Combating multidrug resistance bacteria with essential oils
- 1. COMBATING MULTIDRUG RESISTANT BACTERIA WITH ESSENTIAL OILS Miguel Diaz
- 2. MICROBIAL COMPETITION http://www.livescience.com/ ŌĆó Competition for limited resources ŌĆó Excretion of chemicals that are toxic and inhibit growth http://virtuallaboratory.colorado.edu
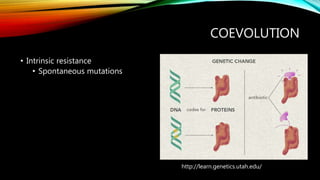
- 3. COEVOLUTION ŌĆó Intrinsic resistance ŌĆó Spontaneous mutations http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
- 4. PATHOGENS ŌĆó Disease causing organisms www.cdc.gov http://www.bacteriainphotos.com/bact eria-photo-gallery.html
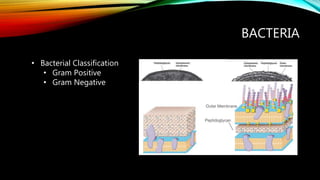
- 5. BACTERIA ŌĆó Bacterial Classification ŌĆó Gram Positive ŌĆó Gram Negative
- 6. DISCOVERY OF ANTIBIOTICS ŌĆó 1928 Alexander Fleming discovered Penicillin ŌĆó Antibiotics have had a significant impact on human health and life ŌĆó ŌĆ£WonderŌĆØ drug http://sciencenational.tumblr.com/
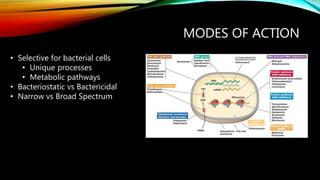
- 7. MODES OF ACTION ŌĆó Selective for bacterial cells ŌĆó Unique processes ŌĆó Metabolic pathways ŌĆó Bacteriostatic vs Bactericidal ŌĆó Narrow vs Broad Spectrum
- 8. ANTIBIOTICS ŌĆó Treat bacterial infections ŌĆó Life saving ŌĆó extending the human lifespan ŌĆó Naturally, Synthetic, Semi-Synthetic ŌĆó Zone of inhibition ŌĆó Minimum Inhibition Concentration (MIC)
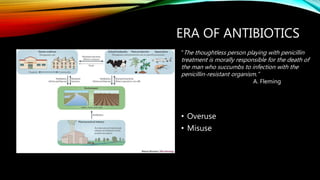
- 9. ERA OF ANTIBIOTICS ŌĆó Overuse ŌĆó Misuse "The thoughtless person playing with penicillin treatment is morally responsible for the death of the man who succumbs to infection with the penicillin-resistant organism.ŌĆØ A. Fleming
- 10. RESISTANCE ŌĆó Intrinsic Evolutionary event ŌĆó Genes chromosomal or plasmid ŌĆó HGT ŌĆó R plasmids https://www.niaid.nih.gov
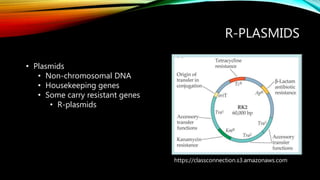
- 11. R-PLASMIDS https://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com ŌĆó Plasmids ŌĆó Non-chromosomal DNA ŌĆó Housekeeping genes ŌĆó Some carry resistant genes ŌĆó R-plasmids
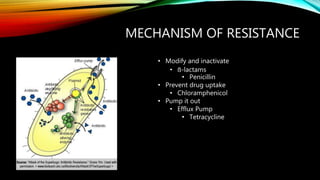
- 13. MECHANISM OF RESISTANCE ŌĆó Modify and inactivate ŌĆó ß║×-lactams ŌĆó Penicillin ŌĆó Prevent drug uptake ŌĆó Chloramphenicol ŌĆó Pump it out ŌĆó Efflux Pump ŌĆó Tetracycline
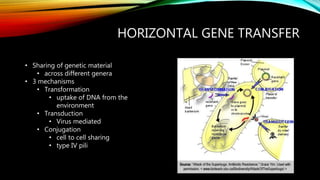
