Cognitive Load Theory and Application in Teaching.pdf
- 1. Cognitive Load Theory and Application in Teaching Tanat Tabtieang MD FRCRT MHPE Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University
- 2. Cognitive Load Theory (CLT) ŌĆó Science of Learning ŌĆó Cognitive Load Theory (CLT) ŌĆó Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning ŌĆó CLT-based Lecture Model ŌĆó My Experience
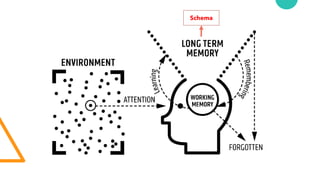
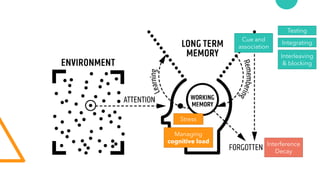
- 6. Schema
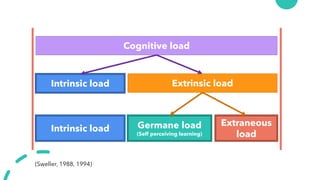
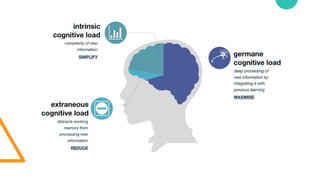
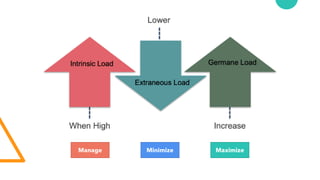
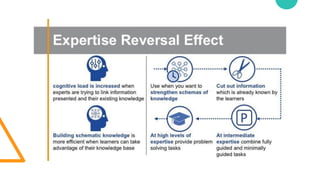
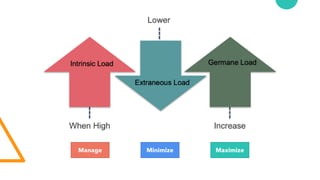
- 11. Intrinsic load Extrinsic load Germane load (Self perceiving learning) Extraneous load Cognitive load (Sweller, 1988, 1994) Intrinsic load
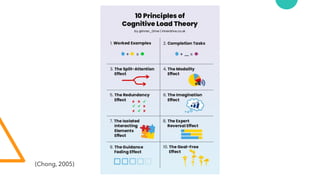
- 14. (Chong, 2005)
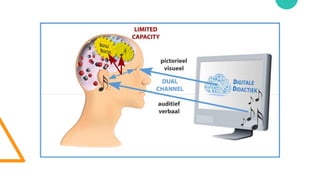
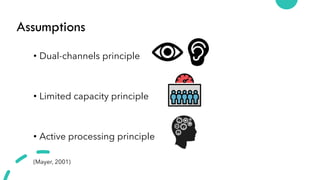
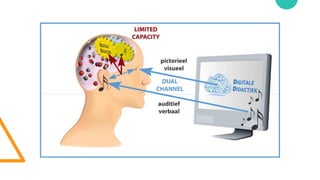
- 27. Assumptions ŌĆó Dual-channels principle ŌĆó Limited capacity principle ŌĆó Active processing principle (Mayer, 2001)
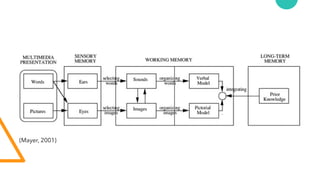
- 29. (Mayer, 2001)
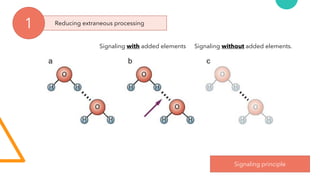
- 33. Reducing extraneous processing 1 Signaling principle Signaling with added elements Signaling without added elements.
