cloudcomputing(bashu).ppt
- 1. GUIDED BY: ASST.PROF.ELINA PATTNAIK PRESENTED BY:- BASHU KUMAR NAYAK KRISHNA CHANDRA BAJORIA REGD NO.:1101292015 REGD NO.:1101292023 BRANCH:CSE BRANCH:CSE SEMESTER:6TH SEMESTER:6TH CLOUD COMPUTING
- 2. CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CLOUD COMPUTING HISTORY TYPES AND STRUCTURE SERVICE MODELS OF CLOUD COMPUTING APPLICATION ADVANTAGES CONCLUSION
- 3. What is Cloud computing “Cloud computing is a style of computing where massively scalable IT-related capabilities are provided as a service across the Internet to multiple external customers”
- 4. History of Cloud Computing 1960 : John McCarthy’s Concept 1999 : Salesforce.com 2000 : Microsoft 2001 : IBM “Computation may someday be organized as a public utility." “Pioneered the concept of delivering enterprise applications via a simple website” “Expanded Sass Concept through web service” 2005 : Amazon 2007 : Google and IBM 2008 : Gartner Research “Launch of Amazon web services” “Start researching Cloud Computing” “Start using Cloud Computing in many organization”
- 5. • Public cloud – suitable for applying to general systems not particular systems and serving massive clients and also cheap price. • Private cloud – suitable for particular systems or needed high security systems through cloud provider. • Hybrid cloud – this system is a composition of Public cloud and Private cloud. It also use for transferring data from one to another cloud. Types of cloud computing
- 6. What is Cloud computing - Structure Cloud Computing Structure User interaction interface Service catalog System management Provisioning toolMonitoring and metering Cloud Servers is how users of cloud interface with the cloud to request services is the list of services that a user can request is the piece which manages the resources available Carves out the systems from the cloud to deliver on the requested service Tracks the usage of the cloud so the resources used can be attributed to a certain user Virtual or physical servers managed by System management
- 7. Cloud Computing - Layers • Saas (Software as a Service) : Application is hosted by a provider and is accessible via the Web ; such as Google apps , Sales Force(CRM) • Paas (Platform as a Service) : Development in the cloud (web) ; such as Microsoft Azure , Google App Engine • Iaas (Infrastructure as a Service) : Computer infrastructure accessible via the web ; such as Amazon Web services , Rankspace cloud
- 8. Organization start to use – Private cloud services are run in datacenters managed by third parties, but also in private datacenters on company property managed by corporate IT staffs. – Corporate IT departments will create clouds within their IT infrastructure and lease cloud power to suppliers and customers. More scalable and customizable – They’re scalable, growing and shrinking as needed. They’re also managed centrally in a virtualized environment. – Cloud computing vendors will make their applications more customizable by end users. Then corporations will move mission-critical unique applications into the cloud. Trend of Cloud Computing
- 9. Cloud will be all desktop software, anyone can access – Local applications will become passé and PCs will become slimmer, more agile gateways to the cloud where the heavy lifting is done. – Business units and even individual employees will be able to control the processing of information directly, without the need for legions of technical specialists. Change from data sharing to application sharing – Cloud computing will develop effective and capable of communicating on the Internet has the potential to enhance the speed and stability of the exchange (Share) from the exchange of information (Data Share) to share in the applications (Application Share) on the cloud environment in the future. Trend of Cloud Computing
- 10. 1. Hybrid Clouds There might finally be an end to the heated debates over public cloud vs. private cloud architecture in enterprise IT. The rise of hybrid clouds – architectures that combine the security of private clouds with the powerful, scalable, and cost-effective benefits of public clouds — should encourage many businesses to adopt a cloud-based infrastructure. Hybrid clouds open up a range of customizable solutions for IT decision- makers, while keeping both security hawks and big data advocates happy. 2. The Industrial Internet Takes Off Look for the Industrial Internet (a.k.a. the Internet of Things) to start transforming operations in 2014, as solutions combining intelligent machines, big data analytics, and end-user applications begin to roll out across major industries. Cloud computing platforms will play a big role in creating the next generation of intelligent, software- defined machines that are operable and controllable entirely from centralized, remote locations. 3. Web-powered Apps If scalability and efficiency are among the key benefits of cloud computing, then developing cloud-based applications that are platform-agnostic is essential. With efforts like famo.us giving new life to HTML5 through JavaScript, the Web will become a major platform for cloud-based applications.
- 11. 4. BYOD and the Personal Cloud in Enterprise IT The BYOD movement is already hitting enterprise environments and is expected to expand in 2014. As end-users put more of their own data into personal cloud services for syncing, streaming, and storage, IT executives are finding ways to incorporate personal cloud services in the enterprise environment through techniques such as Mobile Device Management. 5. Platforms-as-a-Service Continue to Grow More companies will be looking to adopt PaaS solutions in the upcoming years. PaaS allows businesses to lower IT costs while speeding up application development through more efficient testing and deployment. According to analyst firm IDC, the PaaS market is expected to grow from $3.8 billion to $14 billion by 2017. 6. Graphics as a Service Running high-end graphics applications typically requires massive hardware infrastructure, but cloud computing is changing that. With emerging cloud-based graphics technologies by companies like AMD and NVIDIA, end-users will run graphically intense applications using nothing more than an HTML5 web browser.