- 14. HORIZONTAL GENE TRANSFER ŌĆó Sharing of genetic material ŌĆó across different genera ŌĆó 3 mechanisms ŌĆó Transformation ŌĆó uptake of DNA from the environment ŌĆó Transduction ŌĆó Virus mediated ŌĆó Conjugation ŌĆó cell to cell sharing ŌĆó type IV pili
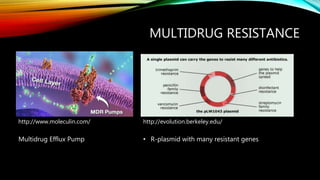
- 15. MULTIDRUG RESISTANCE http://www.moleculin.com/ Multidrug Efflux Pump http://evolution.berkeley.edu/ ŌĆó R-plasmid with many resistant genes
- 16. MULTIDRUG RESISTANCE ŌĆó ESKAPE Pathogens ŌĆó Enterococcus faecium (VRE) ŌĆó Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) ŌĆó Klebsiella and Escherichia coli producing ESBL ŌĆó Acinetobacter baumannii ŌĆó Pseudomonas aeruginosa ŌĆó Enterbacteriaceae
- 17. POST ANTIBIOTIC ERA? ŌĆó Little research and development ŌĆó Mutations can happen quickly and are easily shared ŌĆó What now? ŌĆ£ We are headed to a post antibiotic era, in which common infections and minor injuries can once again killŌĆØ WHO 2015 http://bk.asia-city.com
- 18. ESSENTIAL OILS http://www.questnetproxy.com/ ŌĆó Traditional medicine ŌĆó Topical or inhaled ŌĆó Some toxic if ingested ŌĆó Generally safe ŌĆó Chemotype ŌĆó Changes in chemical phenotype ŌĆó Steam distillation
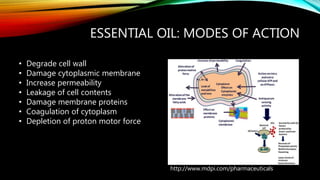
- 19. ESSENTIAL OIL: MODES OF ACTION http://www.mdpi.com/pharmaceuticals ŌĆó Degrade cell wall ŌĆó Damage cytoplasmic membrane ŌĆó Increase permeability ŌĆó Leakage of cell contents ŌĆó Damage membrane proteins ŌĆó Coagulation of cytoplasm ŌĆó Depletion of proton motor force
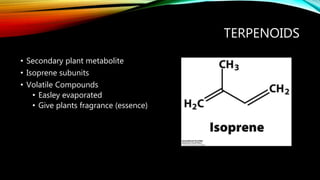
- 20. TERPENOIDS ŌĆó Secondary plant metabolite ŌĆó Isoprene subunits ŌĆó Volatile Compounds ŌĆó Easley evaporated ŌĆó Give plants fragrance (essence)
- 21. MELALEUCA ALTERNIFOLIA http://www.teamessence.com.my/ ŌĆó Native to Australia ŌĆó Aboriginals use it for treating infections ŌĆó Know for its antiseptic, antibiotic properties ŌĆó Main constituents ŌĆó terpinen-4-ol ŌĆó -terpineol
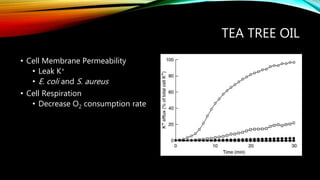
- 22. TEA TREE OIL ŌĆó Cell Membrane Permeability ŌĆó Leak K+ ŌĆó E. coli and S. aureus ŌĆó Cell Respiration ŌĆó Decrease O2 consumption rate
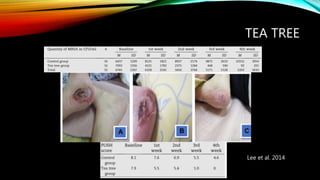
- 23. TEA TREE Lee et al. 2014
- 24. MENTHA PIPERITA https://www.tuinplant.nl ŌĆó Native to Europe and Middle East ŌĆó Menthol and Mentone ŌĆó Medicinal Uses ŌĆó Analgesic, cooling, antiemetic ŌĆó muscle rubs Bakkali et al. 2008
