC EnginesAbdulhakim Mobin
╠²
Internal Combustion Engine
There are two main types of heat engines: internal combustion engines and external combustion engines. In an internal combustion engine, fuel combustion occurs inside the engine cylinder and the hot gases directly power the piston. This includes gasoline/petrol engines. The four strokes of a petrol engine are: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. In the intake stroke, air/fuel mixture enters the cylinder. In the compression stroke, the mixture is compressed. In the power stroke, combustion powers the piston. In the exhaust stroke, spent gases are pushed out.Bike Engines-Two Stroke/Four Stroke Engines Classification



Bike Engines-Two Stroke/Four Stroke Engines ClassificationBike Jinni
╠²
BikeJinni - Bike Engines Classification. Two Stroke/Four Stroke Engines. Engine technical terms. Type of design in Bike Engines. Engine Cooling Systems, spark plug, Working of bike engines.Components & Systems of IC Engine lec-3 fmp211.pptx



Components & Systems of IC Engine lec-3 fmp211.pptxEr.A. Sivarajan
╠²
The document summarizes the key components of an internal combustion engine, including:
1. The cylinder, cylinder block, cylinder head, piston, piston rings, piston pin, connecting rod, crankshaft, flywheel, crankcase, camshaft, and timing gear.
2. It describes the different systems of an IC engine, including the fuel supply system, lubrication system, ignition system, cooling system, and governor system.
3. It provides details on the lubrication system, specifically the types of lubricants and engine lubrication systems like petroil, splash, pressure, semi-pressure, dry sump, and wet sump systems.IC ENGINES.pptx



IC ENGINES.pptxEVINSMANOJ1
╠²
The document provides information on internal combustion engines. It discusses the key components and workings of both spark ignition (SI) and compression ignition (CI) engines.
SI engines use an electric spark to ignite an air-fuel mixture, as in gasoline engines. CI engines compress air to a high temperature and pressure and inject fuel to ignite it, as in diesel engines.
The document also summarizes the four strokes of a four-stroke engine - intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes - and how a two-stroke engine combines the strokes into single revolutions.Recently uploaded (20)
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping



Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports TapingKusal Goonewardena
╠²
Mastering Soft Tissue Therapy & Sports Taping: Pathway to Sports Medicine Excellence
This presentation was delivered in Colombo, Sri Lanka, at the Institute of Sports Medicine to an audience of sports physiotherapists, exercise scientists, athletic trainers, and healthcare professionals. Led by Kusal Goonewardena (PhD Candidate - Muscle Fatigue, APA Titled Sports & Exercise Physiotherapist) and Gayath Jayasinghe (Sports Scientist), the session provided comprehensive training on soft tissue assessment, treatment techniques, and essential sports taping methods.
Key topics covered:
Ō£ģ Soft Tissue Therapy ŌĆō The science behind muscle, fascia, and joint assessment for optimal treatment outcomes.
Ō£ģ Sports Taping Techniques ŌĆō Practical applications for injury prevention and rehabilitation, including ankle, knee, shoulder, thoracic, and cervical spine taping.
Ō£ģ Sports Trainer Level 1 Course by Sports Medicine Australia ŌĆō A gateway to professional development, career opportunities, and working in Australia.
This training mirrors the Elite Akademy Sports Medicine standards, ensuring evidence-based approaches to injury management and athlete care.
If you are a sports professional looking to enhance your clinical skills and open doors to global opportunities, this presentation is for you.Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptx



Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics.pptxSamruddhi Khonde
╠²
¤ōó Comprehensive Guide to Antibiotics & Beta-Lactam Antibiotics
¤ö¼ Antibiotics have revolutionized medicine, playing a crucial role in combating bacterial infections. Among them, Beta-Lactam antibiotics remain the most widely used class due to their effectiveness against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This guide provides a detailed overview of their history, classification, chemical structures, mode of action, resistance mechanisms, SAR, and clinical applications.
¤ōī What YouŌĆÖll Learn in This Presentation
Ō£ģ History & Evolution of Antibiotics
Ō£ģ Cell Wall Structure of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria
Ō£ģ Beta-Lactam Antibiotics: Classification & Subtypes
Ō£ģ Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems & Monobactams
Ō£ģ Mode of Action (MOA) & Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
Ō£ģ Beta-Lactamase Inhibitors & Resistance Mechanisms
Ō£ģ Clinical Applications & Challenges.
¤ÜĆ Why You Should Check This Out?
Essential for pharmacy, medical & life sciences students.
Provides insights into antibiotic resistance & pharmaceutical trends.
Useful for healthcare professionals & researchers in drug discovery.
¤æē Swipe through & explore the world of antibiotics today!
¤öö Like, Share & Follow for more in-depth pharma insights!Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar ║▌║▌▀Żs



Helping Autistic Girls Shine Webinar ║▌║▌▀ŻsPooky Knightsmith
╠²
For more information about my speaking and training work, visit: https://www.pookyknightsmith.com/speaking/Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptx



Unit 1 Computer Hardware for Educational Computing.pptxRomaSmart1
╠²
Computers have revolutionized various sectors, including education, by enhancing learning experiences and making information more accessible. This presentation, "Computer Hardware for Educational Computing," introduces the fundamental aspects of computers, including their definition, characteristics, classification, and significance in the educational domain. Understanding these concepts helps educators and students leverage technology for more effective learning.Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...



