Compensation plan ppt
- 1. Sales Compensation planPresented by:ManavBadhwar
- 2. Company’s General Compensation StructureRanking- It is widely being used in businesses. It sorts job description in the order of worth. It measures only overall appraisals of the relative worth of different jobs. 2. Grading- A system of grades & grade description, against which individuals jobs are compared. The grades are described in terms of job responsibility, skills required, supervision given & received, exposure to unfavorable & hazardous working conditions. 3. Point system- It involves establishing & defining the factors common to most jobs that represent the chief elements of value inherent in all jobs. The specific factors chosen are, minimum education required, mental & physical skills, responsibility, personality requirements.Each factor is assigned a minimum & maximum no of points, different ranges being associated in line with relative importance of the factors.
- 3. 4. Factors comparison method- It employs selected factors & evaluation scales. It compares sales person on a set of selected factors & rank them according with the performance performed by them under such criteria factors.5. Competitors offer- the compensation structure should me made while seeking the competitors offering to their sales staff .Determine Compensation LevelManagement must determine the amount of compensation a salesperson should receive on the average. Management should ascertain whether the caliber of the present sales force measures up to what the company would like to have.Management weighs the worth of individual persons through estimating the sales & profit dollars that would be lost if particular salespeople resigned.Another consideration is the compensation amount the company can afford to pay. The company should make a cost estimate on a break even chart to propose the compensation plan for every individual salespeople.
- 4. Compensation elementsA sales compensation plan has many as four basic elements.1. A fixed element, either a salary or a drawing account, to provide some stability of income.2. A variable element (for example, a commission ,bonus, or profit sharing arrangement) to serve as an incentive.3. An element covering the fringe or “plus factor”, such as paid vacations, sickness & accident benefits, life insurance, pensions.4. An element providing for reimbursement of expenses or payment of expenses allowances.Management selects the combination of elements that best fits the selling situation. The proportions that different elements bear to each other vary of 60:40 to an 80:20 basis.
- 5. Types of compensation plansStraight salary plan- is simplest compensation plan. Salesperson receive fixed sums as regular intervals(usually each week or month sometimes every 2 weeks), representing total payments for their services. Such plans are more common among industrial- goods companies than among consumer- goods companies. Such plans are engaged in trade selling. These jobs, in which selling amounts to mere order taking, abound in the wholesale & manufacturing fields, where consumer necessities are distributed directly to retailers. It is also used for paying driver- salesperson selling liquor & beverages, milk & bread, similarly distributed products.
- 6. 2. Straight commission Plan- The theory supports the individual sales personnel should be paid according to productivity. As sales volume rises to different levels, the commission rates differ for different products, categories of customers, or during selling seasons.This method is common in the clothing, textiles & shoe industries & in drug * hardware wholesaling. Firms selling intangibles, such as insurance & investment securities, manufacturers of furniture, office equipment & business machines also are frequent users of straight- commission plans.3. Salary plus commission- Most sales compensation plans are combinations of salary & commission plans. By a judicious blending of the two basic plans, management seeks both control & motivation. Actual results depend upon management’s skills in designing & administering the plan.
- 7. Use of bonus & Fringe benefitsA bonus is an amount paid for accomplishing a specific sales task, it is paid for reaching sales quota, performing promotional activities, obtaining new accounts, following up leads, setting up displays, or carrying out other assigned works. It is like an additional financial reward to the sales person for achieving results beyond a predetermined minimum.Fringe benefits do not bear direct relationships to job performance they are provided by federal & state law. For example, payment for social security premiums, unemployment compensation, worker’s compensation, pension plan, holiday’s , vacations, hospitalization insurance, ca parking, company providing housing etc.
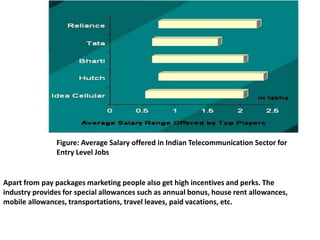
- 8. Figure: Average Salary offered in Indian Telecommunication Sector for Entry Level JobsApart from pay packages marketing people also get high incentives and perks. The industry provides for special allowances such as annual bonus, house rent allowances, mobile allowances, transportations, travel leaves, paid vacations, etc.Â
- 9. Figure: Average salary (in lakhs) offered to entry level employees
- 10. Figure: Average salary offered in BPO and KPONote: The software and hardware industry is in need of talented programmers, testers, developers and analysts to improve their productivity.