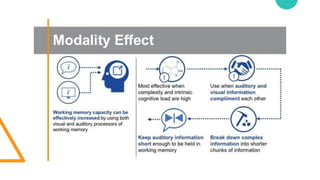
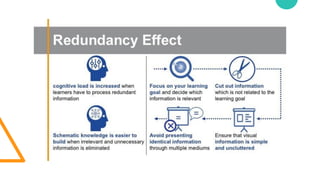
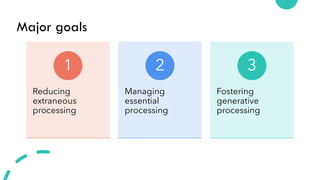
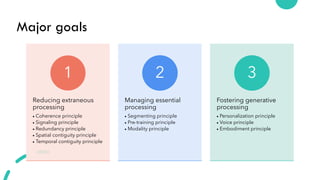
- 42. Major goals Reducing extraneous processing ŌĆó Coherence principle ŌĆó Signaling principle ŌĆó Redundancy principle ŌĆó Spatial contiguity principle ŌĆó Temporal contiguity principle 1 Managing essential processing ŌĆó Segmenting principle ŌĆó Pre-training principle ŌĆó Modality principle 2 Fostering generative processing ŌĆó Personalization principle ŌĆó Voice principle ŌĆó Embodiment principle 3
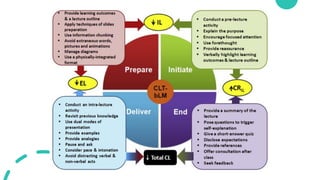
- 46. Prepare ŌĆó Provide learning outcome and a lecture outline ŌĆó Apply techniques for slide preparation ŌĆó Use information chunking ŌĆó Avoid extraneous elements ŌĆó Manage diagrams ŌĆó Use a physically integrated format
- 47. Initiate ŌĆó Conduct pre-lecture activities ŌĆó Explain the purpose ŌĆó Encourage focused attention ŌĆó Use forethought ŌĆó Provide reassurance ŌĆó Verbally highlight the learning outcomes and lecture outline
- 48. Deliver ŌĆó Conduct intra-lecture activities ŌĆó Revisit previously learned knowledge ŌĆó Use dual-mode presentation ŌĆó Provide examples ŌĆó Provide analogies ŌĆó Pause and ask ŌĆó Consider pace and intonation ŌĆó Avoid distracting verbal/non-verbal acts
- 49. End ŌĆó Summarize lectures ŌĆó Pose questions to trigger self-explanation ŌĆó Give short-answer quizzes ŌĆó Disclose expectations ŌĆó Provide references ŌĆó Offer consultations after class ŌĆó Seek feedback
- 50. My Experience
- 51. Objective ŌĆó To study the effect of applying the principles of Cognitive Load Theory to improve lecture-based teaching on the level of cognitive participation and intrinsic motivation, including the level of cognitive load of the learners.
- 52. Indicators ŌĆó Cognitive load (Tremblay et al., 2022) ŌĆó Intrinsic, extraneous Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ germane load ŌĆó Rating scale
- 53. Indicators ŌĆó Learners' Engagement and Motivation Questionnaire ŌĆó Cognitive engagement (Webster & Ho, 1997) ŌĆó Challenge, feedback, control, variety, Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ engagement
- 54. Indicators ŌĆó Learners' Engagement and Motivation Questionnaire ŌĆó Intrinsic motivation ŌĆó Intrinsic Motivation Inventory (IMI) by Edward L. Deci http://selfdeterminationtheory.org/ ŌĆó Interest/enjoyment, Effort/importance, Perceived choice Ó╣üÓĖźÓĖ░ Value/usefulness
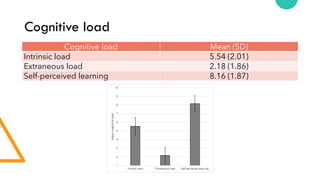
- 55. Cognitive load Cognitive load Mean (SD) Intrinsic load 5.54 (2.01) Extraneous load 2.18 (1.86) Self-perceived learning 8.16 (1.87)
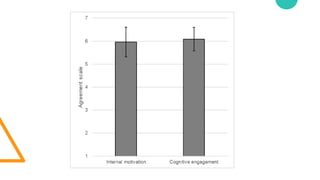
- 57. Internal motivation Internal motivation Mean (SD) Interest/enjoyment 6.19 (0.96) Effort/importance 5.10 (1.58) Perceived choice 6.12 (1.27) Value/usefulness 6.41 (0.79) SUM 5.96 (1.29)
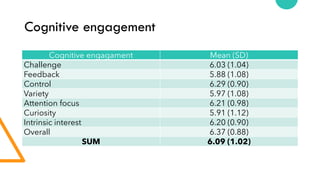
- 58. Cognitive engagement Cognitive engagament Mean (SD) Challenge 6.03 (1.04) Feedback 5.88 (1.08) Control 6.29 (0.90) Variety 5.97 (1.08) Attention focus 6.21 (0.98) Curiosity 5.91 (1.12) Intrinsic interest 6.20 (0.90) Overall 6.37 (0.88) SUM 6.09 (1.02)
- 60. Internal motivation Cognitive load On site (n=71) Online (n=21) p-value Cohen Effect size Intrinsic load 5.46 (1.61) 5.81 (1.91) 0.401 0.199 Extraneous load 1.98 (1.05) 2.89 (2.38) 0.013 0.499 Self-perceiving learning 8.14 (1.10) 8.22 (1.04) 0.759 0.077
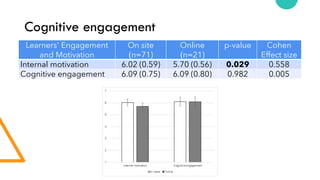
- 61. Cognitive engagement Learners' Engagement and Motivation On site (n=71) Online (n=21) p-value Cohen Effect size Internal motivation 6.02 (0.59) 5.70 (0.56) 0.029 0.558 Cognitive engagement 6.09 (0.75) 6.09 (0.80) 0.982 0.005
- 62. Cognitive Load Theory (CLT) ŌĆó Science of Learning ŌĆó Cognitive Load Theory (CLT) ŌĆó Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning ŌĆó CLT-based Lecture Model ŌĆó My Experience
- 63. What have we learnt today?