Competition act
- 1. 1
- 2. Progression From MRTP Act To Competition Act 2
- 3. ’é× Prevention of concentration of economic power ’é× Control of monopolies ’é× Prohibition of Monopolistic Trade Practices ’é× Prohibition of Restrictive Trade Practices ’é× Prohibition of Unfair Trade Practices 3
- 4. 4 MONOPOLISTIC TRADE PRACTICES (MTP):- ’ü▒ŌĆĢSuch practice indicates misuse of oneŌĆÖs power to abuse the market in terms of production and sale of goods and services.ŌĆ¢ ’ü▒An MTP is likely to have any of the following effects:- ŌĆó Limiting or controlling; ŌĆó Unreasonably raising profits; ŌĆó Unreasonably increasing prices; ŌĆó Adopting unfair or deceptive methods
- 5. 5 RESTRICTIVE TRADE PRACTICES(RTP) : ŌĆó ŌĆĢ The traders, in order to maximise their profits and gain advantage in the market, often indulge in the activities that tend to block flow of capital in production.ŌĆ¢ ŌĆóCommon types of RTPs are:- o Refusal to Deal o Tie- Up Sales o Exclusive Dealings o Price Discrimination o Resale Price Maintenance o Market Restriction
- 6. 6 UNFAIR TRADE PRACTICES(UTP) :- ŌĆó ŌĆĢA trade practice, for the purpose of promoting sale, use or supply of any goods or provision of services, adopts any unfair method or unfair or deceptive practice.ŌĆ¢ ŌĆó PRACTICES WHICH ARE UTPs AS PER THE ACT ARE:- o False representation o False offer or Bargain Price o Offering of gifts, prize, etc., and conducting promotional contests o Product Safety Standards o Hoarding or Destruction of goods
- 7. 7 NEED FOR SUBSTITUTION OF MRTP ACT BY COMPETITION ACT TRIGGER CAUSE No mention of certain offending trade practices- Abuse of Dominance Cartels, Collusion and Price Fixing Bid Rigging Boycotts and Refusal to Deal Predatory pricing FORMATION OF RAGHAVAN COMMITTEE
- 9. ŌŚś "acquisitionŌĆ£ - directly or indirectly, acquiring or agreeing to acquireŌĆö ’āś Shares, voting rights or assets of any enterprise; or ’āś Control over management or control over assets of any enterprise; ŌŚś "cartelŌĆØ ’āś Association of Groups ’āś Objective: To Limit, attempt to control competition ’āś Example: Unilever and Procter & Gamble
- 10. ’āś "relevant marketŌĆ£ - the market which may be determined by the Commission with reference to the relevant product market or the relevant geographic market or with reference to both the markets; ’āś "relevant geographic marketŌĆ£ ŌĆō a market comprising the area in which the conditions of competition for supply of goods or provision of services or demand of goods or services are distinctly homogenous and can be distinguished from the conditions prevailing in the neighboring areas;
- 11. ’āś "relevant product marketŌĆ£ - a market comprising all those products or services which are regarded as interchangeable or substitutable by the consumer, by reason of characteristics of the products or services, their prices and intended use.
