Communicative competence
- 1. COMMUNICATIVECOMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCECOMPETENCE DIDACTIC IIDIDACTIC II DANILZA LORDUY A.DANILZA LORDUY A. 20122012
- 2. ORIGINSORIGINS The idea was originally derived fromThe idea was originally derived from Chomsky’s distinction betweenChomsky’s distinction between competence and performacecompetence and performace  Competence shared knowledge ofCompetence shared knowledge of ideal speaker-listener set in a completelyideal speaker-listener set in a completely homogenous speech community.homogenous speech community. ““Underlying knowledge enables users to produce and understand”Underlying knowledge enables users to produce and understand”
- 3. ORIGINSORIGINS  Performance: process of applyingPerformance: process of applying underlying knowledge to actual languageunderlying knowledge to actual language use.use. ““Should be given under ideal circunstances ( the ideal speaker-Should be given under ideal circunstances ( the ideal speaker- listener know and use language perfectly without making anylistener know and use language perfectly without making any mistakes)”mistakes)”
- 4. ORIGINSORIGINS Hymes Chomsky’view too narrow to describeHymes Chomsky’view too narrow to describe language behavior as a whole.language behavior as a whole.  Sociocultural factors or differential competence in aSociocultural factors or differential competence in a heterogeneous speech community???heterogeneous speech community???  Social life affects outward performance and innerSocial life affects outward performance and inner competence itself.competence itself.  Social factorsSocial factors interfere with or restrict grammar use because the rules of use are dominant over the rules of grammar
- 5. ORIGINSORIGINS ÔÇß Hymes concludes that a linguistic theory must be able to deal with a heterogeneous speech community, differential competence and the role of sociocultural features ÔÇß Performance he defines it as the actual use of language in a concrete situation, not an idealized speaker-listener situation in a completely homogeneous speech community
- 6. ORIGINSORIGINS ÔÇß HymesHymes two kinds of competence: linguistic competence, and the communicative competence ÔÇß Linguistic competence that deals with producing and understanding grammatically correct sentences ÔÇß Communicative competence that deals with producing and understanding sentences that are appropriate and acceptable to a particular situation.
- 7. ORIGINSORIGINS  Hymes coins a term “communicative competence” and defines it as “a knowledge of the rules for understanding and producing both the referential and social meaning of language.”
- 8. ORIGINSORIGINS WiddowsonWiddowson knowing a language is more than how to understand, speak, read,and write sentences, but how sentences are used to communicate.  communicative abilities have to be developed at the same time as the linguistic skills; otherwise the mere acquisition of the linguistic skills may inhibit the development of communicative abilities.  “ usage and use “
- 9. ORIGINSORIGINS  “Usage” makes evident the extent to which the language user demonstrates his knowledge of linguistic rules  “Use” makes evident the extent to which the language user demonstrates his ability to use his knowledge of linguistic rules for effective communication.(Widdowson, 1978)
- 10. ORIGINSORIGINS Teachers should provide linguistic and communicative contexts. ÔÇß Linguistic context focuses on usage to enable the students to select which form of sentence is contextually appropriate ÔÇß Communicative context focuses on use to enable the students to recognize the type of communicative function their sentences fulfill
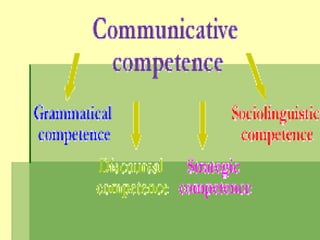
- 11. ORIGINSORIGINS ÔÇß (Canale & Swain, 1980) They strongly believe that the study of grammatical competence is as essential to the study of communicative competence as is the study of sociolinguistic competence. ÔÇß They propose their own theory of communicative competence that minimally includes three main competencies: grammatical, sociolinguistic and strategic competence.
- 12. ORIGINSORIGINS  Grammatical competence includes knowledge of lexical items and of rules of morphology,syntax,sentence―grammar semantics, and phonology.  Sociolinguistic competence is made up of two sets of rules: sociolinguistic rules of use and rules of discourse. They believe that knowledge of these rules will be crucial in interpreting utterances for social meaning
- 13. ORIGINSORIGINS ÔÇß Strategic competence is made up of verbal and non-verbal communication strategies that may be called into action to compensate for breakdowns in communication due to performance variables or to insufficient grammatical competence
- 14. BACHMAN’S VIEWBACHMAN’S VIEW The organizational competence is divided into grammatical competence and textual competence. Bachman’s grammatical competence is consonant with Canale and Swain’s grammatical competence. The textual competence, pertains to the knowledge of conventions for cohesion and coherenceand rehetorical organization. It also includes conventions for language use in conversations, involving starting, maintaining, and closing conversations. Bachman’s textual competence have both the part of Canale and Swain’s discourse competence and the part of their strategic competence.
- 15. BACHMAN’S VIEWBACHMAN’S VIEW  Bachman’s pragmatic competence, mainly focuses on the relationship between what one says in his or her communicative acts and what functions he or she intends to perform through his or her utterances.
- 17. COMMUNICATIVECOMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE THEN…COMPETENCE THEN…  Communicative competence is made up of fourCommunicative competence is made up of four competence areas: linguistic, sociolinguistic,competence areas: linguistic, sociolinguistic, discourse, and strategic.discourse, and strategic.  Linguistic competenceLinguistic competence is knowing how to useis knowing how to use the grammar, syntax, and vocabulary of athe grammar, syntax, and vocabulary of a language. Linguistic competence asks: Whatlanguage. Linguistic competence asks: What words do I use? How do I put them intowords do I use? How do I put them into phrases and sentences?phrases and sentences?
- 18. COMMUNICATIVECOMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE THEN…COMPETENCE THEN…  Sociolinguistic competenceSociolinguistic competence is knowing how to useis knowing how to use and respond to language appropriately, given theand respond to language appropriately, given the setting, the topic, and the relationships among thesetting, the topic, and the relationships among the people communicating.people communicating.  Sociolinguistic competence asks: Which words andSociolinguistic competence asks: Which words and phrases fit this setting and this topic? How can Iphrases fit this setting and this topic? How can I express a specific attitude (courtesy, authority,express a specific attitude (courtesy, authority, friendliness, respect) when I need to? How do I knowfriendliness, respect) when I need to? How do I know what attitude another person is expressing?what attitude another person is expressing?
- 19. COMMUNICATIVECOMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE THEN…COMPETENCE THEN…  Discourse competenceDiscourse competence is knowing how tois knowing how to interpret the larger context and how tointerpret the larger context and how to construct longer stretches of language so thatconstruct longer stretches of language so that the parts make up a coherent whole.the parts make up a coherent whole.  Discourse competence asks: How are words,Discourse competence asks: How are words, phrases and sentences put together to createphrases and sentences put together to create conversations, speeches, email messages,conversations, speeches, email messages, newspaper articles?newspaper articles?
- 20. COMMUNICATIVECOMMUNICATIVE COMPETENCE THEN…COMPETENCE THEN…  Strategic competenceStrategic competence is knowing how to recognizeis knowing how to recognize and repair communication breakdowns, how to workand repair communication breakdowns, how to work around gaps inaround gaps in one’s knowledge of the language, andone’s knowledge of the language, and how to learn more about the language and in thehow to learn more about the language and in the context.context.  Strategic competence asks: How do I know when I’veStrategic competence asks: How do I know when I’ve misunderstood or when someone has misunderstoodmisunderstood or when someone has misunderstood me? What do I say then? How can I express my ideasme? What do I say then? How can I express my ideas if I don’t know the name of something or the right verbif I don’t know the name of something or the right verb form to use?form to use?