- 12. 7. Identity Management in the Cloud Cloud services offer accessibility, convenience, high-power, and redundancy, but with cloud-based applications taking over businesses, there’s a need to rethink security policies. Look for identity management solutions to bring new paradigms of security to the cloud in 2014.
- 13. Applications of Cloud Computing Google App Engine Amazon EC2 & S3 Windows Azure Google App Panda Cloud Dropbox iCloud
- 14. Amazon Web Service  Amazon is the most widely known cloud vendor. Offering services on many different fronts, from storage to platform to databases. To have their finger in a number of cloud technologies. » Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) » Amazon Simple DB » Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) » Amazon CloudFront » Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS)
- 16. Amazon EC2 & S3 Amazon Web Service (AWS) Amazon EC2 Amazon S3 Storage OS Image (AMI) OS Image (AMI)
- 17. Google App Engine Google App Engine (GAE) is a platform for developing and hosting web applications in Google-managed data centers. (GAE is Platform as a Service : PaaS) .[1] GAE is a cloud computing technology. It virtualizes applications across multiple servers.[2]
- 18. Google App Engine Python Scripts Framework WebApp [Django] Source Code Use Develop Console User Web Browser Upload Script SDK 1 2 3 4 Cloud Computing Application Phyton Runtime Library Datastore Big Table Developer
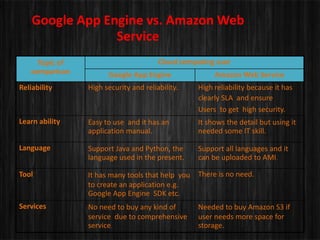
- 19. Google App Engine vs. Amazon Web Service Topic of comparison Cloud computing user Google App Engine Amazon Web Service Reliability High security and reliability. High reliability because it has clearly SLA and ensure Users to get high security. Learn ability Easy to use and it has an application manual. It shows the detail but using it needed some IT skill. Language Support Java and Python, the language used in the present. Support all languages and it can be uploaded to AMI. Tool It has many tools that help you to create an application e.g. Google App Engine SDK etc. There is no need. Services No need to buy any kind of service due to comprehensive service. Needed to buy Amazon S3 if user needs more space for storage.
- 20. ADVANTAGES 1.dynamic reallocation of resources 2.Shared services 3.Scale of economy 4.Reduce spending on technology infrasrtructure 5.Streamline processes 6.Minimize licensing new software
- 21. THREATS ON CLOUD COMPUTING 1.DATA BREACHES:-A data breach is an incident in which sensitive, protected or confidential data has potentially been viewed, stolen or used by an individual unauthorized to do so. Data breaches may involve personal health information (PHI), personally identifiable information (PII), trade secrets or intellectual property. 2.DATA LOSS & LEAKAGE:- With shared infrastructure resources, organizations should be concerned about the service provider's authentication systems that grant access to data. Organizations should also ask about encryption, data disposal procedures, and business continuity.
- 22. 3.ACCOUNT HIJACKING 4.INSECURE APPLICATION PROGRAMMING INTERFACE:- Application programming interfaces (API) are used to establish, manage, and monitor services. These interfaces may be subject to security vulnerabilities that put your users at risk. 5.DATA HANDLING 6.DENIAL OF SERVICE
- 23. CONCLUSION Cloud computing is a major development in information technology, comparable in importance with the mainframe, the minicomputer, the microprocessor, and the Internet. It has the potential to make an increasingly significant contribution to economic activity throughout the world. This potential will only be realized if cloud computing products and services are portable and interoperable.
- 25. Thank you ……… any queries ????
















![Google App Engine
Google App Engine (GAE) is a platform
for developing and hosting web
applications in Google-managed data
centers. (GAE is Platform as a Service :
PaaS) .[1]
GAE is a cloud computing technology.
It virtualizes applications across multiple
servers.[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bdcfadd8-a850-463a-9506-8ea0c923c664-151009123944-lva1-app6891/85/cloudcomputing-bashu-ppt-17-320.jpg)
![Google App Engine
Python Scripts
Framework WebApp [Django]
Source Code
Use
Develop
Console
User
Web Browser
Upload Script
SDK
1
2
3
4
Cloud Computing
Application
Phyton Runtime Library Datastore
Big Table
Developer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bdcfadd8-a850-463a-9506-8ea0c923c664-151009123944-lva1-app6891/85/cloudcomputing-bashu-ppt-18-320.jpg)