- 12. ŌĆó Eliminate practices having appreciable adverse effect on competition ŌĆó Promote and sustain competition ŌĆó Protect consumerŌĆÖs interests ŌĆó Ensure freedom of trade carried on by other participants in markets, in India
- 13. ’āś Consumers: o Wider choice of goods, services and suppliers o Better quality and improved value for money ’āś Businesses o Level playing field o Redressal against anti competitive practices o Competitively priced inputs o Greater productivity and ability to compete in global markets
- 14. ’āśGovernments (Central and State): o Optimal realization from sale of assets o Savings of public money in procurement o Enhanced availability of resources for social sector
- 15. ŌŚś Anti-Competitive Agreements ŌŚś Abuse of Dominance ŌŚś Combinations Regulation ŌŚś Competition Commission of India ŌŚś Competition Advocacy
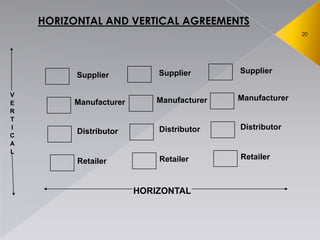
- 16. ŌĆóSection 3 ŌĆō ŌĆóthe agreements which cause or are likely to cause appreciable adverse effect on competition ("AAEC") are anti-competitive agreements ŌĆóSuch agreements may be horizontal or vertical
- 17. ’āś Between enterprises at the same stage of the production chain and that is generally between two rivals ’āś Either fixing prices or for limiting production or for sharing markets ’āś Presumption in the Act that such agreements cause AAEC ’āś Caselet: Indian Oil Corporation Ltd (IOCL) during 2011-12. ’āś Directly or indirectly results in bid rigging or collusive bidding
- 18. ŌŚś Between enterprises at different stages of the production chain, like an arrangement between the manufacturer and a distributor ŌŚś There must be an agreement amongst enterprises or persons; ŌŚś The agreeing parties must be in different markets ŌŚś The agreement should cause or should be likely to cause AAEC
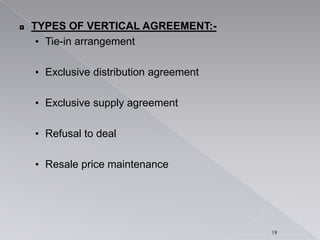
- 19. ŌŚś TYPES OF VERTICAL AGREEMENT:- ŌĆó Tie-in arrangement ŌĆó Exclusive distribution agreement ŌĆó Exclusive supply agreement ŌĆó Refusal to deal ŌĆó Resale price maintenance 19
- 21. ’ü▒ If an enterprise or a group directly or indirectly, imposes unfair or discriminatory: o condition in purchase or sale of goods or service; or o price in purchase or sale (including predatory price) of goods or service ’ü▒ Limits or restricts - o production of goods or provision of services or market therefore; or o technical or scientific development relating to goods or services to the prejudice of
- 22. ’ü▒ Uses its dominant position in one relevant market to enter into, or protect, other relevant market ’ü▒ Imposes unfair price in purchase or sale of goods (predatory price) o Caselet: DLF fined for abuse of dominance 22
- 23. Combination Covers:- ŌŚś Acquisition of shares, voting rights, assets etc. ŌŚś Mergers ŌŚś Amalgamations ŌŚś Acquiring control over another enterprise in the same line of business.
- 24. ŌŚś Proper information about the combination must be provided within 30days of approval by the board of directors. ŌŚś Filing should be done within 7 days of Acquisition ŌŚś The combination provides a post filing review period of 210 days during which no combination must come into effect.
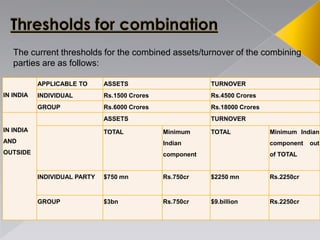
- 25. The current thresholds for the combined assets/turnover of the combining parties are as follows: IN INDIA APPLICABLE TO ASSETS TURNOVER INDIVIDUAL Rs.1500 Crores Rs.4500 Crores GROUP Rs.6000 Crores Rs.18000 Crores IN INDIA AND OUTSIDE ASSETS TURNOVER TOTAL Minimum Indian component TOTAL Minimum Indian component out of TOTAL INDIVIDUAL PARTY $750 mn Rs.750cr $2250 mn Rs.2250cr GROUP $3bn Rs.750cr $9.billion Rs.2250cr
- 26. ŌŚś An acquisition of shares or voting rights in another enterprise- only investment no control ŌŚś Transfer from joint control to sole control (50%) ŌŚś An acquisition of stockŌĆōin-trade, raw materials, stores and spares in the ordinary course of business.
- 27. ŌŚś An acquisition of current assets ŌŚś Any acquisition of shares or voting rights by a person acting as a securities underwriter or a registered stock broker. ŌŚś An acquisition taking place outside India with insignificant effect in markets in India.
