COARTACTION OF AORTA 6th Semester B.SC nursing
- 4. COARACTION OF AORTA A narrowing of the large blood vessel (aorta) that leads from the heart. TYPES:- ? Infantile or pre-ductal type. ? Post-ductal type.
- 6. CLINICAL FEATURES Increased blood pressure in the upper part of the body, result in: ? Headache. ? Dizziness. ? Nose bleed. ? Fainting. ? Cerebrovascular accident.(CVA) Decreased blood pressure in lower extremities results in: ? Absent or diminished femoral and pedal pulse.
- 7. ? Complaints of weakness or pain in legs on exercise. ? Failure to thrive. ? Respiratory distress. ? Poor weight gain. ? Feeding problems. ? Irritability. ? Tachycardia. ? Congestive heart failure. CLINICAL FEATURES
- 8. ? Mottling in lower extremities. ? Mottling of the skin, a lacy pattern of small reddish and pale areas. ? Due to instability of the blood circulation. CLINICAL FEATURES
- 10. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION ? Cardiac examination ? Electrocardiogram ? Chest radiograph ? Echocardiogram ? MRI & Catheterization.
- 11. SURGERY ? End to end anastomosis ? Subclavian flap aortoplasty ? Patch aortoplasty ? Balloon aortoplasty
- 13. ? Antibiotic prophylaxis. ? Cardiology follow up at least 1-2 years is recommended. MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
- 14. AORTIC STENOSIS
- 15. AORTIC STENOSIS ¡°Narrowing of the aortic valves¡± TYPES:- a. Valvular ¨C Stricture of aortic valve b. Sub-valvular stenosis- Below the valve. c. Supravalvular aortic stenosis ¨C Above the valve.
- 17. CLINICAL FEATURES ? Fatigue and exercise intolerance. ? Exertional dyspnea. ? Chest pain. ? Syncope. ? Infant with severe aortic stenosis present with cardiac failure in neonatal period or in first few month of life.
- 18. ? Due to obstruction of blood flow from left ventricle, cause thickening of left ventricular wall in response to increased workload to eject blood. ? Pressure increase in LV as severity in obstruction. ? Heart failure can develop due to excessive workload on LV.
- 19. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION ? Cardiac examination ? Electrocardiogram ? Cardiac catheterization ? Echocardiogram ? Chest radiograph
- 20. ? Child with mild to moderate stenosis don¡¯t need surgery. ? Unless their stenosis is progress. MANAGEMENT
- 21. Management of Valvular aortic stenosis 1. Aortic Balloon valvuloplasty. 2. Valvular aortic stenosis repaired through median sternotomy. *If the child shoes aortic insuffiency still- Aortic valve replacement to be one.*
- 22. b. In Sub-valvular aortic stenosis ? Konno procedure is done to remove the obstructing membrane and fibrous ring below the aortic valve and replacing the valve with artificial valve. MANAGEMENT
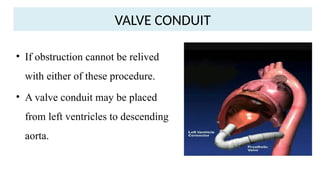
- 23. VALVE CONDUIT ? If obstruction cannot be relived with either of these procedure. ? A valve conduit may be placed from left ventricles to descending aorta.
- 24. c. In Supra-valvular aortic stenosis. ? Surgery is done by incising the narrow segment of aorta and widening the area with a patch graft. MANAGEMENT