Cloud computing
- 1. SUBMITED BY:- Harsh Soni • Cloud computing
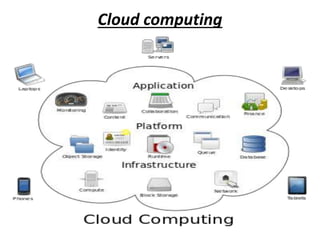
- 2. Cloud computing Cloud computing is the delivery of services of the computing a service rather than a product, whereby shared resources, software, and information are provided to computers and other devices as a utility (like the electricity grid) over a network (typically the Internet). Clouds can be classified as public, private or hybrid.
- 4. Cloud Deployment Models •Public • Private •Hybrid •Community
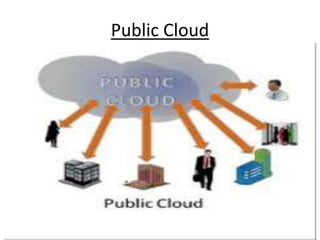
- 5. Public Cloud • A public cloud is a cloud computing model in which services, such as applications and storage, are available for general use over the Internet. Public cloud services may be offered on a pay-per-usage mode or other purchasing models. An example of a public cloud is IBM’s Blue Cloud.
- 6. Public Cloud
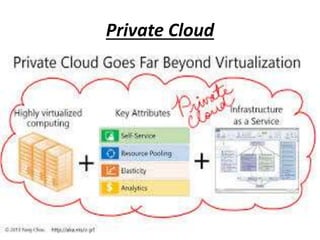
- 7. Private Cloud • A private cloud is a virtualized data centre that operates within a firewall. Private clouds are highly virtualized, joined together by mass quantities of IT infrastructure into resource pools, and privately owned and managed.
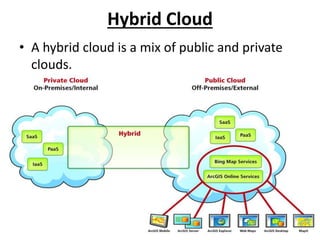
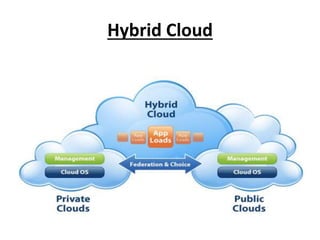
- 9. Hybrid Cloud • A hybrid cloud is a mix of public and private clouds.
- 10. Hybrid Cloud
- 11. Community Cloud • A community cloud is an infrastructure shared by several organizations which supports a specific community.
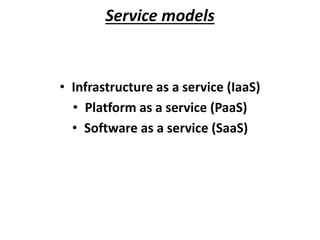
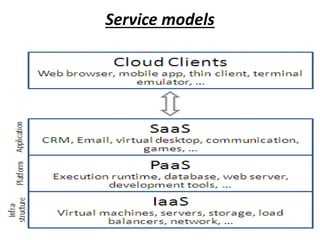
- 12. Service models • Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) • Platform as a service (PaaS) • Software as a service (SaaS)
- 13. Service models
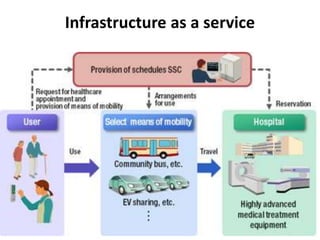
- 14. Infrastructure as a service • To deploy their applications, cloud users install operating-system images and their application software on the cloud infrastructure. In this model, the cloud user patches and maintains the operating systems and the application software. Cloud providers typically bill IaaS services on a utility computing basis: cost reflects the amount of resources allocated and consumed.
- 15. Infrastructure as a service
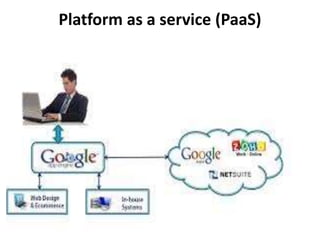
- 16. Platform as a service (PaaS) • In the PaaS models, cloud providers deliver a computing platform, typically including operating system, programming language execution environment, database, and web server. Application developers can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers. With some PaaS offers like Microsoft Azure and Google App Engine, the underlying computer and storage resources scale automatically to match application demand so that the cloud user does not have to allocate resources manually. The latter has also been proposed by an architecture aiming to facilitate real-time in cloud environments.
- 17. Platform as a service (PaaS)
- 18. Software as a service (SaaS) • In the business model using software as a service (SaaS), users are provided access to application software and databases. Cloud providers manage the infrastructure and platforms that run the applications. SaaS is sometimes referred to as "on-demand software" and is usually priced on a pay-per-use basis. SaaS providers generally price applications using a subscription fee.
- 19. Software as a service (SaaS)
- 20. BENEFITS OF CLOUD • Achieve economies of scale • Reduce spending on technology infrastructure. • Globalize your workforce on the cheap. • Streamline processes. • Reduce capital costs. • Improve accessibility • Monitor projects more effectively • Less personnel training is needed. • Minimize licensing new software • Improve flexibility.
- 21. Disadvantages of Cloud Computing • Possible downtime • Security issues. • Cost. • Inflexibility • Lack of support