- 28. ŌŚś A company which owns >25% but <50% of shares or voting rights in another enterprise, can acquire 5% more in a financial year without giving any notice to CCI. ŌŚś Any acquisition that results in more than 25% voting rights requires a notice to be given to CCI. ŌŚś An exception of "enterprise jointly controlled by enterprises that are not part of the same group" has been added.
- 29. ’ü▒ Establishment ŌŚś March 2009 ŌŚś perpetual succession and a common seal ŌŚś Head office ŌĆōdecided by Central Government ’ü▒ Composition ŌŚś Chairperson & Minimum 2 and maximum 6 other Members appointed by the Central Government. ŌŚś Eligibility ŌŚś whole-time Members. ’ü▒ Extension of the executive powers ŌŚś Appointment Director General / others for assisting in conducting enquiries.
- 30. Penalties For : ’āś Non compliance with the orders ’āś Non compliance with the orders / non payment of fine ’āś Non-furnishing of information on combinations ’āś Making false statement or omission to furnish material information ’āś Power to impose lesser penalty ’āś Crediting sums realised by way of penalties to Consolidated Fund of India
- 31. ’é× ADVOCACY PROVISIONS IN THE COMPETITION ACT: ŌĆó Under Section 49 (1), Central Govt. or State Govt. while formulating a law or policy may make a reference to the Commission. ŌĆó Under Section 49 (3), The Commission is mandated to take suitable measures for the promotion of competition advocacy, creating awareness and imparting training about the competition issues. 31
- 32. CCI assumes the role of competition advocacy ’āś Foster conditions leading to competitive market ’āś Develop relationship with the Ministries and Departments of the Government ’āś Encourage debate on competition and promote a better and more informed economic decision making ’āś Be open and transparent ’āś Competition advocacy: Enhanced by establishing good media relations
- 33. ’ü▒Undertake programs and activites for promotion of competition advocacy and create awareness in India as well as abroad ’ü▒Constitute Advocacy Advisory Committee(s) ’ü▒Develop and disseminate advocacy literature
- 34. 34 ’ü▒ Proactive Interactions with the Central and State Governments, civil society ŌĆō concerned with competition matters ’ü▒ The Commission may undertake studies and market research ’ü▒ May encourage academic and professional institutions to include competition law and policy
- 35. FACTORS MRTP COMETITION 1] Time Pre Reforms Post Reforms 2] Objective Prevent concentration of economic powers Prevent practices having an adverse effect on competition 3] Offences recognized Lists out 14 offences Lists out 4 4] Powers Cease and Desist orders Prevent and punish 5] Fund Did not provide for the formation of fund Provides competition fund 6] Entity Status Status of dominant position is considered bad Status of abuse of dominant position is considered bad 7] Registration General registration is mandatory No such requirement
- 36. FACTORS MRTP COMPETITION 8] Role of the commission Only Advisory Can initiate suomotu and levy penalties 9] Focus Consumer Interest Public 10] Appointment of Chairman Central Government Committee consisting of retired judiciary, person with professional expertise etc.
- 37. 37
- 38. World Not A Single Platform For Trade And Commerce ’ü▒World Trade Organization (WTO) promotes global multilateral free trade ’ü▒Trade Barriers: tariffs, quotas, and nontariff barriers and Trading Blocks exist. ’ü▒ Hamper open Free Trade, curb competition and try to create monopolies. ’ü▒ Major Trading Blocs oASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) oEuropean Union (EU) oNAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement) oSAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation)
- 39. 39
- 40. ’ü▒ Introduction ’ü▒ Antitrust : The two central rules set out in Functioning of the European Union. ’é¦ First, agreements between two or more independent market operators which restrict competition are prohibited. ’é¦ Second , it prohibits firms holding a dominant position on a determined market.
- 41. ’ü▒ Cartel : ’é¦ The leniency policy encourages companies to hand over inside evidence of cartels to the European Commission ’ü▒ Mergers : ’é¦ Harm consumers through higher prices, reduced choice or less innovation. ’é¦ The objective - prevent harmful effects on competition. ’é¦ Examines the mergers if the annual turnover of the combined businesses exceeds specified thresholds in terms of global and European sales.
