Cofferdam
- 2. COFFERDAMS Ī░A cofferdam is a temporary structure designed to keep water and/or soil out of the excavation in which a bridge pier or other structure is builtĪ▒.
- 3. REQUIREMENTS ? Cofferdam should be reasonably watertight. ? Absolute water tightness is not desired in a cofferdam. ? Designed in maximum water level. ? Ground water or water lying above ground level should be excluded. ? Materials ©C earth , timber , steel & concrete. ? Constructed at site of work. ? Depend- depth , soil condition , difference in water level, availability of materials.
- 4. USES ? Pile driving operation. ? Place grillage & raft foundation. ? Construct new structures. ? Enclose space for removal. ? Constructing without disturbances.
- 5. FACTORS FOR CHOICE OF TYPE OF COFFERDAMS ?Area to be protected by a cofferdam. ?Depth of water to be dealt. ?Possibility of over topping. ?Nature of velocity of flow. ?Availability of materials at site of work. ?Easy transportation.
- 6. TYPES OF COFFERDAMS ? DIKES ? SINGLE WALL COFFRDAM ? DOBLE WALL COFFERDAMS ? CELLULAR COFFERDAMS ? ROCK-FILLED CRIB COFFERDAMS ? CONCRETE COFFERDAMS
- 7. DIKES Embankment of some materials. ? EARTH ? ROCK ? SAND-BAGS
- 8. EARTH DIKES ? Shallow depth of water 1200 - 1500 mm. ? Low velocity of flow ? Free board-1m. ? Suitable side slope. ? Top width of bank. ? Material-mixture of clay &sand. ? Puddle ©C best material . ? Rip rap ©C protected against wind & wave actions.
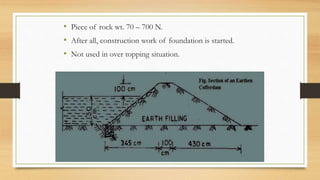
- 9. ? Piece of rock wt. 70 ©C 700 N. ? After all, construction work of foundation is started. ? Not used in over topping situation.
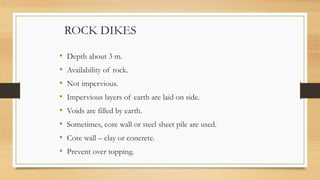
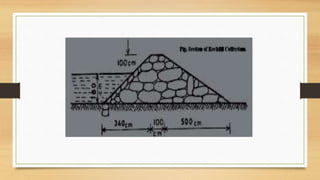
- 10. ROCK DIKES ? Depth about 3 m. ? Availability of rock. ? Not impervious. ? Impervious layers of earth are laid on side. ? Voids are filled by earth. ? Sometimes, core wall or steel sheet pile are used. ? Core wall ©C clay or concrete. ? Prevent over topping.
- 12. SAND ©C BAG DIKES ? Mixture of sand & clay in a bag. ? PRECAUTIONS ? Use empty cement bags. ? Voids of sand bag may exceed ©C 40%. ? Small depth. ? Joints filled with puddle.
- 13. SINGLE WALL COFFERDAM ? Preferred small area. ? Guide piles, wales , struts ©C wood. ? Sheet piles are of wood or steel. ? Wooden piles ©C depth about 10 m. ? More depth - steel piles( 25 m ).
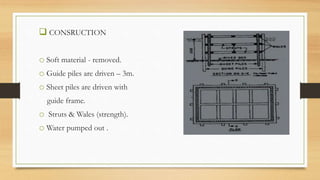
- 14. ? CONSRUCTION o Soft material - removed. o Guide piles are driven ©C 3m. o Sheet piles are driven with guide frame. o Struts & Wales (strength). o Water pumped out .
- 15. DOUBLE WALL COFFERDAMS ? In large area. ? Ohio river type & wood or steel sheeting cofferdam.
- 16. ?OHIO RIVER TYPE COFFERDAM ? Ohio river in USA. ? Used in hard & soft bed (no erosion). ? Unsuitable in deep water & swift flow. Construction ? Wales fixed at 1.50m vertically. ? Wale joints, double vertical planks are provided. ? Tie rods threaded & cross braces fixed. ? Fixes sheet piles. ? Berms (inside & outside) ? Removing safely.
