Common hacking tactics
- 3. Vulnerability scanner A vulnerability scanner is a tool used to quickly check computers on a network for known weaknesses. Hackers also commonly use port scanners. These check to see which ports on a specified computer are "open" or available to access the computer, and sometimes will detect what program or service is listening on that port, and its version number. Spoofing attack (Phishing) A spoofing attack involves one program, system, or website successfully masquerading as another by falsifying data and thereby being treated as a trusted system by a user or another program. The purpose of this is usually to fool programs, systems, or users into revealing confidential information, such as user names and passwords, to the attacker. Â
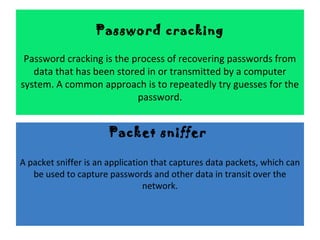
- 4. Password cracking Password cracking is the process of recovering passwords from data that has been stored in or transmitted by a computer system. A common approach is to repeatedly try guesses for the password. Packet sniffer A packet sniffer is an application that captures data packets, which can be used to capture passwords and other data in transit over the network.
- 5. Social engineering A common practice for hackers who use this technique, is to contact the system administrator and play the role of a user who cannot get access to his or her system. Hackers who use this technique have to be quite savvy and choose the words they use carefully, in order to trick the system administrator into giving them information. Key loggers A key logger is a tool designed to record ('log') every keystroke on an affected machine for later retrieval. Its purpose is usually to allow the user of this tool to gain access to confidential information typed on the affected machine, such as a user's password or other private data.
- 6. Trojan horses A Trojan horse is a program which seems to be doing one thing, but is actually doing another. A trojan horse can be used to set up a back door in a computer system such that the intruder can gain access later Viruses A virus is a self-replicating program that spreads by inserting copies of itself into other executable code or documents. Therefore, a computer virus behaves in a way similar to a biological virus, which spreads by inserting itself into living cells.
- 7. Password cracking Password cracking is the process of recovering passwords from data that has been stored in or transmitted by a computer system. A common approach is to repeatedly try guesses for the password. Packet sniffer A packet sniffer is an application that captures data packets, which can be used to capture passwords and other data in transit over the network.