Color Management for Photographers
- 1. COLOR MANAGEMENT FOR PHOTOGRAPHERS A Tom Maddrey Images Workshop Saturday, January 19, 13
- 2. AN INTRODUCTION This seminar is about learning just enough color theory to have a super’¼ücial understanding about WHY things work We are not color scientists, nor should we strive to be, we simply need to know how to get our photographs to look great This class moreso than others will be ’¼ülled with technical speak, I will try to include all relevant de’¼ünitions Saturday, January 19, 13
- 3. WHAT IS A DIGITAL IMAGE? Digital images are a series of 0ŌĆÖs and 1ŌĆÖs that are interpreted by the computer into a full color image The building blocks of digital images are pixels (picture elements) and each pixel has a ŌĆ£Bit-DepthŌĆØ Bit-Depth - The number of bits available to each pixel i.e. 1-bit = 2 options, 0 or 1 (0=black, 1=white) 2-bit = 4 options, 00 or 01 or 10 or 11 (black, dark gray, light gray, white) Saturday, January 19, 13
- 4. WHAT IS A DIGITAL IMAGE (CONT.) 8 Bits = 256 Shades (0-255 in Photoshop Speak) 16 Bits = 65, 536 Shades A Color 8-Bit ’¼üle is made up of three 8-bit channels giving a total bit depth of 24-bit color image (or 16.7 million colors possible) Saturday, January 19, 13
- 5. WHAT IS COLOR? Color is made up of different ŌĆ£HuesŌĆØ which are pure, spectral colors Color is interpreted by our brains, and is not a very complex system For example, two colors of wildly different properties may appear ŌĆ£RedŌĆØ Additive Primaries - Red, Green, Blue Subtractive Primaries - Cyan, Magenta Yellow Saturday, January 19, 13
- 6. COLOR MODELS A ŌĆ£Color ModelŌĆØ is a method of grouping numeric values by a set of primaries RGB, CMY, L*a*b*, CMYK L*a*b* is a color model that represents all the colors humans can ever see RGB needs a ŌĆ£Color SpaceŌĆØ to determine the exact formulation i.e. R255/G0/B0 is different in sRGB than Adobe RGB (1998) Saturday, January 19, 13
- 7. COLOR SPACES A Color Space is a scienti’¼ücally de’¼üned portion of human vision Work in conjunction with a Color Model Often more restrictive than entire visible spectrum Color Spaces can be Device dependent or Device independent Device dependent includes: Epson Printers, Nikon Cameras Device independent includes: L*a*b Color Space Saturday, January 19, 13
- 8. LAB COLOR SPACE Shaped like a sphere L* axis goes from 0-100 and controls lightness a* and b* axis controls the color chosen Includes all colors of human perception Is a Color Space and Color Model Saturday, January 19, 13
- 9. MANAGEMENT VS. CORRECTION Color Management seeks to achieve WYSIWYG by normalizing each part in the color chain Color Correction is altering a part of the color chain to your own preferences or likings A properly set up computer and monitor will render a poor image as a poor image! Saturday, January 19, 13
- 10. CALIBRATION VS. PROFILING Calibration is designed to create and return a device to a known starting point i.e Monitors Pro’¼üling is taking a snapshot of a device in a calibrated state to use as reference If the device deviates from a calibrated state the pro’¼üle is no longer valid! Saturday, January 19, 13
- 11. COLOR GAMUT Color Gamut can best be thought of like crayons A color gamut describes all possible colors of a pro’¼üle Saturday, January 19, 13
- 12. COLOR TRANSLATION When going from one color gamut to another (as in from ’¼üle to print), we need to ŌĆ£translateŌĆØ the colors We do this with ŌĆ£Gamut MappingŌĆØ This translation (such as Adobe RGB to sRGB) is the source of many poor prints and colors Saturday, January 19, 13
- 13. RENDERING INTENTS If a color is available in one color space and not in another, the color is considered ŌĆ£Out- of-GamutŌĆØ Out of Gamut colors need to be compressed or clipped to ’¼üt in the destination color space Clipping - Moving OOG colors to ŌĆ£Nearest NeighborŌĆØ color in Gamut Compression - Compresses OOG colors to maintain relationships between colors, but affect other colors as well Saturday, January 19, 13
- 14. RENDERING INTENTS (CONT.) Perceptual - Transforms OOG colors to the new space so the image is ŌĆ£perceivedŌĆØ in the same way Good for lots of OOG colors Relative Colormetric - Uses Gamut Clipping to adjust only those OOG colors and moves them to the nearest color match in the destination, does not affect other colors Good when not many OOG colors Saturday, January 19, 13