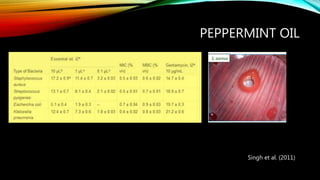
- 25. PEPPERMINT OIL Singh et al. (2011)
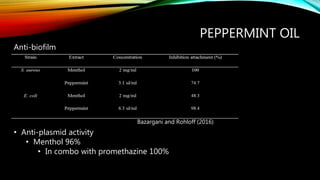
- 26. PEPPERMINT OIL Bazargani and Rohloff (2016) ŌĆó Anti-plasmid activity ŌĆó Menthol 96% ŌĆó In combo with promethazine 100% Anti-biofilm
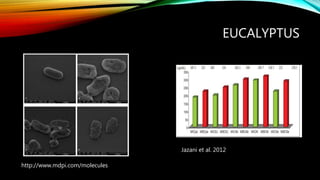
- 27. EUCALYPTUS CAMALDULENSIS https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/82/Eu calyptus_trunk_zebra_pattern.jpg ŌĆó Indigenous to Australia ŌĆó Medicinal Purpose ŌĆó anesthetic, antiseptic, astringent ŌĆó Constitutes ŌĆó p-cymene (35.0%) ŌĆó cryptone (13.7%) ŌĆó tanins (11%) ŌĆó terpinen-4-ol (5.7%)
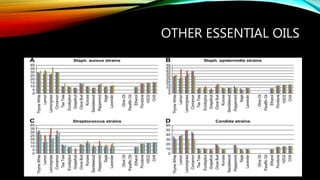
- 30. ESSENTIAL OILS AND MDRO ŌĆó Essential oils can reduce the use of antibiotic ŌĆó Preventative measures ŌĆó Reduce inflammation response ŌĆó Antiseptic ŌĆó Cleaning hospital surfaces ŌĆó Alternative treatments ŌĆó Effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria ŌĆó Synergistic effects ŌĆó In combination with antibiotics ŌĆó Decrease MIC ŌĆó Increase zone inhibition
- 31. REFRENCES ŌĆó Bazargani MM, Rohloff J. 2016. Antibiofilm activity of essential oils and plant extracts against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli biofilms. Food Control 61:156ŌĆō164. ŌĆó www.cdc.gov ŌĆó Cox.S.D. 2000. The model of antimicrobial action of the essential oil of Melaleuca alternifolia. J. Appl. Microbiol. 88:170ŌĆō175. ŌĆó Jazani NH, Mikaili P, Shayegh J, Haghighi N, Aghamohammadi N, Zartoshti M. 2012. The hydro-alcoholic extract of leaves of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh. has antibacterial activity on multi-drug resistant bacteria isolates. J. Appl. Biol. Sci. 6:37ŌĆō40. ŌĆó Knezevic P, Aleksic V, Simin N, Svircev E, Petrovic A, Mimica-Dukic N. 2016. Antimicrobial activity of Eucalyptus camaldulensis essential oils and their interactions with conventional antimicrobial agents against multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Ethnopharmacol. 178:125ŌĆō136. ŌĆó Lee RLP, Leung PHM, Wong TKS. 2014. A randomized controlled trial of topical tea tree preparation for MRSA colonized wounds. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 1:7ŌĆō14. ŌĆó Singh R, Shushni MAM, Belkheir A. 2015. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of Mentha piperita L. Arab. J. Chem. 8:322ŌĆō328.