Colloids
- 2. True Solutions (Suspensions) Colloidal Solutions Suspensions: Classes of solutions  Heterogeneous mixtures  Relatively large particles e.g. whole blood many medicines (Shake well before using)
- 3. Colloids:  Heterogeneous mixtures (micro)  Dispersed particles: 1 to 500-1000 nm Hydrophilic colloids (eucolloids) Hydrophobic colloids (aggregation)
- 4. CCoollllooiiddss Colloids are mixtures of a solvent and suspended particles. Particles are too small to see but are larger than molecules. Due to their small size they do not settle out of solution. There are several types of colloid: aerosol (gas + liquid or solid, e.g. fog and smoke), foam (liquid + gas, e.g. whipped cream), emulsion (liquid + liquid, e.g. milk), sol (liquid + solid, e.g. paint), solid foam (solid + gas, e.g. marshmallow), solid emulsion (solid + liquid, e.g. butter), solid sol (solid + solid, e.g. pearl, opal).
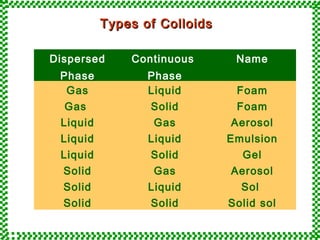
- 5. TTyyppeess ooff CCoollllooiiddss Dispersed Phase Continuous Phase Name Gas Liquid Foam Gas Solid Foam Liquid Gas Aerosol Liquid Liquid Emulsion Liquid Solid Gel Solid Gas Aerosol Solid Liquid Sol Solid Solid Solid sol
- 6. PPrrooppeerrttiieess:: Brownian motion Tyndall Effect (Reflection and light scattering) Coagulation peptization Dialysis
- 7. TTyynnddaallll EEffffeecctt Tyndall effect: ability of a Colloid to scatter light. The beam of light can be seen through the colloid.
- 8. Hydrophilic & Hydrophobic CCoollllooiiddss Focus on colloids in water. “Water loving” colloids: hydrophilic. “Water hating” colloids: hydrophobic. Molecules arrange themselves so that hydrophobic portions are oriented towards each other. If a large hydrophobic macromolecule (giant molecule) needs to exist in water (e.g. in a cell), hydrophobic molecules embed themselves into the macromolecule leaving the hydrophilic ends to interact with water.
- 9. Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic CCoollllooiiddss Sodium stearate has a long hydrophobic tail (CH3(CH2)16-) and a small hydrophobic head (-CO2-Na+). The hydrophobic tail can be absorbed into the oil drop, leaving the hydrophilic head on the surface. The hydrophilic heads then interact with the water and the oil drop is stabilized in water.
- 10. Particle Sizes BBeeccoommee LLaarrggeerr Solutions Colloidal Dispersions Suspensions All particles are on Particles of at least one Particles of at least the order of atoms, component are large one component ions, or small clusters of atoms, ions, may be individually molecules (0.1-1 nm) or small molecules, or seen with a low-are very large ions or power microscope molecules (1-1000 nm) (over 1000 nm) Most stable to gravity Less stable to gravity Unstable to gravity Most homogeneous Also homogeneous, Homogeneous only but borderline if well stirred
- 11. Solutions Colloidal Dispersions Suspensions Transparent (but Often translucent or Often opaque but, often colored) opaque, but may be may appear translucent transparent No Tyndall effect Tyndall effect Not applicable (suspensions cannot be transparent) No Brownian Brownian movement Particles separate unless movement system is stirred Cannot be separated Cannot be separated Can be separated by by filtration by filtration filtration HHoommooggeenneeoouuss ———————— ttoo ———————— HHeetteerrooggeenneeoouuss ————>>