Company law
- 2. DEFINE COMPANY Section 3(1) of the Company Act, 1956 defines Company as â Company means a Company Formed and registered under this act or an existing Companyâ. According to Haney â A Company is incorporated Association, which is an artificial person created by law, having separate Entity, With a perpetual succession and a common sealâ. According to Marshall â A company is a person, artificial, Invisible, Intangible, and existing only in the Eyes of law. Being a mere creature of law, it possesses only those properties which the charter of its creation confer upon it, either expressly or incidental to its mere existenceâ.
- 3. Features of Company Artificial person. Separate legal Entity. Perpetual succession. Separate Property. Common Seal. Capacity to sue. Transferability of shares. Limited liability. Limitation of action.
- 4. LIFTING OF CORPORATE VEIL? The Company is Distinct person separate from its member . This principle is called âveil of corporateâ. The Advantage of incorporation Can be enjoyed only by those who honestly use veil of company for collective benefit of the company and also of its member. Where there is the dishonest and fraudulent intension to utilize the facility of incorporation, the law can remove the corporate veil. and identify the person who are behind and responsible for commission/ perpetration of fraud. This concept is called âlifting of corporate veil.â For e.g.- case of Salomon vs. Salomon and co.
- 5. Can a company become a member of another company? A company being juristic person and a legal entity may become a member of another company, if it is so authorized by its memorandum, to purchase or invest in shares. However, subsidiary company cannot be a member of its holding company. (Section 42) Any allotment or transfer of shares in a holding company to its subsidiary is void except subsidiary co. may (1) Hold shares in the holding co. in the capacity of legal representative of a diseased shareholder. (2) Holds such shares as trustees. (3) Remain a member of its holding company, if it was the member before April 1 st 1956, but may not vote at the meeting of the holding co. or any class of its member.
- 6. The Number of member in the company Registered as a public company is reduced to 5. comment? A public company should have minimum of 7 members (section 12). If at any time members of public company falls below 7 and it continues its business for more then 6 months, then, every such member who were aware of this fact are personally liable for all debts contracted after 6 months. (Section 45).
- 7. Types of public financial Institution? Section 4A(1) of Companies act deals with public financial institution. Types of PFI are as follows:- (1)The industrial credit and investment corporation of India. (ICICI) (2) Industrial finance corporation of India. (IFCI) (3) Industrial development bank of India. (IDBI) (4) Life insurance Corporation of India. (LIC) (5) The infrastructure Development finance corporation limited. (IDFC) Section 4A(2) the central govt. is empowered to specify other institution, as it may fit, to be PFI by issuing the notification in the official gazette. However, no institution shall be so specified unless (a) it has been established or constituted by or under any central act, or (b) Not less then 51% of paid up share capital of such an institution is held or controlled by the central government.
- 8. Note on Government Companies? Section (617) Any company in which not less then 51% of paid up share capital is held by (1) The central govt. (2) Any state govt. or govt. or (3) partly by central government and partly by one or more state government
- 9. Note on Holding company. section 4(4) & Subsidiary company 4(1). Holding company :- A company shall be deemed to be the holding company of another if, but only if, that other company is its subsidiary. Subsidiary company :- When B Ltd and C Ltd, The subsidiary of A Ltd, hold together more then half of the equity share capital of the D Ltd shall be deemed to be the subsidiary of A Ltd. This relationship will apply even though (a) D Ltd is not the subsidiary of B Ltd or C Ltd, or (b) Although A Ltd has not made any direct investment in D Ltd or (c) B Ltd or C Ltd singly do not hold more then 50% shares in D Ltd.
- 10. Provision of co. act relating to registration of non profit organization? According to section 13 the name of a limited company should end with the word âlimitedâ in the case of public company. With word âprivate limited in case of private company. Section 25 of co. act,1956 permits the registration, under the license granted by the central government, of an Association not for profit with limited liability without adding the word limited or the word private limited in its name. Condition for grant of license (a) if it is about to form limited company for promoting commerce, science, religion, charity or any other useful object, and (b) intents to apply its profits, if any, or other income in promoting its object and to prohibit the payment of any dividend to its member. The license may be granted by the central government on such condition and subject to such regulations, as it thinks fit.
- 11. Procedure for registration of company under section 25? The promoters must apply to the central government for the license under section 25 for registration of the company without the word âlimitedâ as part of its name. The promoter must comply with the condition subject to with the license is issued. Thereafter apply to registrar for incorporation of the company in the manner in which any other company is registered i.e. filing of documents like Memorandum of association, Article of Association e.t.c. in prescribed form.
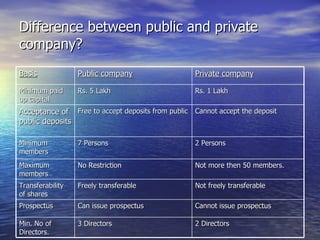
- 12. Difference between public and private company? Basis Public company Private company Minimum paid up capital Rs. 5 Lakh Rs. 1 Lakh Acceptance of public deposits Free to accept deposits from public Cannot accept the deposit Minimum members 7 Persons 2 Persons Maximum members No Restriction Not more then 50 members. Transferability of shares Freely transferable Not freely transferable Prospectus Can issue prospectus Cannot issue prospectus Min. No of Directors. 3 Directors 2 Directors
- 13. Conversion of public company into private company? Pass a special resolution altering article of the company, incorporating the provision given in section 3(1)(iii). Pass special resolution authorizing the conversion of public company into private company. Change the name of company so as to contain in the word private. This alteration do not require special resolution. Apply to the central govt. for the approval to the proposed conversion. the conversion shall have effect only upon the approval of the central government. Within the one month of receipt of approval from central government, file with the ROC, a printed copy of altered articles containing the provision of section 3(1)(iii).
- 14. Conversion of Private company into public company? Take necessary decision in its board meeting and fix on time, Place, agenda for annual general meeting . Amend memorandum to change its name by removing the word private by a special resolution. Approval of central govt. is not required in this case. Increase the no. of shareholder to at least 7 and no. of director to 3 . Must pass the special resolution deleting from its article the requirement of private company under section 3(1)(iii). Such other article which do not apply to the public company should be deleted and those which apply should be inserted. A copy of special resolution should be passed with in 30 day with the registrar of co. it becomes a public company on the date of alteration. Section 44(1)(a). Within 30 days of passing of special resolution, a prospectus or a statement in lieu of prospectus must be filled with the registrar . Section 44(1). The company has to apply to the registrar for the issue of fresh certificate of incorporation, for the changed name.
- 15. Document to be filed with ROC during incorporation of the company? Section 33 Memorandum of association of company. Article of Association of a company. Agreement, if any, which the company proposes to, enter into with any individual for appointment as its managing and whole time director.
- 16. Certificate of incorporation? After all the documents are registered and all the payments of fees are done, the registrar of company issue the certificate that the company is incorporated. Section 35 provides that certificate of incorporation issued by register in respect of any association, shall be conclusive evidence of the fact that all the requirement of act have been complied with in respect of registration and matter precedent and incidental thereto, and that the association is the company authorized to be registered and duly registered in the act. Case law:- Document for registration was filled on 6 th January. Some shares were allotted on 6 th January itself even before the certificate of incorporation was issued. ROC issued COI on 8 th January, but dated as 6 th January. Held that Allotment was valid & COI is conclusive Evidence of all that it contain. (Jubilee cotton mill vs. Lewis)