Colloborative computing
- 1. COLLABORATIVE COMPUTING BY SUSHMITA DEY SAN JOSE STATE UNIVERSITY DR. RAMAMURTI SRIDAR
- 2. BACKGROUND • When multiple and distributed computers cooperate to solve a large computing problem then it is known as Collaborative Computing . • In Collaborative Computing resources of 100 thousands or more computers in a network around the world are used to solve a single large computing problem, which cannot be solved by a single machine and require more CPU cycles. • Scientists working in space technology and particle physics laboratory require a large computing resources to analyze and process Big Data created during their research experiments
- 3. BACKGROUND • In United States, NASA uses collaborative computing to build Climate models for weather forecasting. • CERN at Switzerland is the largest particle physics laboratory. • Scientist use large particle accelerator to conduct fundamental research on matters and particles to learn about our Universe.
- 4. USE CASE • CERN hosts Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world’s largest and most powerful particle accelerator. • CERN requires very large computing resources to store, distribute and analyze the ~30 Petabytes (30 million Gigabytes) of data annually generated by the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN on the Franco-Swiss border
- 5. VIEW OF THE LHC TUNNEL Markus Schulz, CERN, IT Department CERN build the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) the world’s largest particle accelerator (27 km long, 100 m under ground) First beam in 2008 Start of the physics program autumn 2009
- 6. THE LHC COMPUTING CHALLENGE ÔÇû Signal/Noise <10-12 ÔÇû Data volume ÔÇó High rate * large number of channels * 4 experiments ÔÉ® 30 PetaBytes of new data each year ( 40 Million CDs) ÔÇû Compute power ÔÇó Event complexity * Nb. events * thousands users ÔÉ® >>200 Thousands of (today's) fastest CPUs, 45 PB disks ÔÇû Worldwide analysis & funding ÔÇó Computing funding locally in major regions & countries ÔÇó Efficient analysis everywhere The Needle
- 7. USE CASE • CERN uses Worldwide LHC Computing Grid (WLCG) project, a global collaboration of more than 170 computing centers in 42 countries, linking up national and international grid infrastructures to meet its very large computing resources requirements. • Every day WLCG processes more than 1.5 million 'jobs', corresponding to a single computer running for more than 600 years.
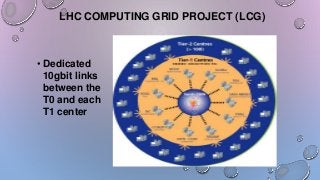
- 8. LHC COMPUTING GRID PROJECT (LCG) • Dedicated 10gbit links between the T0 and each T1 center
- 9. DATA FLOW TO THE CERN COMPUTER CENTER
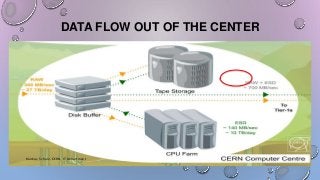
- 10. DATA FLOW OUT OF THE CENTER Markus Schulz, CERN, IT Department
- 13. WHAT ARE THE WEAKNESS/THREATS FOR THIS TECHNICAL ENTITY? • RELIABILITY • INTEROPERABI LITY
- 14. WHAT ARE THE STRENGTH/OPPORTUNITIES FOR THIS TECHNICAL ENTITY? • Worldwide LHC Computing Grid (WLCG) project is a successful example of Collaborative Computing. • UC Berkeley has created BONIC, a software platform for creating collaborative computing for volunteer computing and desktop Grid computing. • Volunteer computing is a special case of Collaborative Computing where people can donate idle cycles of their home computer to support scientific research. • Universities can use collaborative computing to create a virtual supercomputing center for their academics and researchers working on computing-intensive experiments. • Scientists can access a powerful collaborative computing machine using the idle time on your computer (windows, mac, Linux, or android) to cure diseases, study global warming, discover pulsars, and do many other types of scientific research.
- 15. WHAT IS THE FUTURE FOR THIS TECHNICAL ENTITY? • Future of collaborative computing will be evolving to meet the growing need from Scientific Community from around the world. • Research is going to support Computing as Service – similar to public clouds like AWS • Self-healing of the Collaborative Computing Grid to improve the availability and reliability of the computing grid. • Monitoring of the computers by host organization.
- 16. WHO ARE THE CURRENT PLAYERS – GIVE EXAMPLES OF CURRENT USAGE/USERS IN BUSINESS? • AWS – AMAZON WEB SERVICES • AZURE - MICROSOFT • GCE- GOOGLE COMPUTING ENGINE
- 17. CITATION • HTTP://HOME.CERN/ABOUT • HTTP://BOINC.BERKELEY.EDU/ • HTTPS://RUN2-13TEV.WEB.CERN.CH/?PAGE=3 • HTTP://INDICO.CERN.CH/EVENT/68690/CONTRIBUTION/2/ATTACHMENTS/1026356/1461 428/CMS_COMPUTING_MODEL.PDF • HTTP://HOME.CERN/ABOUT/COMPUTING/WORLDWIDE-LHC-COMPUTING-GRID