communication-protocols
- 1. Communication Protocols • Describes the rules that govern the transmission of data over the communication Network. • Provide a method for orderly and efficient exchange of data between the sender and the receiver.
- 2. Roles of Communication Protocol 1. Data Sequencing – to detect loss or duplicate packets. 2. Data Routing – to find the most efficient path between source and a destination. 3. Data formatting – defines group of bits within a packet which constitutes data, control, addressing and other information. 4. Flow control – ensures resource sharing and protection against traffic congestion by regulating the flow of data on communication lines.
- 3. Roles of Communication Protocol 5. Error control – detect errors in messages. Method for correcting errors is to retransmit the erroneous message block. 6. Precedence and order of transmission – condition all nodes about when to transmit their data and when to receive data from other nodes. Gives equal chance for all the nodes to use the communication channel. 7. Connection establishment and termination – 8. Data security – Prevents access of data by unauthorized users.
- 4. The OSI Model • OSI is short for Open Systems Interconnection. • OSI model was first introduced by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1984 – Outlines WHAT needs to be done to send data from one computer to another. – Protocols stacks handle how data is prepared for transmittal • Contains specifications in 7 different layers that interact with each other.
- 5. What is “THE MODEL?” • Commonly referred to as the OSI reference model. • Open system interconnection (OSI) model is a framework for defining standards for linking heterogeneous computer systems, located anywhere. • The OSI model is a theoretical blueprint that helps us understand how data gets from one user’s computer to another. • It is also a model that helps develop standards so that all of our hardware and software talks nicely to each other.
- 6. 7 Layer OSI Model • Why use a reference model? – Serves as an outline of rules for how protocols can be used to allow communication between computers. – Each layer has its own function and provides support to other layers. • Other reference models are in use. – Most well known is the TCP/IP reference model.
- 7. 7 Layer OSI Model • Open system interconnection (OSI) model is a framework for defining standards for linking heterogeneous computer systems, located anywhere.
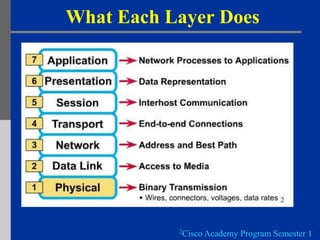
- 8. What Each Layer Does 2 2Cisco Academy Program Semester 1
- 9. Application Layer • Gives end-user applications access to network resources • Where is it on my computer? – Workstation or Server Service in MS Windows 3 3Graphic courtesy of http://www.hawkclan.com/zxonly/iso/slide2.html
- 10. Presentation Layer • Provides common data formatting between communicating devices • Components make sure the receiving station can read the transferred data 3 3Graphic courtesy of http://www.hawkclan.com/zxonly/iso/slide2.html
- 11. Session Layer • Allows applications to maintain an ongoing session • Example – NetBIOS • Where is it on my computer? – Workstation and Server Service (MS) – Windows Client for NetWare (NetWare) 3 3Graphic courtesy of http://www.hawkclan.com/zxonly/iso/slide2.html
- 12. Transport Layer • Provides reliable data delivery • It’s the TCP in TCP/IP • Receives info from upper layers and segments it into packets • Can provide error detection and correction 3 3Graphic courtesy of http://www.hawkclan.com/zxonly/iso/slide2.html
- 13. Network Layer • Provides network- wide addressing and a mechanism to move packets between networks (routing) • Responsibilities: – Network addressing – Routing • Examples: – IP from TCP/IP 3 – IPX from IPX/SPX 3Graphic courtesy of http://www.hawkclan.com/zxonly/iso/slide2.html
- 14. Network Addresses • Network-wide addresses • Used to transfer data across subnets • Used by routers for packet forwarding • Example: – IP Address • Where is it on my computer? – TCP/IP Software
- 15. Data Link Layer • Places data and retrieves it from the physical layer and provides error detection capabilities 3 3Graphic courtesy of http://www.hawkclan.com/zxonly/iso/slide2.html
- 16. Sub-layers of the Data Link Layer • MAC (Media Access Control) – Gives data to the NIC – Controls access to the media through: • CSMA/CD Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection • Token passing • LLC (Logical Link Layer) – Manages the data link interface (or Service Access Points (SAPs)) – Can detect some transmission errors using a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC). If the packet is bad the LLC will request the sender to resend that particular packet.
- 17. Physical Layer • Determines the specs for all physical components – Cabling – Interconnect methods (topology / devices) – Data encoding (bits to waves) – Electrical properties • Examples: – Ethernet (IEEE 802.3) – Token Ring (IEEE 802.5) – Wireless (IEEE 802.11b) 3 3Graphic courtesy of http://www.hawkclan.com/zxonly/iso/slide2.html
- 18. Physical Layer (cont’d) • What are the Physical Layer components on my computer? • NIC – Network Interface Card – Has a unique 12 character Hexadecimal number permanently burned into it at the manufacturer. – The number is the MAC Address/Physical address of a computer • Cabling – Twister Pair – Fiber Optic – Coax Cable
- 19. How Does It All Work Together 2 2Cisco Academy Program Semester 1
- 20. The TCP/IP Model • Another Model is the TCP/IP Model. • There is no universal agreement regarding how to describe TCP/IP with a layered model. • Most descriptions present three to five layers. • We use the four layer structure that incorporates the Presentation and Session layers with the Application layer.
- 21. Comparing TCP/IP With OSI 2 2Cisco Academy Program Semester 1
- 22. The TCP/IP Model (4 Layer) • Application Layer – Interacts with user processes • Transport Layer – TCP guarantees data is received and sent accurately • Internet Layer – IP separates upper layers from the network and manages the connections across the network • Network Access Layer – Incorporates the Network and Physical layers of the OSI model 4 4 http://www.pku.edu.cn/academic/research/computer-center/tc/html/TC0102.html
- 23. Remembering the 7 Layers 7 - Application All 6 - Presentation People 5 - Session Seem 4 - Transport To 3 - Network Need 2 - Data Link Data 1 - Physical Processing