- 42. ’āś Liberalization : ’é¦ Opening of the services such as transport, energy, postal services and telecommunications to competition. ’ü▒ Benefits- ’é¦ lower prices ’é¦ New/Alternative services (more efficient and consumer- friendly than before. This helps to make economy more competitive.) ’āś State Aid : ’é¦ Prohibited unless it is justified by reasons of general economic development. ’é¦ Role of European Commission is of ensuring that State aid complies with EU rules.
- 43. International : ’é¦ The integration of national economies also enables companies to organize cartels and other anti-competitive practices on an international or even global basis. ’é¦ Cooperation with other competition authorities takes place at two levels: 1. Bilateral 2. Mutilateral
- 44. ’üČ US Antitrust LawŌĆöaka competition law ’üČ Originated from trusts in US in 1800s which were set up in the US in the late 1800s to control entire markets for petroleum, transport, banking, rail and other industry sectors. ’üČ Trusts undermined free market economics by restricting competition, and the US antitrust laws were enacted to redress this issue. ’üČ Antitrust laws composed of ŌĆō widely drafted antitrust statutes ŌĆō given meaning through case law.
- 45. 45 PURPOSE To promote effective and stable competition and prohibit anti-competitive monopolists and conspiracies. Following help understand the importance of protecting ones company and the significance of managing ones risk 1. Civil antitrust punishments 2. Criminal antitrust punishments ’ü▒Price-fixing ’ü▒Horizontal market allocations ’ü▒Bid-rigging ’ü▒Other antitrust wrongdoing.
- 46. 1. Monopolisation ŌĆó Monopolisation itself ŌĆó Attempted monopolisation ŌĆó Conspiracy to monopolise. 2. Conspiracy to restrain trade ŌĆó conspiracies to retain trade itself ŌĆó ŌĆĢper seŌĆ¢ restraints of trade A third offence, ŌĆĢabuse of dominant position.ŌĆ¢ ŌĆó It is not forbidden under US antitrust laws expressly, it is nonetheless part of the competition laws of the EU and Canada and can therefore affect US businesses who function internationally.
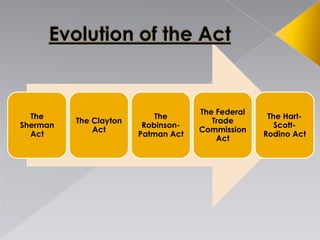
- 47. The Sherman Act The Clayton Act The Robinson- Patman Act The Federal Trade Commission Act The Hart- Scott- Rodino Act
- 48. 48
- 49. ’é× CCI imposes Penalty of Rs. 62.31 Crores on Three Companies for Forming a Cartel in a Tender for Indian Railways. ’é× The penalty has been imposed after CCI took up a case of suo motto basis based on information given by M/s Diesel Loco Modernisation Works(DLMW), a unit of Indian Railways at Patiala, Punjab. The case relates to a DLMW tender wherein the three vendors quoted identical rates for feed valves. 49
- 50. ’é× Progression from MRTP to Competition ’é× World is not the single platform for trade and commerce. 50
- 51. 51
































![FACTORS MRTP COMETITION
1] Time Pre Reforms Post Reforms
2] Objective Prevent concentration of
economic powers
Prevent practices having an
adverse effect on
competition
3] Offences recognized Lists out 14 offences Lists out 4
4] Powers Cease and Desist orders Prevent and punish
5] Fund Did not provide for the
formation of fund
Provides competition fund
6] Entity Status Status of dominant position
is considered bad
Status of abuse of dominant
position is considered bad
7] Registration General registration is
mandatory
No such requirement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitionact-140403055136-phpapp02/85/Competition-act-35-320.jpg)
![FACTORS MRTP COMPETITION
8] Role of the
commission
Only Advisory Can initiate suomotu
and levy penalties
9] Focus Consumer Interest Public
10] Appointment of
Chairman
Central Government Committee consisting
of retired judiciary,
person with
professional expertise
etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/competitionact-140403055136-phpapp02/85/Competition-act-36-320.jpg)