- 17. ? WOOD OR STEEL SHEETING COFFERDAMS ? Depth ( 6-10 m) ? For small & ordinary type ? No possibility of driven of guide piles steel (depth) sheet piles are used. ? Tie rods connects guide piles.
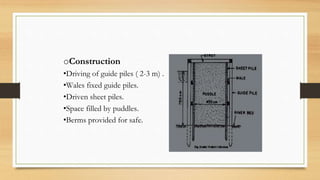
- 18. oConstruction ?Driving of guide piles ( 2-3 m) . ?Wales fixed guide piles. ?Driven sheet piles. ?Space filled by puddles. ?Berms provided for safe.
- 19. CELLULAR COFFERDAM ? Large areas. ? Steel sheet piles. ? Diaphragm cells & Circular cells.
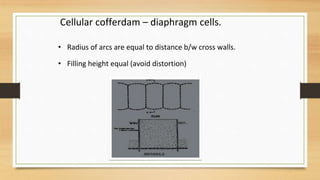
- 20. ? Radius of arcs are equal to distance b/w cross walls. ? Filling height equal (avoid distortion) Cellular cofferdam ©C diaphragm cells.
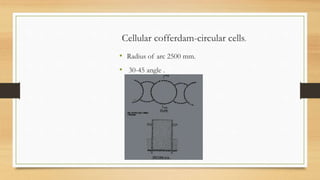
- 21. Cellular cofferdam-circular cells. ? Radius of arc 2500 mm. ? 30-45 angle .
- 22. ? Advantages ?Fast construction work of cells. ?Self-supporting unit. ?Less quantity of steel per running length (circular cells). ?Little false work is required.
- 23. ROCK FILLED CRIB COFFERDAM ? Crib is a box / a Cell open at bottom(timber). ? Rock / gravel / earth (overturning & sliding). ? Depth 10-20 m. ? Limited space. ? Cheap material (timber). ? Swift water flow.
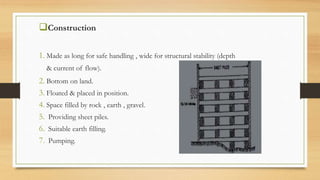
- 24. ?Construction 1. Made as long for safe handling , wide for structural stability (depth & current of flow). 2. Bottom on land. 3. Floated & placed in position. 4. Space filled by rock , earth , gravel. 5. Providing sheet piles. 6. Suitable earth filling. 7. Pumping.
- 25. CONCRETE COFFERDAM ? Frame work of precast R.C.C. piles & sheets. ? Driven as steel sheet piles. ? Disadvantage (COSTLY). ? Avoid vibration (pile foundation).
- 26. PREVENTION OF LEAKAGE IN COFFERDAM Leakage through sheet piling & under flow. ? Fissures / cracks of rock ©C Pumping cement grout by pipes (100mm dia ). ?Clay , sand , ashes etc. ©C dumped around cofferdam. ?Single wall cofferdam ©C Placing V- shaped wooden on outside & Filling puddles. ?Leakage in sheet piling ©C box(sawdust & ashes) hold near joints , leads to sealing.
- 27. ?Interlocks of steel sheet piles ©C grease. ?Double wall cofferdam ©C ? Driving piles through filling. ? Filling the holes with quick swelling material. ? Forcing clay cylinders for better compactness.
- 28. ADVANTAGES OF COFFERDAM ? Poor environment. ? Safe environment. ? Design responsibility. ? Easy work. ? Re-usability of materials.
- 29. PUDDLE FOR COFFERDAM o Clay & sand / clay & gravel. o Clay - cohesive & impermeable. ? Test for cohesive ©C 40 mm dia 250 mm length cylinder water(sufficient) .Suspended from one end(wet) ,not break-cohesion. ? Test for impermeability ©C Plastic mass spread ,water stored above . Water held for some time ©Cimpermeable. o Layers of 80 mm , well rammed (water should added).
- 30. FACTORS AFFECTING DESIGN OF A COFFERDAM ?Hydrostatic head of water ?Dimensions of area. ?Sub-soil condition. ?Fluctuations of outside water level. ?Possibility of erosion. ?Floating logs. ?Presence of ice.
- 31. CONCLUSION ?Purely theoretically cofferdam will fail reasonably. ?More than theory practical knowledge & experience are necessary for good construction of cofferdams.
- 32. ĪŁĪŁTHANK YOU