Hannah Borhan and Pietro Gagliardi OECD present 'From classroom to community ...EduSkills OECD
╠²
Hannah Borhan, Research Assistant, OECD Education and Skills Directorate and Pietro Gagliardi, Policy Analyst, OECD Public Governance Directorate present at the OECD webinar 'From classroom to community engagement: Promoting active citizenship among young people" on 25 February 2025. You can find the recording of the webinar on the website https://oecdedutoday.com/webinars/
Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptx



Dr. Ansari Khurshid Ahmed- Factors affecting Validity of a Test.pptxKhurshid Ahmed Ansari
╠²
Validity is an important characteristic of a test. A test having low validity is of little use. Validity is the accuracy with which a test measures whatever it is supposed to measure. Validity can be low, moderate or high. There are many factors which affect the validity of a test. If these factors are controlled, then the validity of the test can be maintained to a high level. In the power point presentation, factors affecting validity are discussed with the help of concrete examples.How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 Sales



How to Configure Deliver Content by Email in Odoo 18 SalesCeline George
╠²
In this slide, weŌĆÖll discuss on how to configure proforma invoice in Odoo 18 Sales module. A proforma invoice is a preliminary invoice that serves as a commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer.Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptx



Interim Guidelines for PMES-DM-17-2025-PPT.pptxsirjeromemanansala
╠²
This is the latest issuance on PMES as replacement of RPMS. Kindly message me to gain full access of the presentation. NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdf



NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION - 5TH SEM.pdfDolisha Warbi
╠²
NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT AND EDUCATION, Introduction, definition, types - macronutrient and micronutrient, food pyramid, meal planning, nutritional assessment of individual, family and community by using appropriate method, nutrition education, nutritional rehabilitation, nutritional deficiency disorder, law/policies regarding nutrition in India, food hygiene, food fortification, food handling and storage, food preservation, food preparation, food purchase, food consumption, food borne diseases, food poisoningDot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Dot NET Core Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatFull-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHat



Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatScholarhat
╠²
Full-Stack .NET Developer Interview Questions PDF By ScholarHatASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By Scholarhat



ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatScholarhat
╠²
ASP.NET Web API Interview Questions By ScholarhatMeeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoy



Meeting the needs of modern students?, Selina McCoyEconomic and Social Research Institute
╠²
NAPD Annual Symposium
ŌĆ£Equity in our Schools: Does the system deliver for all young people?ŌĆØInventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory App



Inventory Reporting in Odoo 17 - Odoo 17 Inventory AppCeline George
╠²
This slide will helps us to efficiently create detailed reports of different records defined in its modules, both analytical and quantitative, with Odoo 17 ERP.classification of Internal combustion engines
- 1. AENG 251- Farm Power and Machinery Er. N. Hari Assistant professor Department of Agricultural Engineering Agricultural College, Aswaraopet PROF. JAYASHANKAR TELANGANA STATE AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY Rajendranagar, Hyderabad ŌĆō 500 030
- 2. classified in two types They are four stroke and two stroke engines. 1. When the cycle is completed in two revolutions of the crankshaft, it is called four stroke cycle engines. 2. When the cycle is completed in one revolution of the crankshaft, it is called two stroke cycle engines. classification of Internal combustion engines
- 3. I.C. engines are of two types: (i) Petrol engine (carburetor type, spark ignition engine), and (ii) diesel engine (compression ignition engine). Petrol engine: It is the engine, in which liquid fuel is atomized, vaporized and mixed with air in correct proportion before entering onto the engine cylinder during suction stroke. The fuel is ignited in the cylinder by an electric spark. Diesel engine: In this engine, during suction stroke, only air is entered into the cylinder and compressed. The fuel is injected through fuel injectors and ignited by heat of compression.
- 4. ’āś Eco-friendly: It is also known to be eco-friendly as it helps to shorten the amount of carbon monoxide released into the air. ’āś Efficient Properties: compared to other types of fuels diesel engine has a better burning properties. ’āś Durable: this engine requires less maintenance so it tends to last for a long period of time and this are also considerably durable compared to its counterparts. ’āś Less Noisy and Compact: This is another advantage of these engines because it is less noisy and compact in size. Features of Diesel Engine
- 5. Working components of I.C.Engine
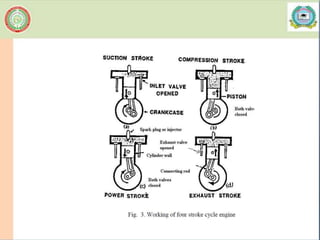
- 6. Working of two stroke cycle engine
- 8. Scavenging: The process of removal of burnt or exhaust gases from the engine cylinder is known as scavenging. Entire burnt gases do not go out in normal stroke, hence some type of blower or compressor is used to remove the exhaust gases in two stroke cycle engine. When the piston is at the top of its stroke, it is said to be at the top dead centre (TDC). When the piston is at the bottom of its stroke, it is said to be at its bottom dead centre (BDC). In two stroke cycle engine.
- 14. Key points ’é¦ The pressure in the engine cylinder is less than atmospheric pressure during this stroke in Suction stroke ’é¦Both valves are closed during this stroke in Compression stroke ’é¦there is only one power stroke and three idle strokes. ’é¦Scavenging: The process of removal of burnt or exhaust gases from the engine cylinder is known as scavenging. ’é¦Thermal efficiency varies between 32 and 38% in Diesel engine ’é¦Thermal efficiency varies between 25 and 32% in Petrol engine