- 15. ICC PROFILES Input Pro’¼üles, Display Pro’¼üles, and Output Pro’¼üles Input Pro’¼üles - Describe how a camera or scanner ŌĆ£SeesŌĆØ color Display Pro’¼üles - Describe how a monitor ŌĆ£ReproducesŌĆØ color Output Pro’¼üles - Describes how a printer ŌĆ£RendersŌĆØ color Pro’¼üles can be ŌĆ£AssignedŌĆØ or embedded in an image Saturday, January 19, 13
- 16. PHOTOSHOP DEMO #1 Saturday, January 19, 13
- 17. PHOTOSHOP AND COLOR MANAGEMENT Photoshop 5.0 was the ’¼ürst version to have built in color management with .icc pro’¼üles Photoshop has ŌĆ£Working SpacesŌĆØ that is the color management you are working in, separate from your display You always want your working space to have more information than the most restrictive process (i.e. printing) Saturday, January 19, 13
- 18. WORKING SPACES sRGB - Useful if your output is only low res, such as web or tv Adobe RGB (1998) - Useful all around working space, including PrePress (CMYK), most useful for 8-bit work ProPhoto RGB - VERY large working space, includes all color, even some outside CIE LAB, best for 16-bit work Saturday, January 19, 13
- 19. PHOTOSHOP COLOR SETTINGS To access, Command/Control - Shift - K Broken Down into: Settings, Working Spaces, Color Management Policies, Conversion Options, and Advanced Controls We will look in depth at these setting in the next Photoshop demo Saturday, January 19, 13
- 20. ASSIGN AND CONVERT TO PROFILE Assign Pro’¼üle tells PS what pro’¼üle is associated with the numbers in the image Useful when a document does not have an embedded pro’¼üle Convert to Pro’¼üle is where you convert between color spaces Useful when you are moving the image to another place (i.e. an offsite printer Saturday, January 19, 13
- 21. SOFT PROOFING LIKE A PRO Soft Proo’¼üng is a way to preview what the ’¼ünal output (usually from a printer) will look like before you print! Soft proo’¼üng most closely approximates the ’¼ünal print on your screen Takes a while to get used to, but is the single most important thing you can do to get good images the ’¼ürst time Set up the proof Adjust contrast, saturation, curves Compare with original Saturday, January 19, 13
- 22. A QUICK PRINTING PRIMER After you soft proof your image, the next step is to take it to print When printing, you need to make sure you are applying color management at least once, and not twice! Print with Preview in PS PhotoShop Manages Color Document is selected Every Printer Driver is Different, but all need NO COLOR MANAGEMENT Saturday, January 19, 13
- 23. PHOTOSHOP DEMO #2 Saturday, January 19, 13
- 24. CALIBRATING A MONITOR When Calibrating a monitor, here are a quick list of settings: White Point: D65 or 6500K Gamma 2.2 Update display pro’¼üles at least every month Every two weeks would be preferred Inexpensive choices: ColorMunki, Eye One Display LT Saturday, January 19, 13
- 25. PROFILING A PRINTER Printer pro’¼üles are custom to that particular printer, ink set, and paper There are good starting points with generic pro’¼üles, but a custom pro’¼üle is light years beyond these generics Newer printers are beginning to include a spectrophotometer in the printer itself Saturday, January 19, 13
- 26. PROFILING A PRINTER (CONT.) The ’¼ürst step is to print a target with no color management whatsoever This means off in Photoshop Dialog and off in Printer Dialog Next you use a photospectrometer to measure the targets against a known set of reference points The program adjusts for the differences Saturday, January 19, 13
- 27. PROFILE CREATION DEMO Saturday, January 19, 13
- 28. PROGRAMS AND ADDONS There are numerous programs to help tweak color ensure quality Apple Color Sync Color Think Saturday, January 19, 13
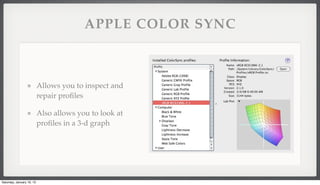
- 29. APPLE COLOR SYNC Allows you to inspect and repair pro’¼üles Also allows you to look at pro’¼üles in a 3-d graph Saturday, January 19, 13
- 30. COLORTHINK 2 Performs the same functions as Color Sync, but also allows you to compare pro’¼üles and gamuts Saturday, January 19, 13
- 31. FINAL DEMOS Saturday, January 19, 13